Cloud computing privacy issues, challenges and solutions
There are many cloud computing initiatives that represent a lot of benefit to enterprise customers. However, there are a lot of challenges and concerns regarding the security and the privacy of the customer data that is hosted on the cloud. We explore in this paper the various aspects of cloud computing regarding data life cycle and its security and privacy challenges along with the devised methodology to address those challenges. We mention some of the regulations and law requirements in place to ensure cloud customer data privacy. © 2017 IEEE.
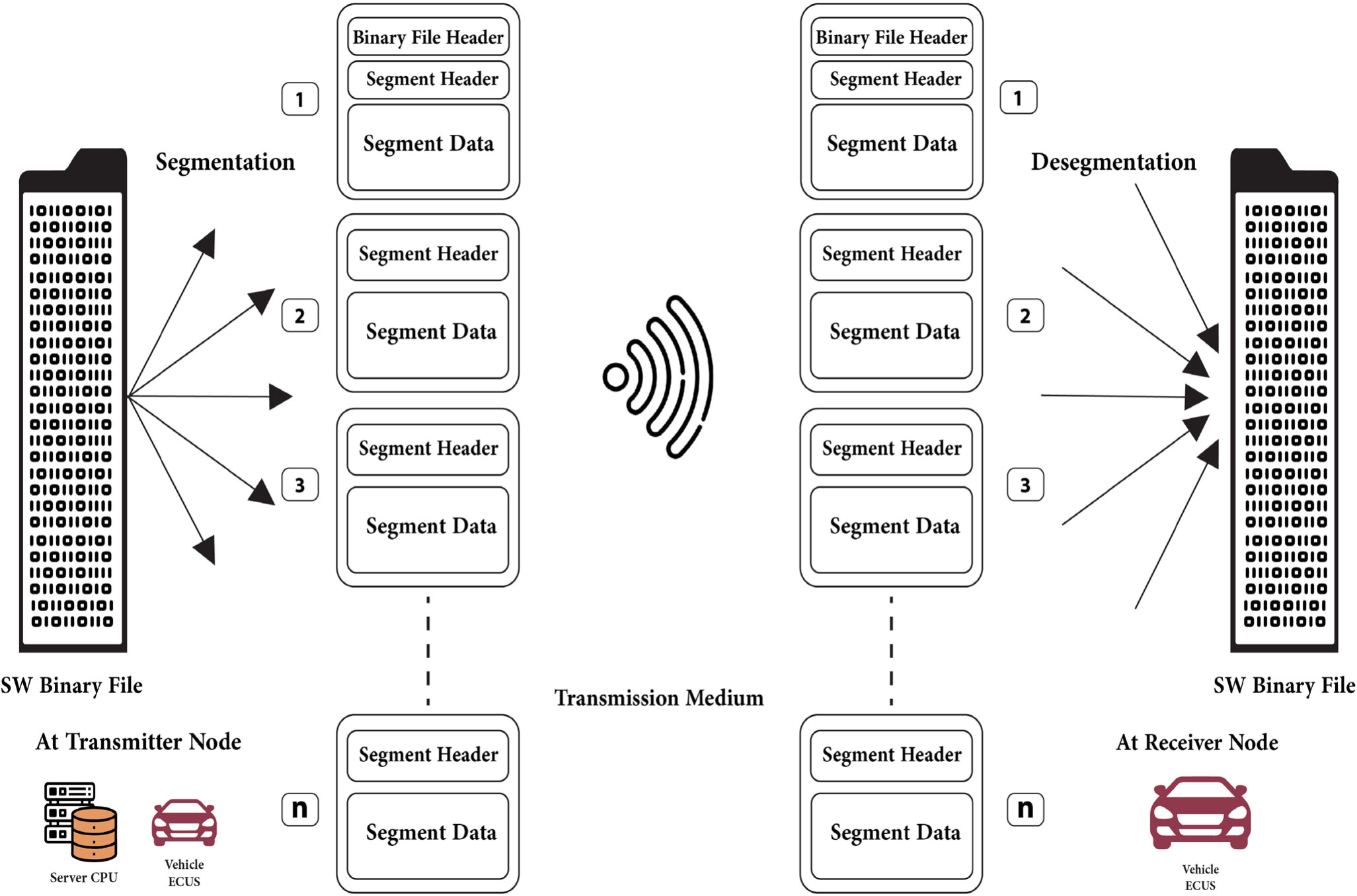
Segmented OTA Platform Over ICN Vehicular Networks
The Internet Protocol (IP) architecture could not fully satisfy the Vehicular Ad-hoc Networks (VANETs) needed efficiency, due to their dynamic topology and high mobility. This paper presents a technique that updates the software of Electronic Control Units (ECUs) in vehicles using segmented Over The Air (OTA) platform over Information-Centric Network (ICN) architecture. In VANET, the amount of time for active vehicles’ connectivity varies due to the vehicular network’s dynamic topologies. The importance of Flashing Over The Air (FOTA) has been illustrated as well as the impact of applying the

Detection and Countermeasures of DDoS Attacks in Cloud Computing
Greater portions of the world are moving to cloud computing because of its advantages However, due to its distributed nature, it can be easily exploited by Distributed Denial of Service (DDoS) attacks. In distributed DDoS attacks, legitimate users are prevented from using cloud resources. In this paper, the various DDoS detection and defenses mechanisms cloud computing are reviewed. We propose a new technique based on Remote Triggered Black Hole (RTBH) to prevent DDoS attacks before it target to cloud resources. © 2018 IEEE.
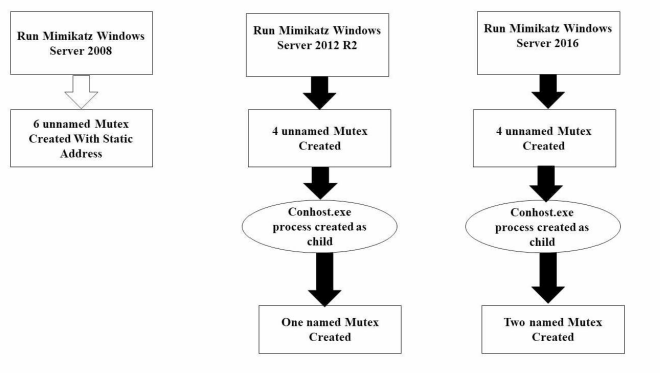
Detecting Mimikatz in Lateral Movements Using Mutex
Advanced Persistent Threat (APT) is a stealthy computer network attack. Its threat lies in the fact that unauthorized access to a network is gained and the attackers, whether a person or a group may remain undetected for an extended period. APT group can spread and gain access to the most valuable assets in the targeted organization. Depending on the tools used by APT group it can be hard and complex to respond to those groups and their tools. Mimikatz is one of the most powerful tools used by many APT groups, penetration testers and malware. In this paper, we focus on lateral movement and APT
Cooperation incentives in wireless ad hoc networks
Mobile ad hoc networks heavily rely on nodes' cooperation for packet forwarding. As a result, misbehaving, malicious, and selfish nodes can significantly degrade the performance of the network. To cope with this issue and to stimulate cooperation among selfish mobile nodes, a continuous research effort is done on identifying nodes trust and reputation. In this paper, we survey recently proposed reputation and incentive schemes for ad hoc networks. In order to help in the design of different reputation systems tailored to specific applications and network topologies, we classify the different
Traffic Analysis for Real Time Applications and its Effect on QoS in MANETs
Quality of Service (QoS) is one of the major challenges in Mobile Ad-hoc Networks (MANETs), due to their nature and special characteristics. QoS depends on different and multiple metrics such as routing protocols, route stability, channel rate quality, bandwidth, ... etc. Most of studies focus on the above metrics and some of them proposed enhancements. However, there are still unfilled gaps that need to be tackled. In this paper, we focus on the impact of QoS parameters on MANETs. The main objective is to identify the suitable applications in MANETs with respect to the network parameters. ©
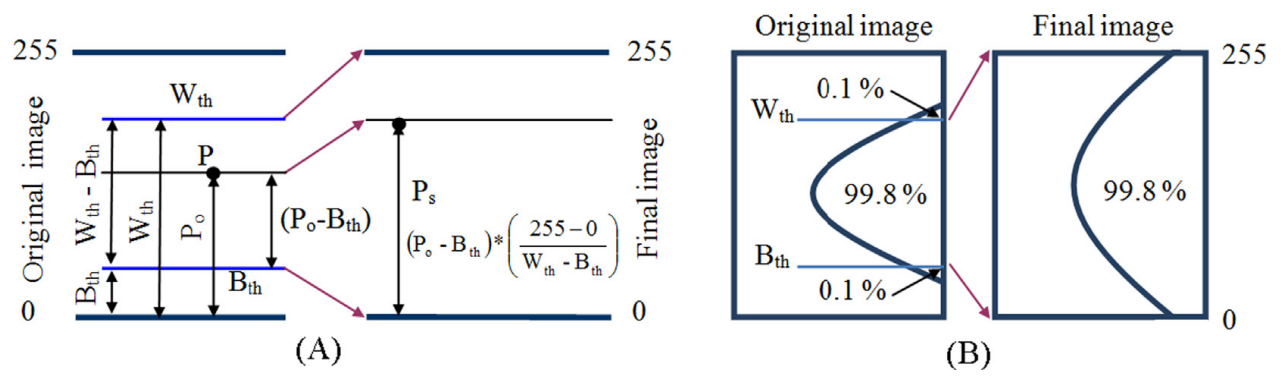
Automated detection and classification of galaxies based on their brightness patterns
Clues and traces of the universe's origin and its developmental process are deeply buried in galaxy shapes and formations. Automated galaxies classification from their images is complicated due to the faintness of the galaxy images, conflicting bright background stars, and image noise. For this purpose, the current work proposes a novel logically structured modular algorithm that analyses galaxy morphological raw brightness data to automatically detect galaxy visual center, region, and classification. First, a novel selective brightness threshold is employed to eliminate the effect of bright
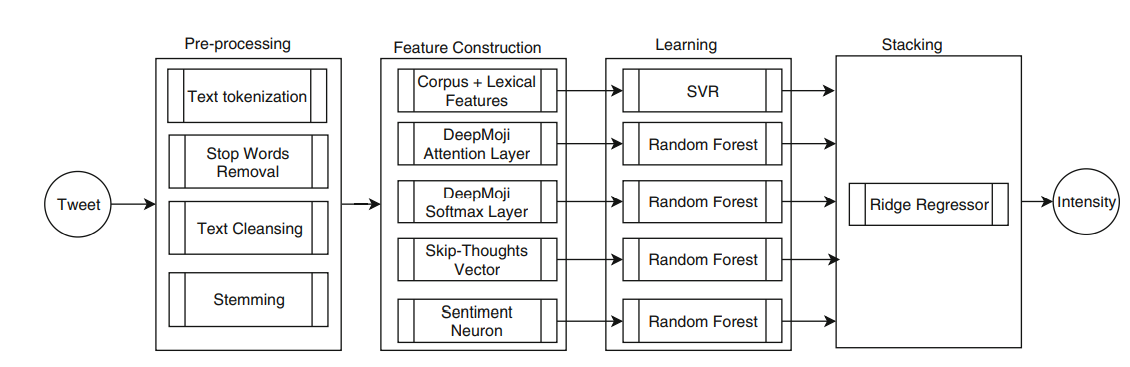
A Transfer Learning Approach for Emotion Intensity Prediction in Microblog Text
Emotional expressions are an important part of daily communication between people. Emotions are commonly transferred non verbally through facial expressions, eye contact and tone of voice. With the rise in social media usage, textual communication in which emotions are expressed has also witnessed a great increase. In this paper automatic emotion intensity prediction from text is addressed. Different approaches are explored to find out the best model to predict the degree of a specific emotion in text. Experimentation was conducted using the dataset provided by SemEval-2018 Task 1: Affect in
Simultaneous human detection and action recognition employing 2DPCA-HOG
In this paper a novel algorithm for Human detection and action recognition in videos is presented. The algorithm is based on Two-Dimensional Principal Components Analysis (2DPCA) applied to Histogram of Oriented Gradients (HOG). Due to simultaneous Human detection and action recognition employing the same algorithm, the computational complexity is reduced to a great deal. Experimental results applied to public datasets confirm these excellent properties compared to most recent methods. © 2011 IEEE.
Face and gesture recognition for human computer interaction employing 2DHoG
Face and hand gesture recognition is one of the most challenging topics in computer vision. In this paper, a novel algorithm presenting a new 2D representation of histogram of oriented gradients is proposed, where each bin represents a range of angles dealt with in a separate layer employing 2DPCA. This method maintains the spatial relation between pixels which enhance the recognition accuracy. In addition it can be applied on either face or hand gesture images. Experimental results confirm excellent properties of the proposed algorithm and promotes it for real time applications © 2013 IEEE.
Pagination
- Previous page ‹‹
- Page 2
- Next page ››
