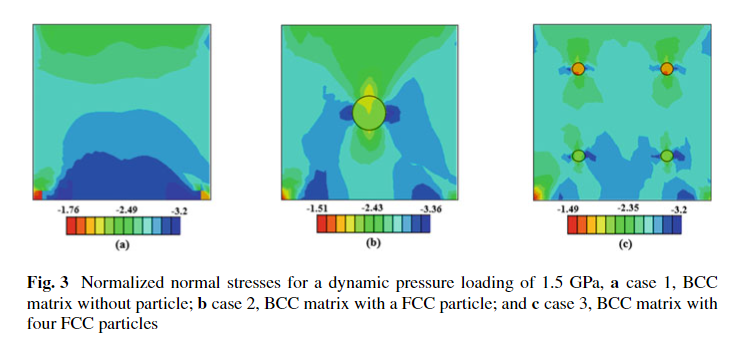
A 3D Multiple-Slip Crystal-Plasticity Model for Precipitate Hardening in Additively Manufactured High Strength Steels
Additive Manufacturing (AM) revolutionized the manufacturing of complex geometry products, especially in medical and aerospace fields. High-strength precipitate hardened (PH) stainless steels provide unique properties in term of strength and corrosion resistance for critical applications in both fields. In the current study, a 3D multiple-slip crystal-plasticity dislocation densities-based model is used to study the effect of copper precipitate hardening in high-strength stainless steels. The proposed approach accurately predicts the complex structure of martensite and properly represents the
Engineered magnetic oxides nanoparticles as efficient sorbents for wastewater remediation: a review
The rapid urbanization and industrialization is causing worldwide water pollution, calling for advanced cleaning methods. For instance, pollutant adsorption on magnetic oxides is efficient and very practical due to the easy separation from solutions by an magnetic field. Here we review the synthesis and performance of magnetic oxides such as iron oxides, spinel ferrites, and perovskite oxides for water remediation. We present structural, optical, and magnetic properties. Magnetic oxides are also promising photocatalysts for the degradation of organic pollutants. Antimicrobial activities and
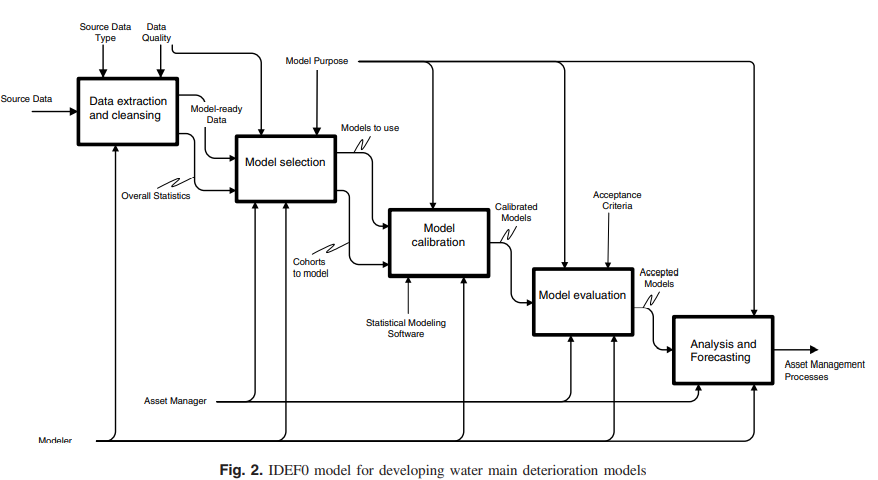
Comparison of statistical deterioration models for water distribution networks
The use of water main break history as a proxy for condition has become common practice because of the high costs associated with direct assessments. Statistical deterioration models predict future water main breaks on the basis of historical patterns. Many municipalities are beginning to understand the value of utilizing water pipe break histories to manage their noncritical distribution networks via deterioration models. This paper presents a generic IDEF0 process model for developing water main deterioration models. Two common statistical deterioration models for water pipes are compared
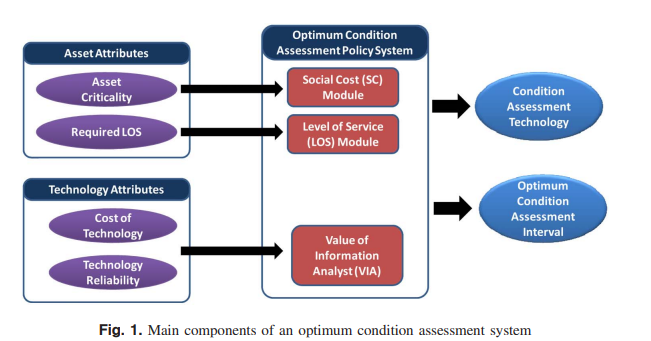
Optimizing inspection policies for buried municipal pipe infrastructure
Condition assessment is an integral component in any infrastructure asset management system. Without condition information, asset managers lack the ability to make appropriate decisions regarding needed maintenance, rehabilitation, and replacement of infrastructure. Existing and emerging technologies for assessing the condition of water and sewer pipes provide a better picture of the state of these buried assets. Unfortunately, many of these technologies are costly and provide results that are not always highly reliable. This paper presents a methodology to assist asset managers in balancing
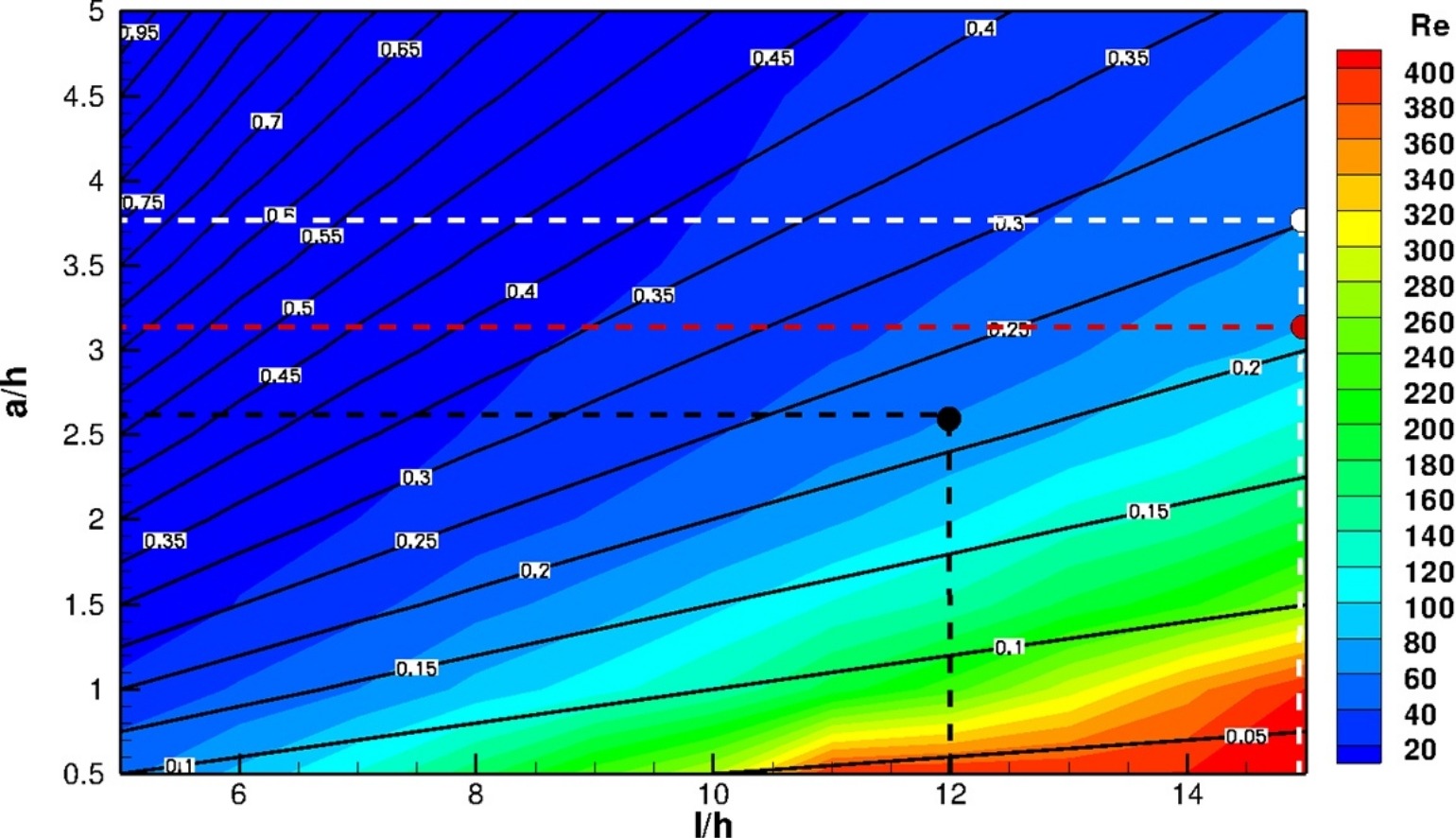
A Hydro-Kinematic approach for the design of compact corrugated plate interceptors for the de-oiling of produced water
A Hydro-Kinematic approach is proposed for the design of compact corrugated plate interceptors (CPIs) for the de-oiling of produced water. For a given set of design targets of a specific flow rate, maximum retention time and minimum captured oil droplet diameter, the Hydro-Kinematic approach proposes a systematic way to determine the CPI unit dimensions and operating conditions with the minimum volume and area per unit input flow rate. The approach takes into account the hydrodynamic constraints in the design of the CPI imposed by the behavior of the dispersed oil droplets in response to the
The synthesis, production & economic feasibility of manufacturing PLA from agricultural waste
Synthetic plastics are extensively used in several applications including packaging, containers, bottles, trays, and boxes. However, these plastics are based on synthetic components which are not biodegradable, thus they rigorously effect the environment causing water, air pollution and high health risks. Moreover, Individuals are exposed to chemicals during manufacturing or usage of synthetic plastic that can easily migrate to the surrounding such as styrene from polystyrene, plasticizers from polyvinyl chloride (PVC), antioxidants from polyethylene, and acetaldehyde from polyethylene
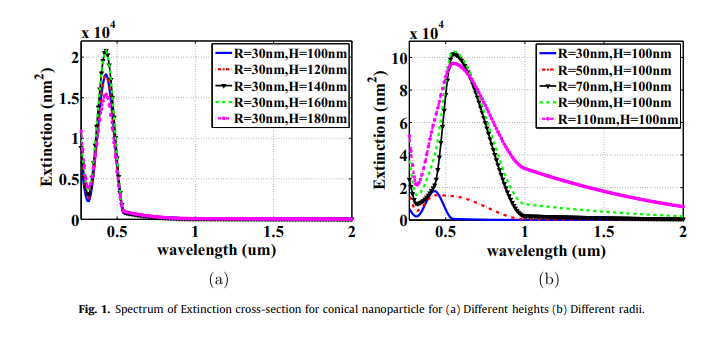
J-V characteristics of plasmonic photovoltaics with embedded conical and cylindrical metallic nanoparticles
Plasmonic photovoltaics (PVs) are promising structures that improve thin-film photovoltaics performance, where optical absorption is improved via embedding metallic nanoparticles in the PV's active layer to trap the incident optical wave into the photovoltaic cell. The presented work investigates the design of PV with both structures of conical and cylindrical metallic nanoparticles through studying their extinction cross-sections and electric field distributions. Also, the impact of these nanoparticles in silicon PVs on the optical absorption enhancement is investigated. The figure of merit
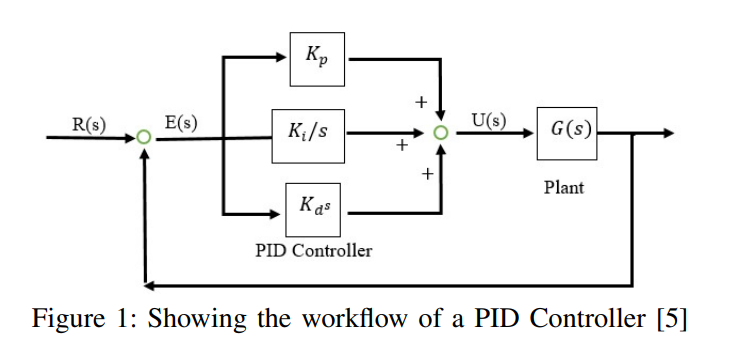
Wastewater Treatment Model with Smart Irrigation Utilizing PID Control
In this paper the activated sludge wastewater treatment process is modeled mathematically and explored. In addition, irrigation was recommended as a valid application for the reuse of wastewater. Other wastewater treatment processes (WWTP) were compared to the one chosen to justify the choice and a detailed expiation of the general wastewater treatment process was provided. Furthermore, PI, and PID controller were developed to further improve the performance of the activated sludge process. The controllers were devolved and tuned using MATLAB, and SIMULINK, and had a positive correlation on
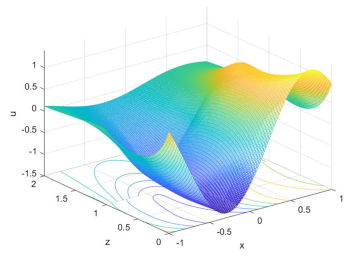
Thermoelastic wave propagation in a piezoelectric layered half-space within the dual-phase-lag model
We investigate linear, thermoelastic wave propagation in a layered piezoelectric material composed of a slab bonded to a half-space substrate of a dissimilar material, within dual-phase-lag model and under thermomechanical loads. One of the aims of the present work is to formulate a set of boundary conditions that is compatible with the field equations. Normal mode technique is used to obtain a solution to the considered problem. The model allows for a jump in temperature at the interface, and this can be used to evaluate a material constant of the slab. It turns out, particularly, that a
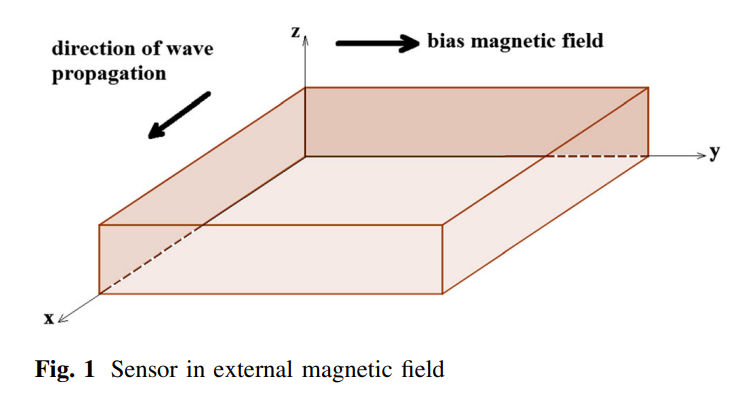
Magnetic field effect on piezo-thermoelastic wave propagation in a half-space within dual-phase-lag
The current work is concerned with the study of wave propagation in a half-space of a piezo-thermoelastic material under a bias tangential magnetic field within dual-phase-lag (DPL). This is relevant to the design and performance of piezoelectric devices working under a bias magnetic field, for example, the DC magnetic field piezoelectric sensors widely used in various areas of technology. The characteristic time for the problem under consideration is in the range of picoseconds, which is comparable to the thermal relaxation times in many metals. Exact analytic expressions for the mechanical
Pagination
- Previous page ‹‹
- Page 4
- Next page ››
