Publications
Filter by
Positive selection as a key player for SARS-CoV-2 pathogenicity: Insights into ORF1ab, S and E genes
The human β-coronavirus SARS-CoV-2 epidemic started in late December 2019 in Wuhan, China. It causes Covid-19 disease which has become pandemic. Each of the five-known human β-coronaviruses has four major structural proteins (E, M, N and S) and 16 non-structural proteins encoded by ORF1a and ORF1b together (ORF1ab) that are involved in virus pathogenicity and infectivity. Here, we performed
Corneal Biomechanics Assessment Using High Frequency Ultrasound B-Mode Imaging
Assessment of corneal biomechanics for pre- and post-refractive surgery is of great clinical importance. Corneal biomechanics affect vision quality of human eye. Many factors affect corneal biomechanics such as, age, corneal diseases and corneal refractive surgery. There is a need for non-invasive in-vivo measurement of corneal biomechanics due to corneal shape preserving as opposed to ex-vivo
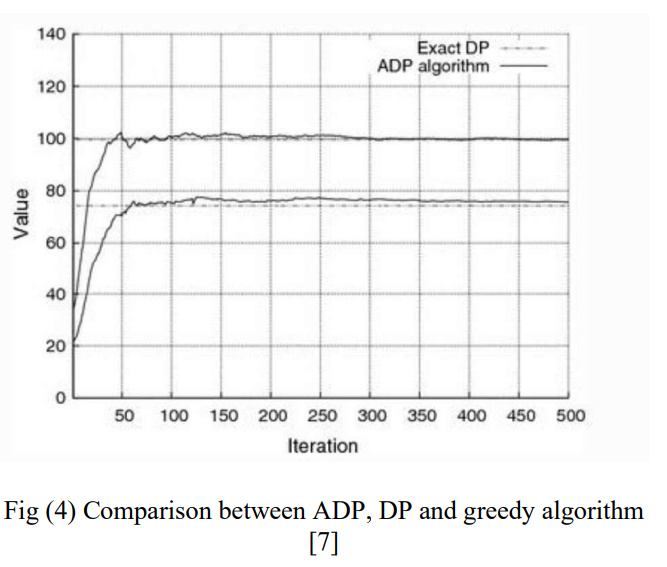
Dynamic Programming Applications: A Suvrvey
Dynamic programming is a mathematical optimization first invented in 1950s and lived till our times to make optimizations and reduce complexity in several different fields like bioinformatics, Electric vehicles, energy consumption, medical field and much more as a proof of being a powerful technique. In this paper, the various fields and aspects in which Dynamic programming has a significant
Detection of Mammalian Coding Sequences Using a Hybrid Approach of Chaos Game Representation and Machine Learning
Mammalian protein-coding sequence detection provides a wide range of applications in biodiversity research, evolutionary studies, and understanding of genomic features. Representation of genomic sequences in Chaos Game Representation (CGR) helps reveal hidden features in DNA sequences due to its ability to represent sequences in both numerical and graphical levels. Machine learning approaches can
Convolutional Neural Network with Attention Modules for Pneumonia Detection
In 2017, pneumonia was the primary diagnosis for 1.3 million visits to the Emergency Department (ED) in the United States. The mortality rate was estimated to be 5%-10% of hospitalized patients, whereas it rises to 30% for severe cases admitted to the Intensive Care Unit (ICU). Among all cases admitted to ED, 30% were misdiagnosed, and they did not suffer from pneumonia, which raises a flag for
Insilico Codon Bias Correction for Transgenic Biological Protein Sequences for Vaccine Production
Codon optimization is primarily used in enhancing the levels of protein expression in the host species. Each species has its own codon usage bias, which represents the codons abundance frequency in that species. Using the host usage profile contributes to personalize the synthesis of the DNA vaccines that can achieve highly active vectors the host cells. For optimizing protein expression levels in
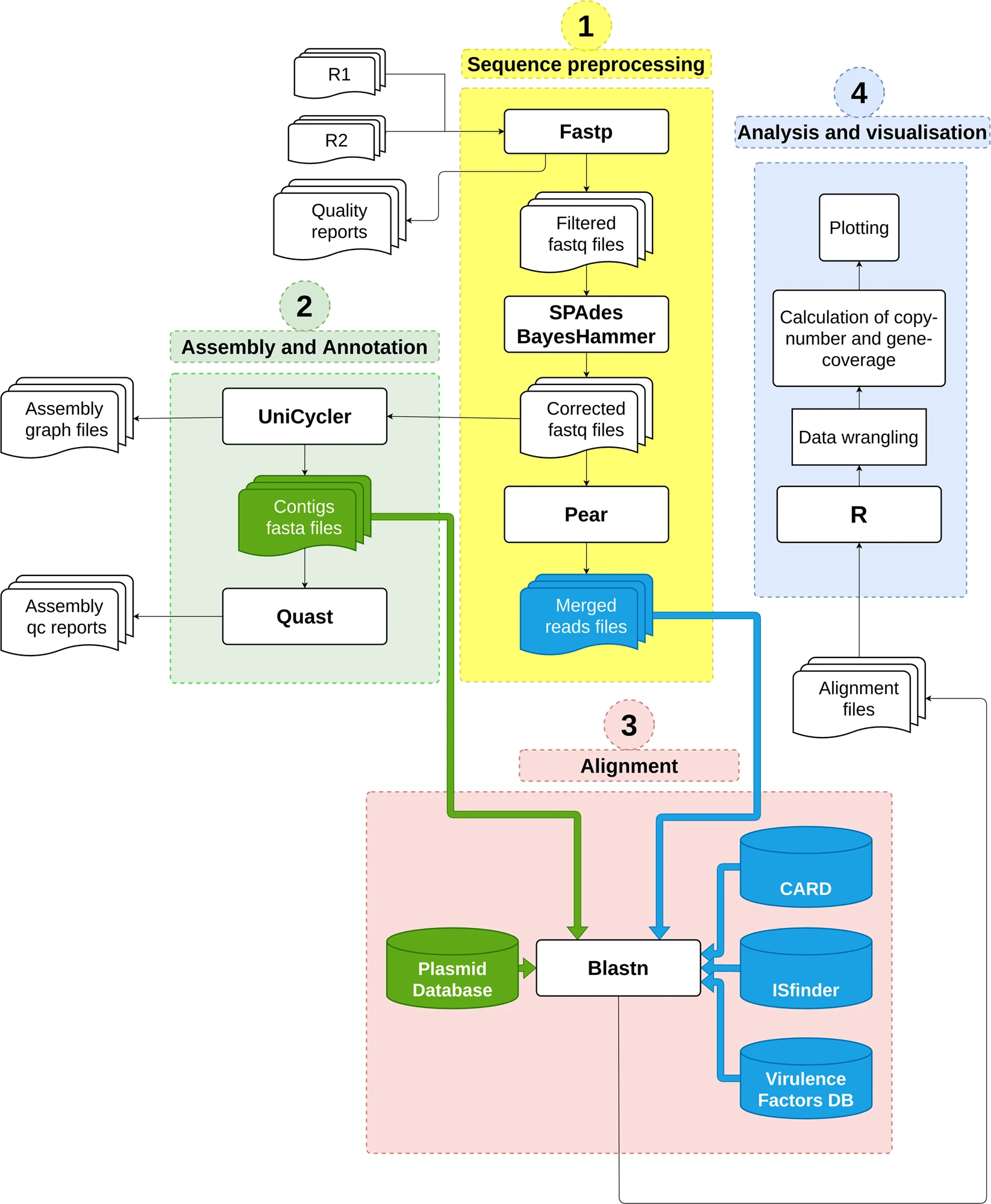
Genotypic characterization of multiple drug resistant Escherichia coli isolates from a pediatric cancer hospital in Egypt
Infection with multiple drug resistant (MDR) Escherichia coli poses a life threat to immunocompromised pediatric cancer patients. Our aim is to genotypically characterize the plasmids harbored in MDR E. coli isolates recovered from bacteremic patients of Children’s Cancer Hospital in Egypt 57357 (CCHE 57357). In this study, 21 carbapenem-resistant E. coli (CRE) isolates were selected that exhibit
In-Silico Comparative Analysis of Egyptian SARS CoV-2 with Other Populations: A Phylogeny and Mutation Analysis
In the current SARS-CoV2 pandemic, identification and differentiation between SARS-COV2 strains are vital to attain efficient therapeutic targeting, drug discovery and vaccination. In this study, we investigate how the viral genetic code mutated locally and what variations is the Egyptian population most susceptible to in comparison with different strains isolated from Asia, Europe and other
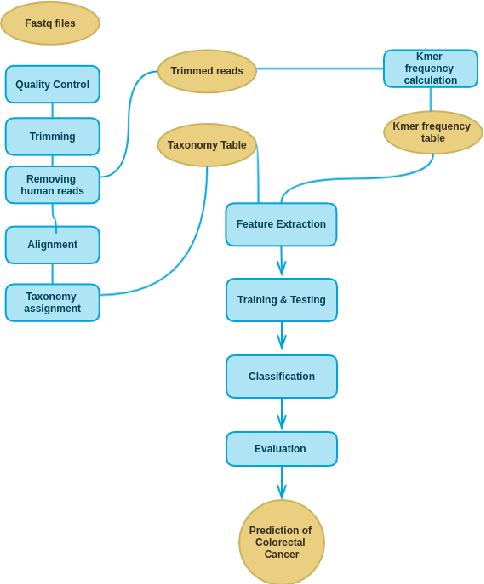
A Hybrid Machine Learning Approach for the Phenotypic Classification of Metagenomic Colon Cancer Reads Based on Kmer Frequency and Biomarker Profiling
Human Microbiome plays a critical role in health and the environment. Colorectal cancer (CRC) is the most common cause of death in many countries, and hence early diagnosis of CRC may help in increasing the survival rate. Tracking changes in the microbiome structure of human gut opens new gates towards the detection and prediction of the risk of CRC. Recently, machine learning became a powerful
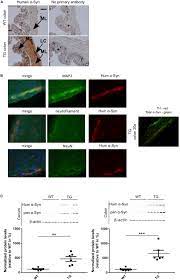
Enriched environmental conditions modify the gut microbiome composition and fecal markers of inflammation in parkinson’s disease
Recent findings suggest an implication of the gut microbiome in Parkinson’s disease (PD) patients. PD onset and progression has also been linked with various environmental factors such as physical activity, exposure to pesticides, head injury, nicotine, and dietary factors. In this study, we used a mouse model, overexpressing the complete human SNCA gene (SNCA-TG mice) modeling familial and

