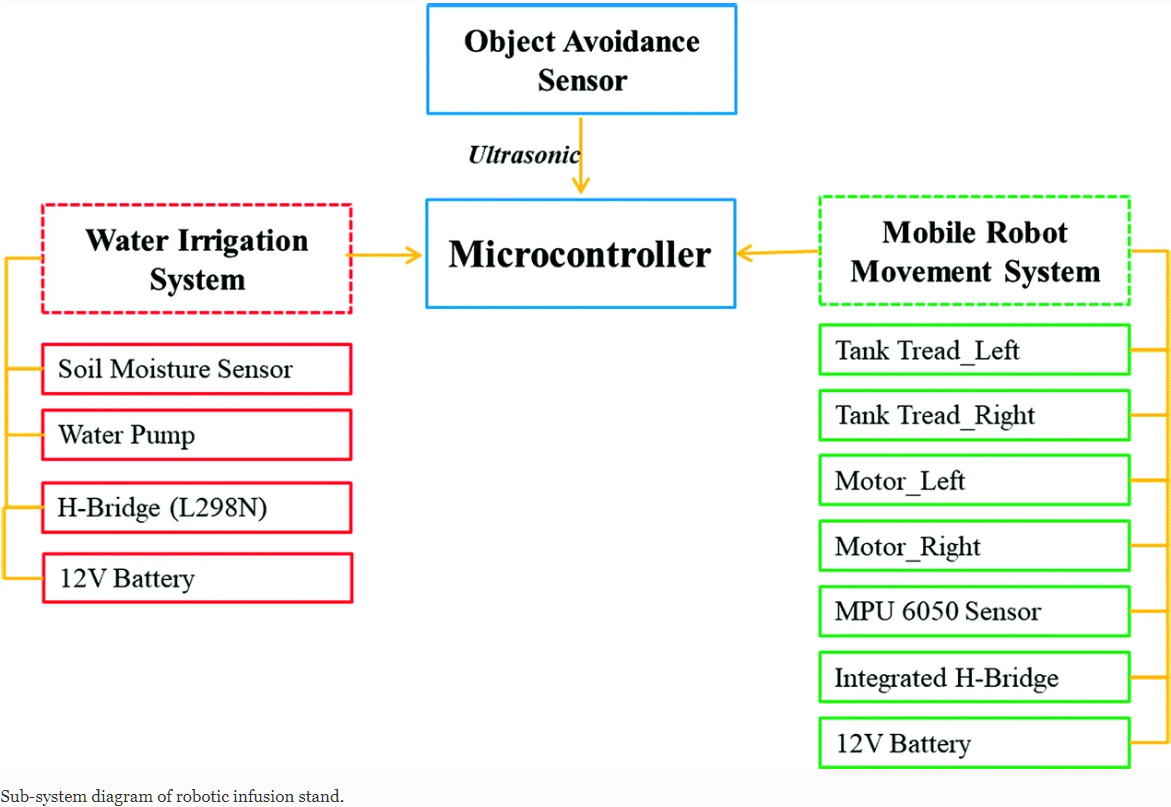
Optimal Proportional Integral Derivative (PID) Controller Design for Smart Irrigation Mobile Robot with Soil Moisture Sensor
Uncertainty on the condition of the weather always give a major headache to the agricultural industry as the cultivated plant that is grown on a large scale commercially rely on the condition of the weather. Therefore, to reduce the interdependency on the weather itself, a recommendation to develop a prototypic mobile robot for smart irrigation is submitted. Smart irrigation system is an essential tool from yield point of view and scarcity of the water. This smart irrigation system adopts a soil moisture sensor to measure the moisture content of the soil and automatically provide a signal to
Fractional-order bio-impedance modeling for interdisciplinary applications: A review
Bio-impedance circuit modeling is a popular and effective non-invasive technique used in medicine and biology to fit the measured spectral impedance data of living or non-living tissues. The variations in impedance magnitude and/or phase at different frequencies reflect implicit biophysical and biochemical changes. Bio-impedance is also used for sensing environmental changes and its use in the agriculture industry is rapidly increasing. In this paper, we review and compare among the fractional-order circuit models that best fit bio-impedance data and the different methods for identifying the
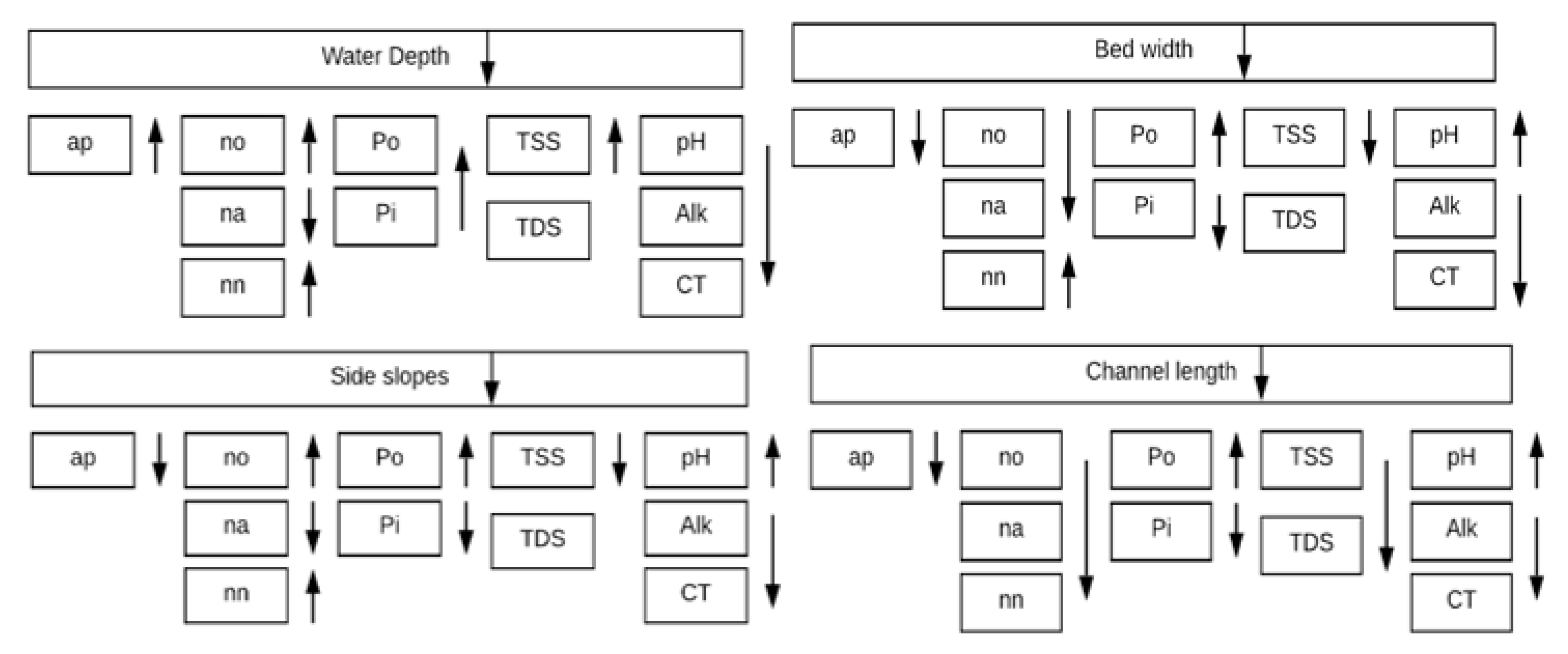
Studying the effect of channel geometry on different water quality variables for effective designs and waste allocation plans for waterways
It is necessary to study the parameters that affect water quality in order to devise mitigation measures if water quality would be at risk or negatively affected by those parameters. Those parameters are physical, chemical, biological, and hydraulic characteristics. This research will study the effect of channel geometry on different water quality variables, which is important in designing new irrigation canals in order to see how its geometry will affect water quality and lessen any negative impact if possible also this study could aid in designing more reliable waste allocation plans for
Towards evolving sensor actor networks
Sensor Actor NETworks (SANET) represent a major component of ubiquitous service environments promising interesting solutions to a wide range of problems. Despite the obvious increase in the research activities proposing architectures and protocols for SANETs, we are still no where near the production of industrial-grade SANET software that can be relied upon for mission critical applications. The cost of programming, deploying and maintaining SANET environments is still highly prohibitive due to the lack of industrial tools capable of realizing adaptive SANET software in a cost effective way

Memristive Bio-Impedance Modeling of Fruits and Vegetables
Recent works show that the plants can exhibit nonlinear memristive behavior when excited with low-frequency signals. However, in the literature, only linear bio-impedance models are extensively considered to model the electrical properties of biological tissues without acknowledging the nonlinear behavior. In this paper, we show with experiments, for the first time, the pinched hysteresis behavior in seven fruits and vegetables including tomato, orange, lemon, aubergine, and kiwi which exhibit single pinch-off point, and others such as carrot and cucumber exhibit double pinch-off points (i.e
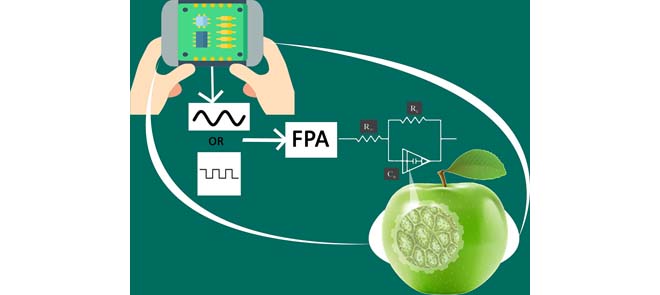
Extracting Optimized Bio-Impedance Model Parameters Using Different Topologies of Oscillators
This paper demonstrates the possibility of extracting the single-dispersion and double-dispersion Cole-bio-impedance model parameters using oscillators (sinusoidal or relaxation). The method is based on replacing selected components in the oscillator structure with the biological sample under test and then using the Flower Pollination optimization Algorithm (FPA) to solve a set of nonlinear equations in order to extract the unknown model parameters. Minimum component sinusoidal oscillators and relaxation oscillators are used in this work and experimental results on three samples of four
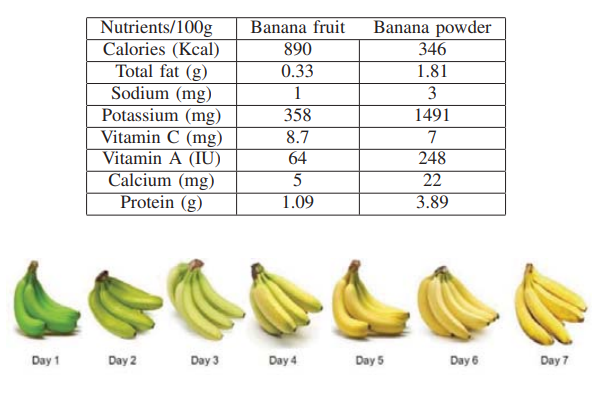
Banana ripening and corresponding variations in bio-impedance and glucose levels
This paper studies banana fruit ripping using the Cole-impedance model fitted over the measured bio-impedance data by monitoring the changes in the model parameters during the different ripping stages. A set of twenty bananas are tested for 84 hours, and impedance measurements are done every 12 hours using an SP150 electrochemical station. The changes in model parameters are related to the physical changes in the fruit as well as with the glucose concentration, which increases with time. © 2019 IEEE.
Extraction of bioimpedance phase information from its magnitude using a non-uniform Kramers–Kronig transform
A novel non-uniform Kramers–Kronig Transform algorithm for bioimpedance phase extraction is proposed and tested in this work. The algorithm error is studied and compared with a previously proposed phase extraction technique, also based on the Kramers–Kronig transform. Results using simulated datasets and experimental datasets confirm the excellent performance of the algorithm. © 2020, European Biophysical Societies' Association.
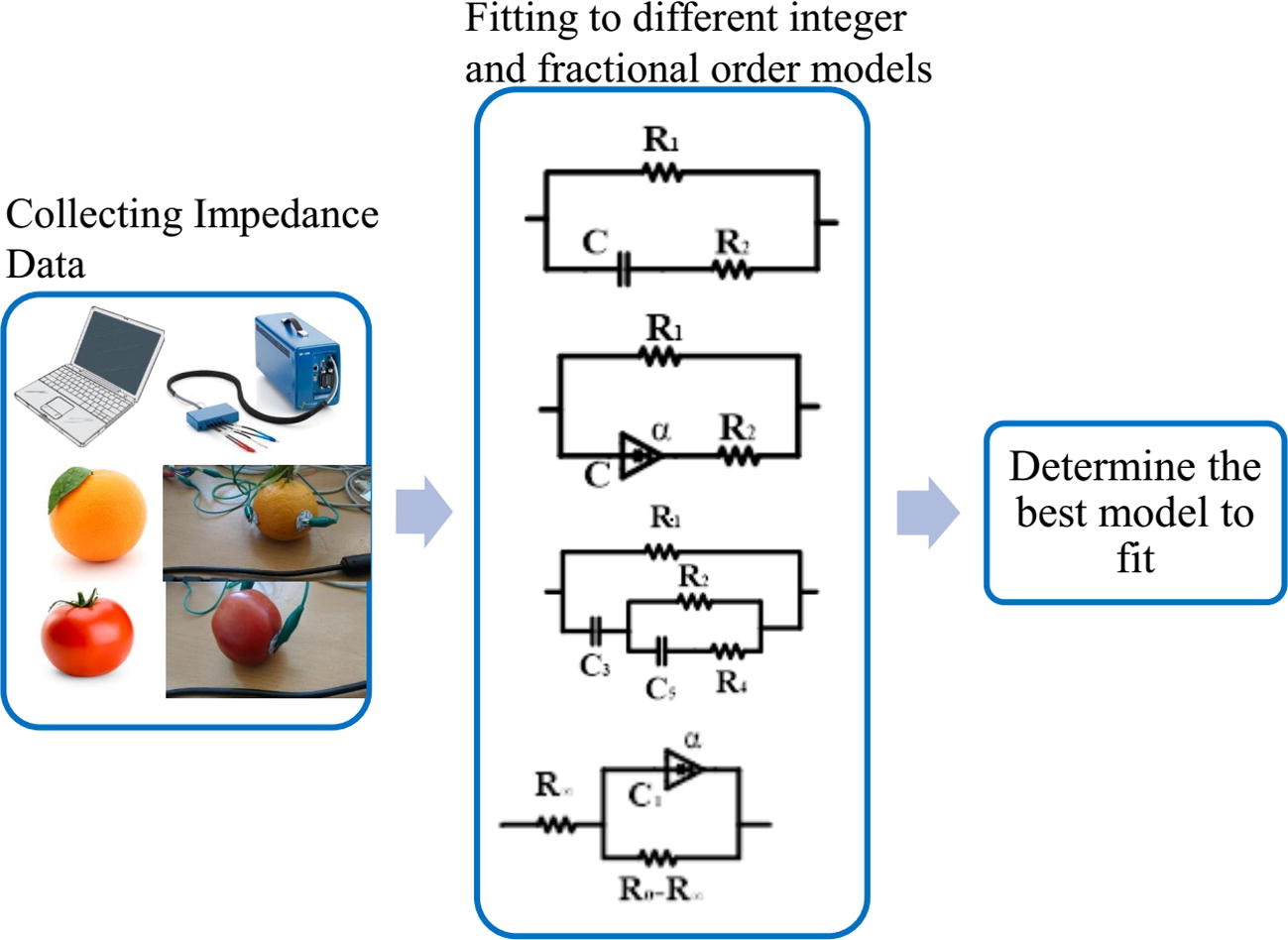
Experimental comparison of integer/fractional-order electrical models of plant
In this paper, different integer and fractional-order models are studied from electrical point of view, these models are used to fit the measured impedance data for different types of fruits and vegetables. Experimental work is done on eight different models for six types of fruits to verify the best fitting model. Electric impedance is measured in the range of frequencies (200 mHz–200 Khz) using a non-destructive method, where the tissues are not damaged by electrode insertion. Moreover, two integer order models have been extended to the fractional order domain where data analysis and fitting
Extraction of Phase Information from Magnitude-Only Bio-impedance Measurements Using a Modified Kramers–Kronig Transform
The need for portable and low-cost bio-impedance analyzers that can be deployed in field studies has significantly increased. Due to size and power constraints, reducing the hardware in these devices is crucial and most importantly is removing the need for direct phase measurement. In this paper a new magnitude-only technique based on modified Kramers–Kronig transforms is proposed and tested. Comparison with impedance measurements of fresh and aging tomato samples using a precise industry standard impedance analyzer is carried out and explained. Error and noise analysis of the proposed
Pagination
- Page 1
- Next page ››
