Active Morphing Control of Airfoil At Low Reynolds Number Using Level-Set Method
The active control of flow around an airfoil through morphing is numerically investigated. The lock-in phenomenon was predicted while using a fixed grid. Galerkin/Least-Squares Finite Element Method was used to simulate incompressible flow over an airfoil with leading edge morphing at a Reynolds number, Re = 5000, and angle of attack, α = 6°. The numerical simulation was carried out using the in-house FORTRAN code. The code was validated with the literature by simulating the flow over an oscillating cylinder. The paperwork implemented a locally oscillating surface on the airfoil with a
Modeling and control of 3-omni wheel Robot using PSO optimization and Neural Network
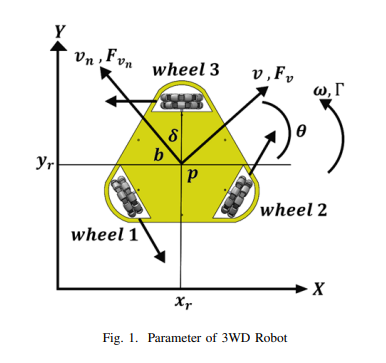
Omni mobile robots are one of the mobile robots that interact with humans in many areas where it is needed to be collaborative and accurate. Committing robotics with artificial intelligence-based controllers became nowadays mandatory for more association of these robots with distinct environments. This paper proposes the distinction of the 3WD Omni Vision feedback model between Simscape and actual information to obtain a surmised model. Study applying some artificial control procedures on this model for path planning and speed control as the artificial neural system and PSO optimization
Direct Power Control of a three-phase PWM-Rectifier based on Petri nets for the selection of Switching States
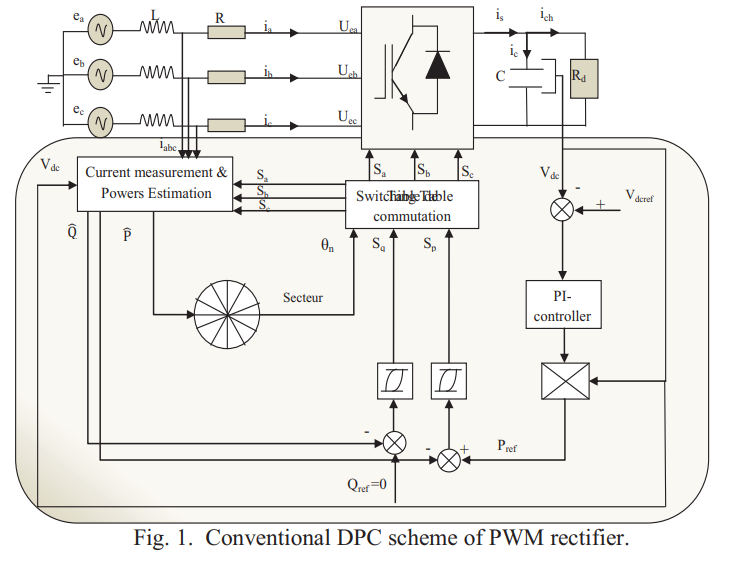
This article proposes a new simple scheme for direct power control of a PWM rectifier without a switch table and voltage sensor. The selection of the switching state of the converter is based on the transition of a Petri net, using the instantaneous active and reactive power tracking errors and the angular position of the network line voltage estimated as variables of Controller input based on Petri nets. Simulation and experimental results demonstrated better performance and verified the validity of the new command with the Petri nets applied to the bridge rectifier connected to the
All-Dynamic Synchronization of Rotating Fractional-Order Chaotic Systems
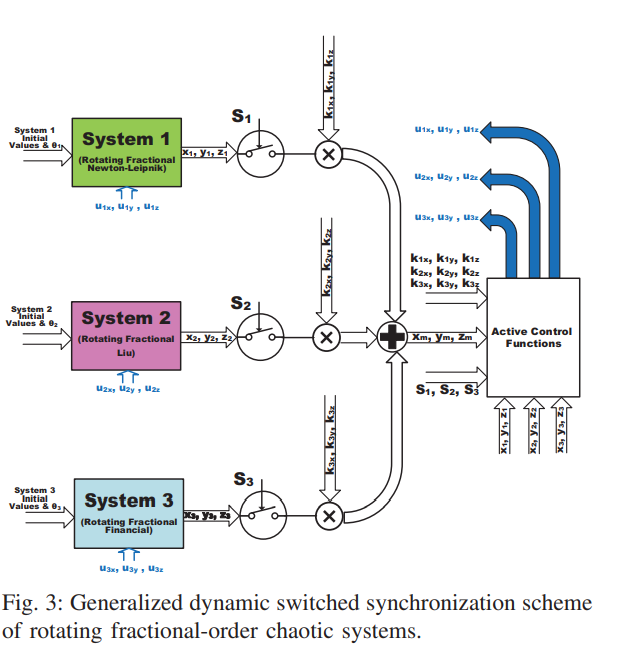
This paper proposes generalized controllable strange attractors through dynamic rotation of fractional-order chaotic systems. Dynamic rotation angle enables the generation of multi-scroll and multi-wing attractors from single and double-scroll ones. The rotating systems are integrated with a generalized dynamic switched synchronization scheme. Dynamic control switches determine whether each system plays the role of master or slave. Based on dynamic scaling factors, the master can be one system or a combination of several ones with new strange attractors. The rotating fractional-order systems
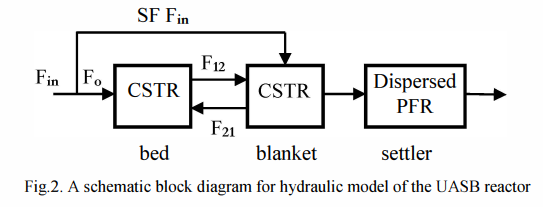
Mathematical modeling of Upflow Anaerobic Sludge Blanket reactor in domestic wastewater treatment
This paper introduces a dynamic model to adequately describe an Upflow Anaerobic Sludge Blanket (UASB) reactor. Some available models of a UASB reactor are discussed in order to modify their drawbacks and propose a new improved model with less complexity and more reliability. The developed model is a combination of two recent models introduced in Sweden. According to this model, a UASB rector is divided hydraulically into three compartments with integration of a kinetic model. Simulations are performed to investigate the validity of the developed model which indicates a good agreement with
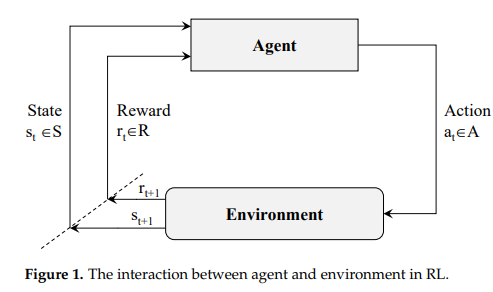
Drone deep reinforcement learning: A review
Unmanned Aerial Vehicles (UAVs) are increasingly being used in many challenging and diversified applications. These applications belong to the civilian and the military fields. To name a few; infrastructure inspection, traffic patrolling, remote sensing, mapping, surveillance, rescuing humans and animals, environment monitoring, and Intelligence, Surveillance, Target Acquisition, and Reconnaissance (ISTAR) operations. However, the use of UAVs in these applications needs a substantial level of autonomy. In other words, UAVs should have the ability to accomplish planned missions in unexpected
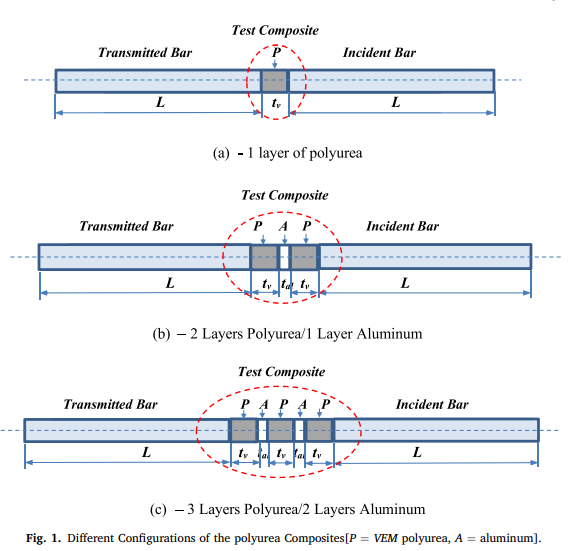
Dynamic behavior of polyurea composites subjected to high strain rate loading
A comprehensive theoretical and experimental investigation is presented of the behavior of polyurea composites subjected to high strain-rate impact loading. The composites under consideration consist of an assembly of steel sections and inserts manufactured from layers of polyurea or polyurea augmented with aluminum layers (AL). A finite element model (FEM) is developed to predict the dynamics of this class of polyurea composites by integrating the dynamics of the solid steel sections with those of polyurea using the Golla-Hughes-Mctavish (GHM) mini-oscillator approach. The predictions of the
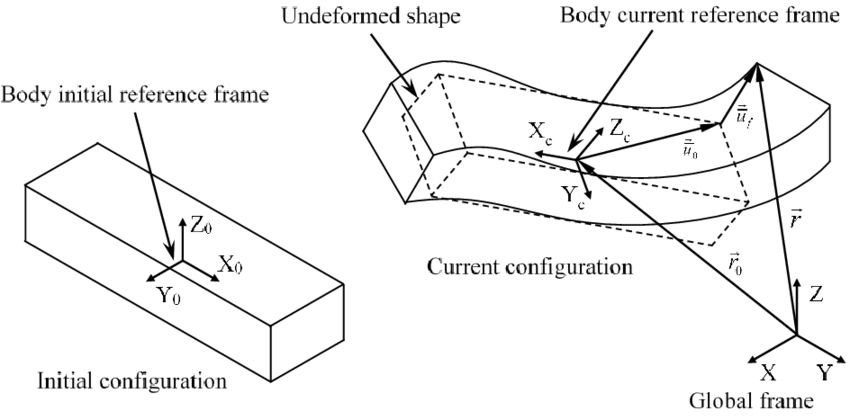
Effect of cracks in wind turbine blades on natural frequencies during operation
Most publications that are concerned with the crack detection via analyzing Eigenfrequencies or deformation modes of wind turbine blades (WTBs) are done in stationary condition. This paper however proposes a novel approach that could study the effect of WTB cracks during rotation at any speed without the need to stop the turbine by using multibody analysis. This approach will reduce the cost of its maintenance substantially, since it will avoid the cost of downtime for wind turbine during crack detection. This approach considers both the increase in stiffness due to rotation (known as
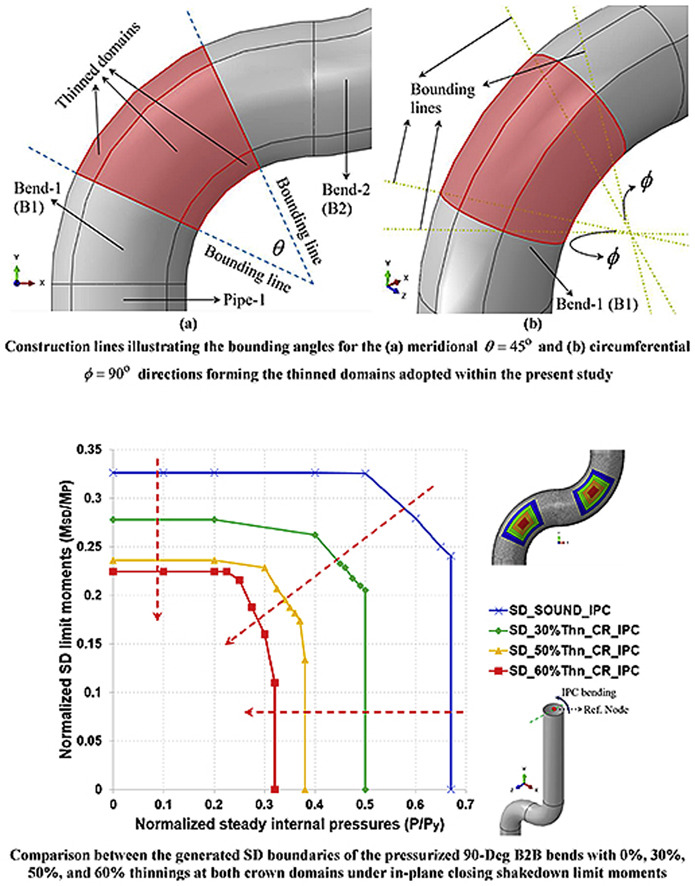
Effect of wall thinning on the Shakedown Interaction Diagrams of 90-degree back-to-Back Bends Subjected to Simultaneous Steady Internal Pressures and Cyclic In Plane Bending Moments
This research studies the effect of wall thinning on generated shakedown (SD) interaction diagrams of pressurized low-carbon steel 90-degree (90-Deg) back-to-back (B2B) bends. More precisely, the SD limit moments are determined for various steady internal pressure spectra thus generating the targeted SD boundaries. The SD limit moments are computed utilizing a direct non-cyclic technique termed: SD-DNT short for Shakedown-Direct Noncyclic Technique. The bends analyzed are subjected to simultaneous steady internal pressure spectra and cyclic in-plane closing (IPC) and in-plane opening (IPO)
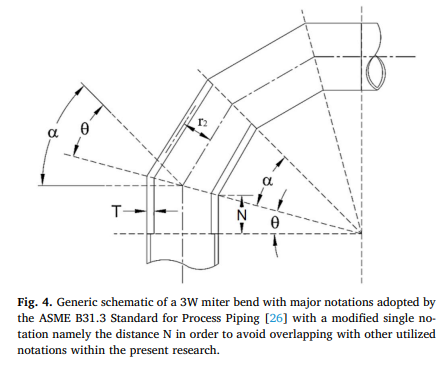
Load carrying capacities of pressurized 90 degree miter and smooth bends subjected to monotonic in-plane and out-of-plane bending loadings
The present research focuses on generating interaction diagrams (i.e. limit moment boundaries vs steady internal pressure spectra) of pressurized 90 o miter and smooth bends. One-, two-, three-, and four-weld miter bends are modelled and analyzed. Additionally, 90 o smooth bends (SBs) bearing the miter bends’ same material and major geometric parameters are analyzed thus providing broader range of comparisons concerning structural responses to external applied loadings. All bends analyzed are subjected to steady internal pressure spectra and monotonic in-plane closing, in-plane opening, and
Pagination
- Previous page ‹‹
- Page 12
- Next page ››
