Determining the effect of changing channel geometry of irrigation canals on dissolved oxygen concentration
Dissolved oxygen (DO) is an important water quality parameter. It is considered the most important parameter. DO concentration in water is affected by different parameters such as volume flow rate, water velocity, and re-aeration rate. Those parameters are directly affected by the geometry of the waterway. Thus, studying the impact of changing channel geometry on DO is very important. Many researchers studied the effect of influential parameters on water quality variables but the influence of channel geometric parameters on DO was not studied thoroughly before. This research aims to study the
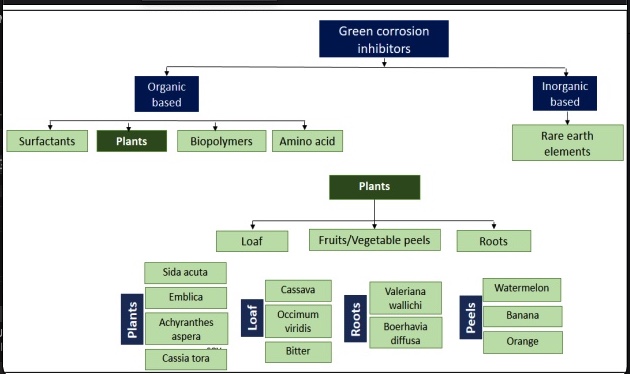
A critical review on green corrosion inhibitors based on plant extracts: Advances and potential presence in the market
Corrosion occurs in all sectors including oil pipelines, drinking water and sewerage in the majority of cases linked to corrosion of steel. Good corrosion management includes optimising corrosion control actions and minimising lifecycle corrosion costs whilst meeting environmental goals. The toxicity of commonly used synthetic inhibitors are the subject of recent legislations (REACH and PARCOM) have led to search on more eco-friendly corrosion inhibitors. Extensive research is conducted to assess the corrosion inhibition rate of diverse green inhibitors. However, it was not adequately
Multiplicity per rapidity in Carruthers and hadron resonance gas approaches
The multiplicity per rapidity of the well-identified particles π-, π+, k-, k+, p¯ , p, and p- p¯ measured in different high-energy experiments, at energies ranging from 6.3 to 5500 GeV, is successfully compared with the Cosmic Ray Monte Carlo event generator. For these rapidity distributions, we introduce a theoretical approach based on fluctuations and correlations (Carruthers approach) and another one based on statistical thermal assumptions (hadron resonance gas approach). Both approaches are fitted to both sets of results deduced from experiments and simulations. We found that the

Labour productivity in building construction: A field study
This paper describes a field study conducted over a period of 11-months on labour productivity observed during the construction of a new university campus in Cairo, Egypt. The campus is being built on 127 acres and the field study was conducted during the construction of two main buildings; each of 20,000 m 2 built up area. The study utilized work sampling (WS), craftsman questionnaire (CQ), and foreman delay survey (FDS) methods to analyze labour productivity of three indicative and labour-intensive trades, namely formwork, masonry work, and HVAC duct installation. The results were also
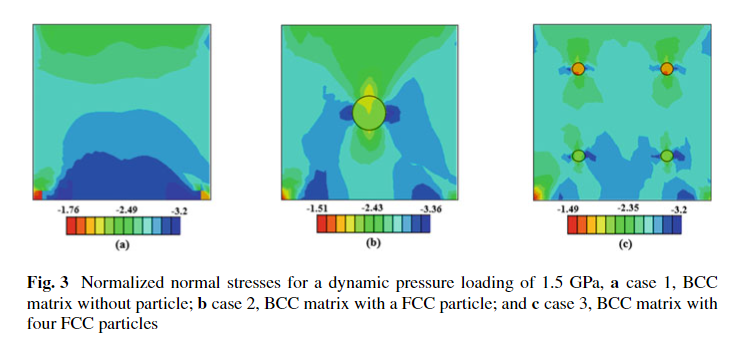
A 3D Multiple-Slip Crystal-Plasticity Model for Precipitate Hardening in Additively Manufactured High Strength Steels
Additive Manufacturing (AM) revolutionized the manufacturing of complex geometry products, especially in medical and aerospace fields. High-strength precipitate hardened (PH) stainless steels provide unique properties in term of strength and corrosion resistance for critical applications in both fields. In the current study, a 3D multiple-slip crystal-plasticity dislocation densities-based model is used to study the effect of copper precipitate hardening in high-strength stainless steels. The proposed approach accurately predicts the complex structure of martensite and properly represents the
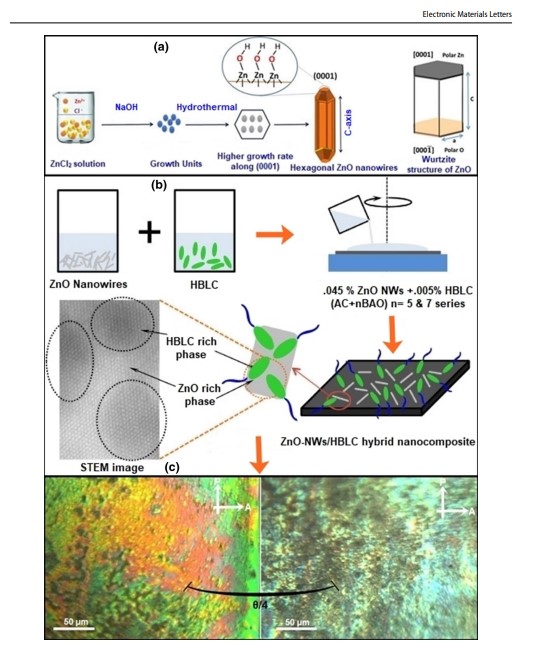
Soft, Self-Assembly Liquid Crystalline Nanocomposite for Superior Switching
Abstract: Liquid crystal (LC) has long been a feature in Materials Science and Nanotechnology, have recently been extended into the appealing domain of complex hybrid materials. The crystalline structural effects of alkoxy chain lengths and the mesogen properties of hydrogen-bonded (n-OBASA) complexes (n = 5,6,7) have been investigated in recent studies. The LC-based hybrid nanocomposite materials–obtained by the homogeneous dispersion of zinc oxide nanowires (ZnO NWs) as a dopant into hydrogen-bonded liquid-crystalline compounds—seem to be particularly promising in this article. Optimizing
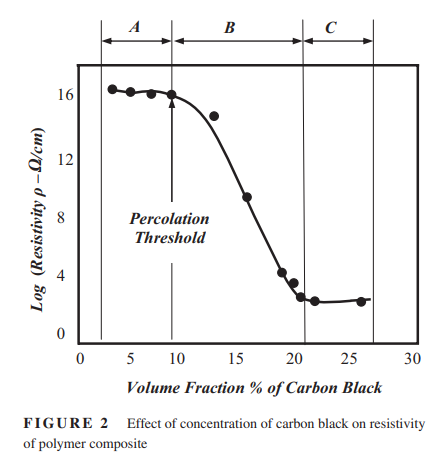
Dynamic behavior and damping characteristics of carbon black polymer composites at high strain rates
The dynamic stress–strain behavior and the damping characteristics of carbon black (CB)/polymer composites at high strain rates are measured using the split Hopkinson pressure bar. These characteristics are determined for polyurethane impregnated with 20% CB nanoparticles and compared with those of pristine polyurethane at strain rates ranging between 2,400 and 7,000 s−1. The obtained results indicate that the CB/polymer composites exhibit highly hysteretic stress–strain characteristics and have high storage modulus as well as high loss factor as compared to pristine polyurethane polymers
Effect of covering irrigation channels on total dissolved solids and total suspended solids
The increase in the evaporation rate is one of the crucial effects of climate change. Water losses due to evaporation are considered as an important challenge that faces the agriculture sector considering the recent water crisis in Egypt. So, covering irrigation canals with the aim to decrease evaporation could be a good solution for this problem, especially if the coverage is expected to be used for power production by covering these canals with solar panels. However, the main concern is the effect of the covering on the quality of water. So, this research study investigates the effect of
Hybrid treatment system for real textile wastewater remediation based on coagulation/flocculation, adsorption and filtration processes: Performance and economic evaluation
This research investigates the feasibility of using hybrid treatment system based on coagulation/flocculation, adsorption and filtration processes for real textile wastewater treatment. Ferric Chloride (FeCl3) was used as a coagulant, Nano Zero-Valent Iron (nZVI) as adsorbent and Micro Zeolite (MZ) as filter media for the removal of chemical oxygen demand (COD), total suspended solids (TSS), color, total nitrogen (TN) and turbidity from raw textile effluents. Batch and continuous feed scaling-up studies (full design and set-up studies) were conducted to evaluate the performance of the
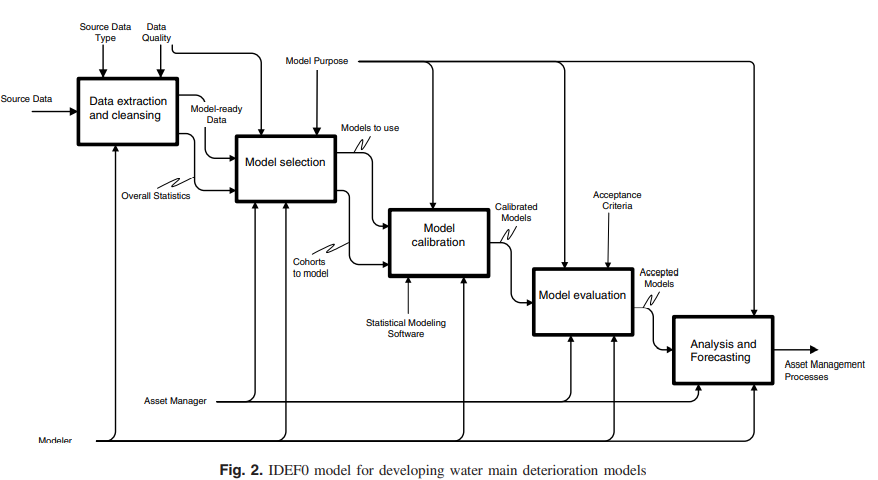
Comparison of statistical deterioration models for water distribution networks
The use of water main break history as a proxy for condition has become common practice because of the high costs associated with direct assessments. Statistical deterioration models predict future water main breaks on the basis of historical patterns. Many municipalities are beginning to understand the value of utilizing water pipe break histories to manage their noncritical distribution networks via deterioration models. This paper presents a generic IDEF0 process model for developing water main deterioration models. Two common statistical deterioration models for water pipes are compared
Pagination
- Previous page ‹‹
- Page 6
- Next page ››
