
Pinched hysteresis with inverse-memristor frequency characteristics in some nonlinear circuit elements
Abstract Pinched hysteresis is considered to be a signature of the existence of memristance. However, here we report on a model that exhibits pinched hysteresis yet it may represent a nonlinear inductor or a nonlinear capacitor (both with quadratic nonlinearity) or a derivative-controlled nonlinear resistor/transconductor. Further, the lobe area of the pinched hysteresis loop in these devices has inverse-memristor characteristics; i.e. it is observed to widen rather than decline with increased operating frequency. Experimental results are provided to validate the model. © 2015 Elsevier Ltd.
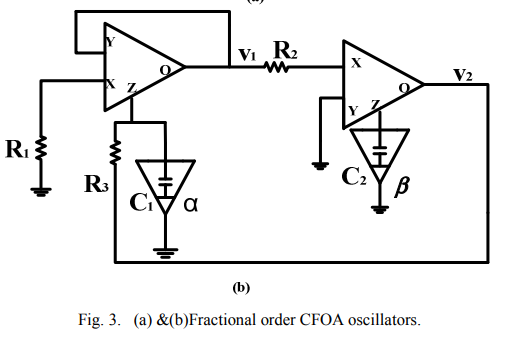
Current feedback operational amplifier (CFOA) based fractional order oscillators
This paper presents a study of fractional order oscillators based on current feedback operational amplifiers (CFOA). Two general cases have been discussed for the oscillation frequency and condition with the use of two fractional order elements of different orders. Design procedure for the two general cases is illustrated with numerical discussions. Circuit simulations for some special cases are presented to validate the theoretical findings. The simulations have been done using Ad844 commercial CFOA model © 2014 IEEE.
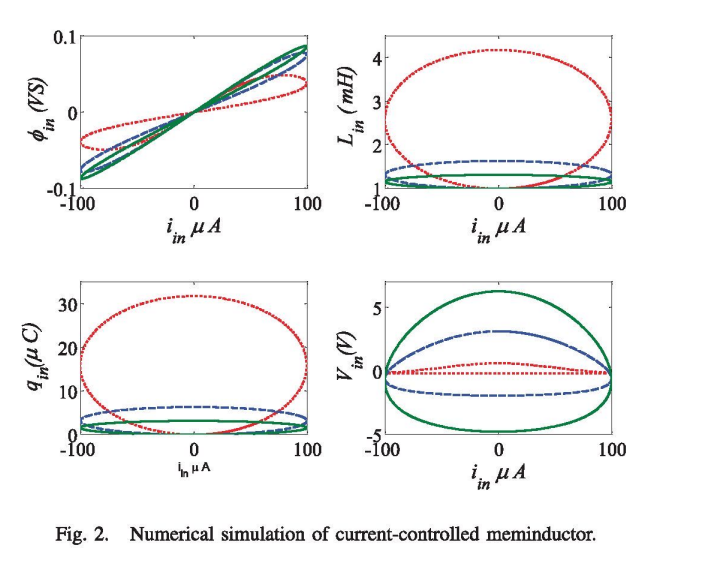
Memristor-less current- and voltage-controlled meminductor emulators
This paper introduces two mathematical models of meminductor based on a simple symmetrical double-loop equation with their generic formulas and analysis. Moreover, new circuits based on CCII are developed for emulating the behavior of the current-controlled and voltage-controlled models. The proposed circuits are realized without using a memristor unlike the previous emulators. Finally, the proposed emulators are verified using PSPICE simulations. © 2014 IEEE.
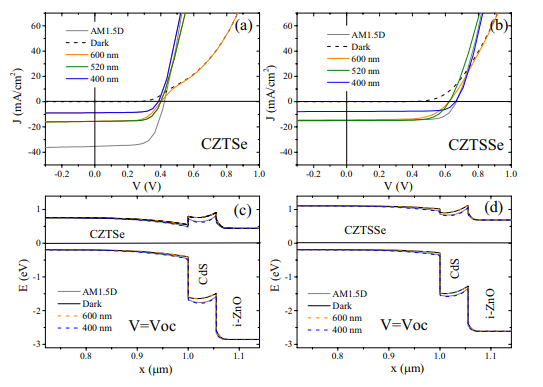
Spectral current-voltage analysis of kesterite solar cells
Current-voltage analysis using different optical band pass filters has been performed on Cu2ZnSnSe4 and Cu2ZnSn(S,Se) 4 thin-film solar cells. When using red or orange light (i.e. wavelengths above 600 nm), a distortion appears in the I-V curve of the Cu 2ZnSnSe4 solar cell, indicating an additional potential barrier to the current flow in the device for these conditions of illumination. This barrier is reduced when using a Cu2ZnSn(S,Se)4 absorber. Numerical simulations demonstrate that the barrier visible under red light could be explained by a positive conduction band offset at the front
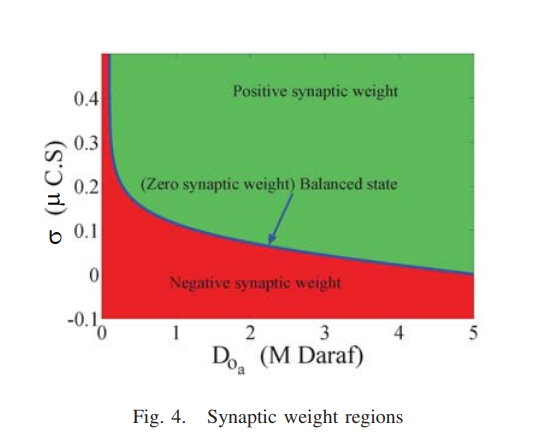
On the mathematical modeling of memcapacitor bridge synapses
Mem-element based synaptic bridge is very promising topic due to its learning capability where the synaptic bridge can be build using either memristors or memcapacitors. In this paper, the detailed mathematical analysis of memcapacitor bridge circuit is introduced. This mathematical analysis is build when a current input signal is applied to excite the bridge. Closed form expressions for the required pulse width; synaptic weight; and conditions for positive, negative and zero synaptic weight are derived. The obtained expressions are verified using SPICE simulations showing very good matching.
Current source based standard-cell model for accurate timing analysis of combinational logic cells
Timing verification is an essential process in nanometer design. Therefore, static timing analysis (STA) is currently the main aspect of performance verification. Traditional STA is based on lookup tables with input slew and output load capacitance. It is becoming insufficient to accurately characterize many significant aspects of the conventional cell delays models, such as: the process variations, nonlinear waveforms, nonlinear loads, and multiple inputs switching (MIS). Therefore, the current trend in modern designs is to use current source based models (CSM), which model MOSFETs as a
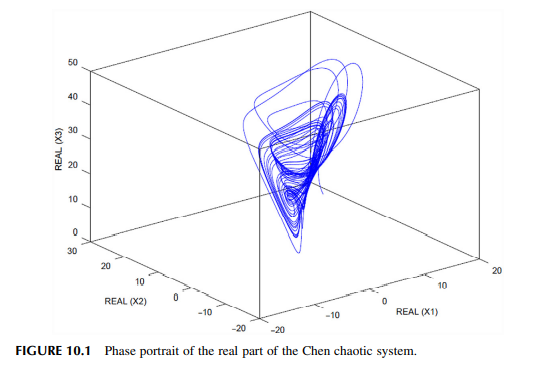
Sliding mode stabilization and synchronization of fractional order complex chaotic and hyperchaotic systems
This chapter is intended to design and analyze several sliding mode techniques for the stabilization and synchronization of fractional order complex chaotic and hyperchaotic systems. Considering that chaos is a hot topic nowadays due to the vast number of real physical systems such as mechanical, electrical, and chemical systems in which this phenomenon is found; this book chapter will provide novel sliding mode approaches for the stabilization and synchronization of chaotic and hyperchaotic systems. Fractional order chaotic and hyperchaotic systems have been proved to be difficult to
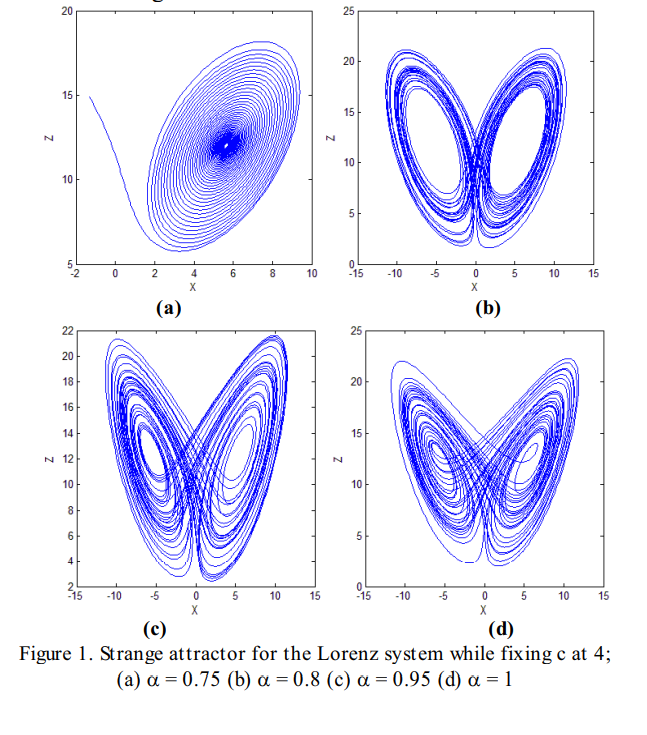
Image encryption in the fractional-order domain
This paper presents a new image encryption scheme based on the fractional-order Lorenz system which gives more degrees of freedom in key generation. In the modified fractional-order system, the key length is doubled using the three fractional-orde r parameters beside the three initial conditions, which makes it invulnerable to brute-force attacks. In addition, using a very simple algorithm, based on pixel confusion only, strongly encrypted images are produced. Such an algorithm can be used in real time applications. To evaluate the algorithm and analyze the encryption results, a standard image
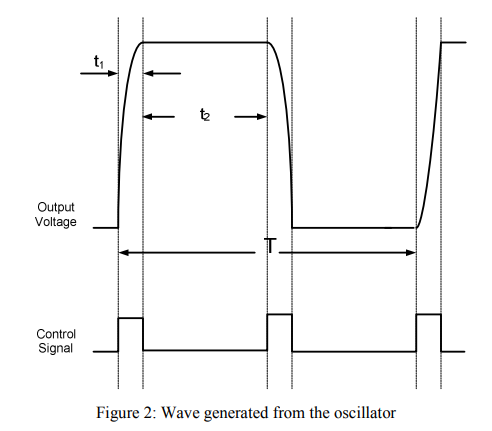
Design methodology for square wave resonant clock generators
Resonant clocking is a promising low power alternative for conventional clocking method. In this work, a design methodology is presented for square wave resonant clocking technique to assure minimum power consumption. These equations were verified by designing a differential clock generator which showed 55% power savings compared to conventional clocking. © 2012 IEEE.
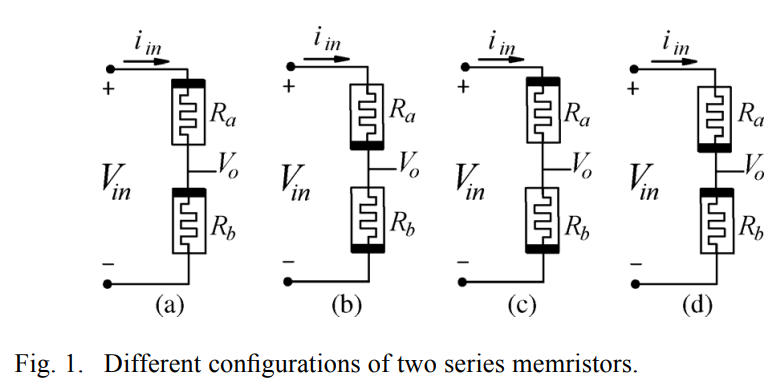
Generalized analysis of symmetric and asymmetric memristive two-gate relaxation oscillators
Memristive oscillators are a novel topic in nonlinear circuit theory, where the behavior of the reactive elements is emulated by the memristor. This paper presents symmetric and asymmetric memristive two-gate relaxation oscillators. First, the analysis of the two series memristors is introduced to study the effect of changing their polarities, as well as the mobility factor to be used in the two-gate relaxation oscillator instead of the RC circuit. The generalized analysis for the proposed memristive two-gate oscillator is introduced, where the generalized expressions for the oscillation
Pagination
- Previous page ‹‹
- Page 28
- Next page ››
