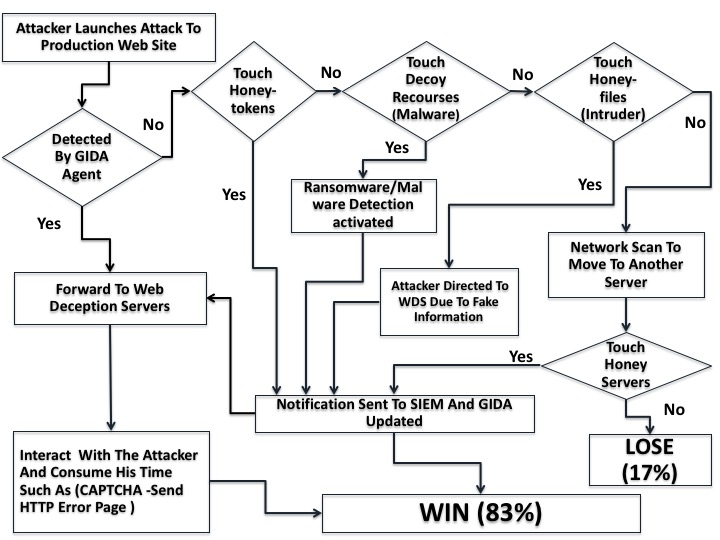
A New Web Deception System Framework
Web applications have many vulnerabilities that allow attackers to compromise sensitive data and gain unauthorized access to the production web servers. Compromised web-sessions represent a major threat. Current random attacks draw attention to the need for new protection and detection tools. In this paper, we propose a web deception scheme to mitigate web attacks in the production web site. The solution is more like a call for arms, using game theory, honeyweb, and honeytokens with ransomware and intrusion detection. The proposed scheme is explained in details as well as simulation results. ©

Crypto-SAP Protocol for Sybil Attack Prevention in VANETs
VANETs are considered as sub-category from MANETs. They provide the vehicles with the ability of communication among each other to guarantee safety and provide services for drivers. VANETs have many network vulnerabilities like: Working on wireless media makes it vulnerable to many kinds of attacks and nodes can join or leave the network dynamically making change in its topology which affects communication links stability. In VANETs, each car works as a node and router, so if a malicious attacker joins the network, the attacker could send false messages to disrupt the network operation and
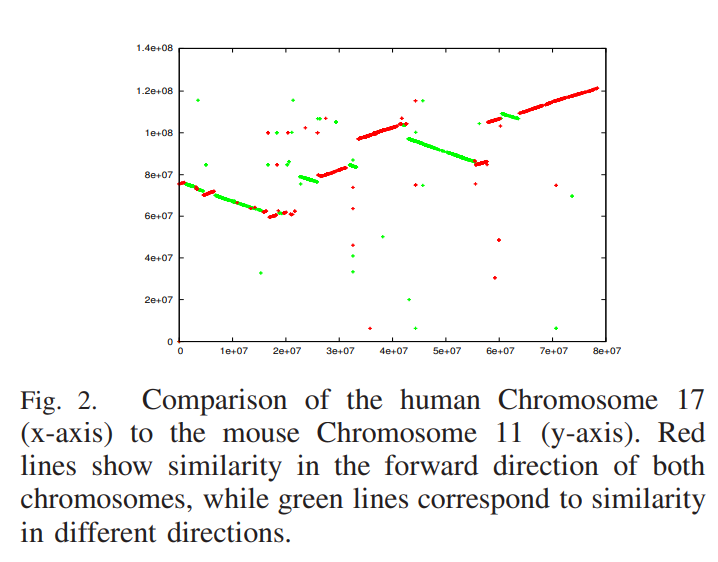
WinBioinfTools: Bioinformatics tools for windows cluster
Open source bioinformatics tools running under MS Windows are rare to find, and those running underWindows HPC cluster are almost nonexisting, in spite of the fact that Windows is the most popular operating system. Therefore, we introduce WinBioinfTools, an open source toolkit containing a number of bioinformatics tools running under Windows High Performance Computing Server 2008. The current version contains three programs for biological sequence analysis: 1) CoCoNUT for pairwise genome comparison, 2) WinBLAST for biological database search, and 3) WinPSA for global pairwise sequence
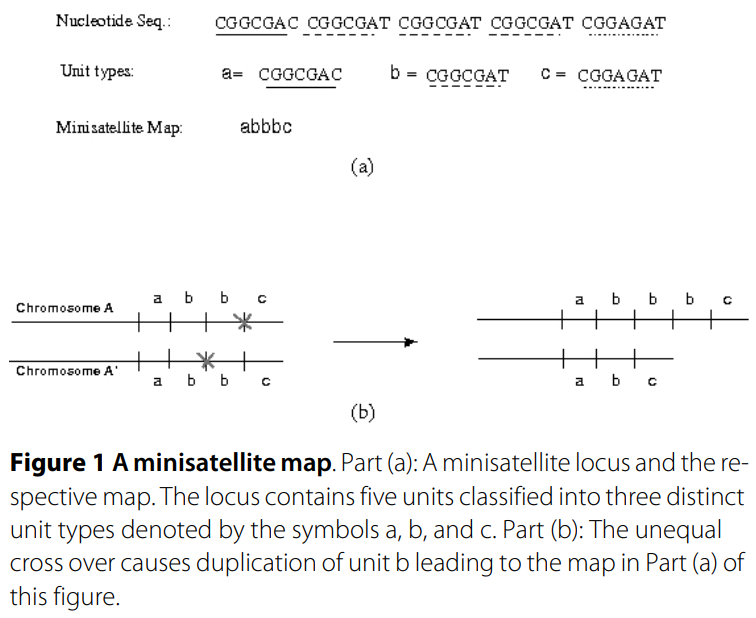
WAMI: A web server for the analysis of minisatellite maps
Background. Minisatellites are genomic loci composed of tandem arrays of short repetitive DNA segments. A minisatellite map is a sequence of symbols that represents the tandem repeat array such that the set of symbols is in one-to-one correspondence with the set of distinct repeats. Due to variations in repeat type and organization as well as copy number, the minisatellite maps have been widely used in forensic and population studies. In either domain, researchers need to compare the set of maps to each other, to build phylogenetic trees, to spot structural variations, and to study duplication
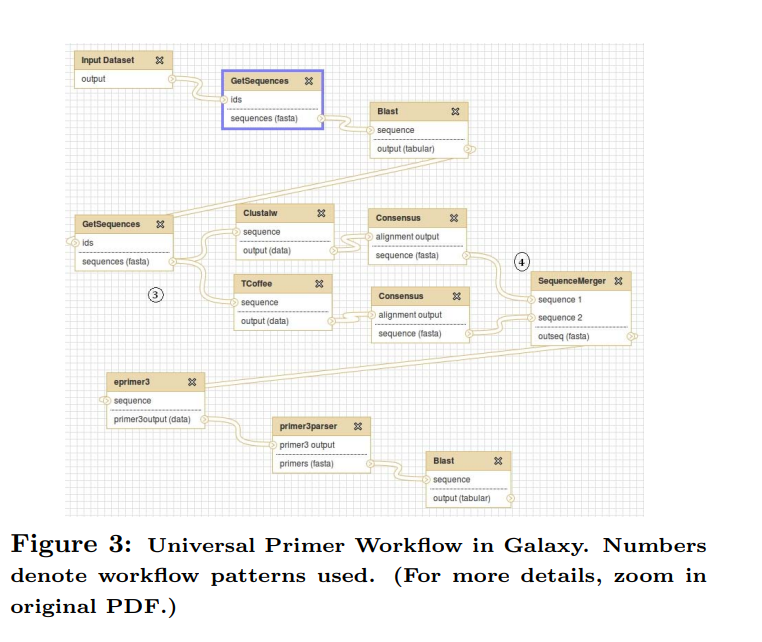
Meta-workflows: Pattern-based interoperability between Galaxy and Taverna
Taverna and Galaxy are two workflow systems developed specifically for bioinformatics applications. For sequence analysis applications, some tasks can be implemented easily on one system but would be difficult, or infeasible, to be implemented on the other. One solution to overcome this situation is to combine both tools in a unified framework that seamlessly makes use of the best features of each tool. In this paper, we present the architecture and implementation of a high-level system that provides such a solution. Our approach is based on meta-workflows and workflow patterns. We present a
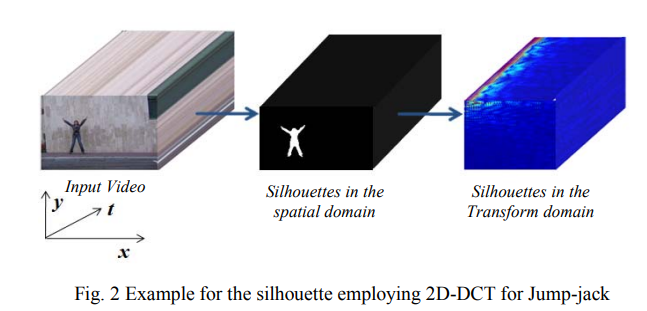
Human action recognition employing TD2DPCA and VQ
A novel algorithm for human action recognition in the transform domain is presented. This approach is based on Two- Dimensional Principal Component Analysis (2DPCA) and Vector Quantization (VQ). This technique reduces the computational complexity and the storage requirement by at least a factor of 45.27, and 12 respectively, while achieving the highest recognition accuracy, compared with the most recently published approaches. Experimental results applied on the Weizmann dataset confirm the excellent properties of the proposed algorithm, which lends itself to real-time economic implementation

Human action recognition employing 2DPCA and VQ in the spatio-temporal domain
In this paper a novel algorithm for human action recognition is presented. This approach is based on Two-Dimensional Principal Component Analysis (2DPCA) and Vector Quantization (VQ) in the spatial-temporal domain. This method reduces computational complexity by a factor of 98, while maintaining the storage requirement and the recognition accuracy, compared with some of the most recent approaches in the field. Experimental results applied on the Weizmann dataset confirm the excellent properties of the proposed algorithm. © 2010 IEEE.
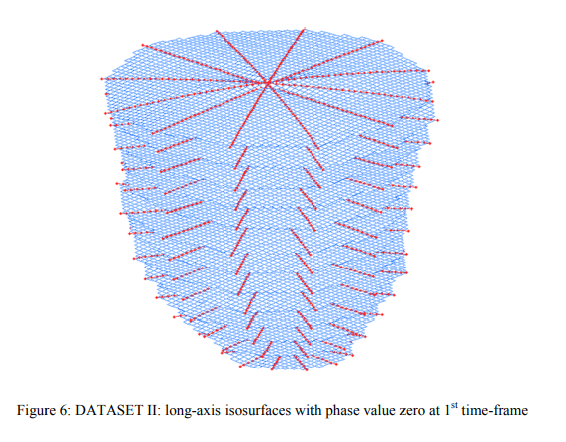
3D motion tracking of the heart using Harmonic Phase (HARP) isosurfaces
Tags are non-invasive features induced in the heart muscle that enable the tracking of heart motion. Each tag line, in fact, corresponds to a 3D tag surface that deforms with the heart muscle during the cardiac cycle. Tracking of tag surfaces deformation is useful for the analysis of left ventricular motion. Cardiac material markers (Kerwin et al, MIA, 1997) can be obtained from the intersections of orthogonal surfaces which can be reconstructed from short- and long-axis tagged images. The proposed method uses Harmonic Phase (HARP) method for tracking tag lines corresponding to a specific
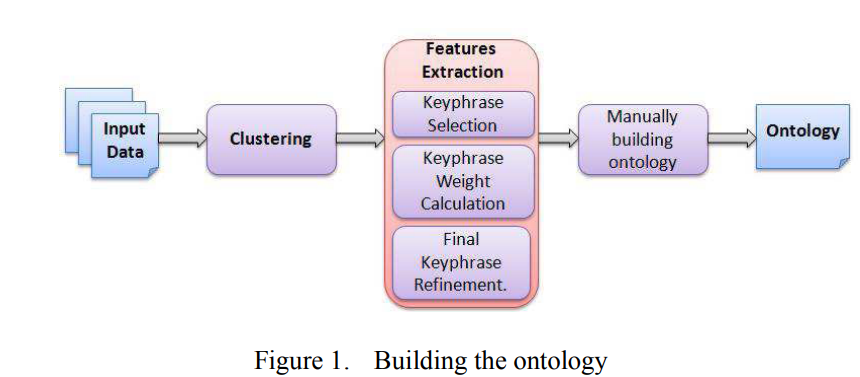
TopicAnalyzer: A system for unsupervised multi-label Arabic topic categorization
The wide spread use of social media tools and forums has led to the production of textual data at unprecedented rates. Without summarization, classification or other form of analysis, the sheer volume of this data will often render it useless and human analysis on this scale is next to impossible. The work presented in this paper focuses on investigating an approach for classifying large volumes of data when no training data and no classification scheme are available. Motivation for this work lies in encountering a real life problem which is further described in the paper. The presented system
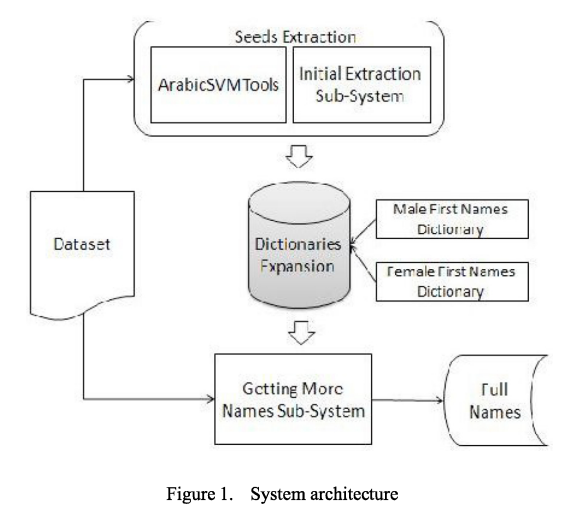
Person name extraction from modern standard Arabic or colloquial text
Person Name extraction from Arabic text is a challenging task. While most existing Arabic texts are written in Modern Standard Arabic Text (MSA) the volume of Arabic Colloquial text is increasing progressively with the wide spread use of social media examples of which are Facebook, Google Moderator and Twitter. Previous work addressed extracting persons' names from MSA text only and especially from news articles. Previous work also relied on a lot of resources such as gazetteers for places, organizations, verbs, and person names. In this paper we introduce a system for extracting persons'
Pagination
- Previous page ‹‹
- Page 18
- Next page ››
