Security in Ad hoc networks: From vulnerability to risk management
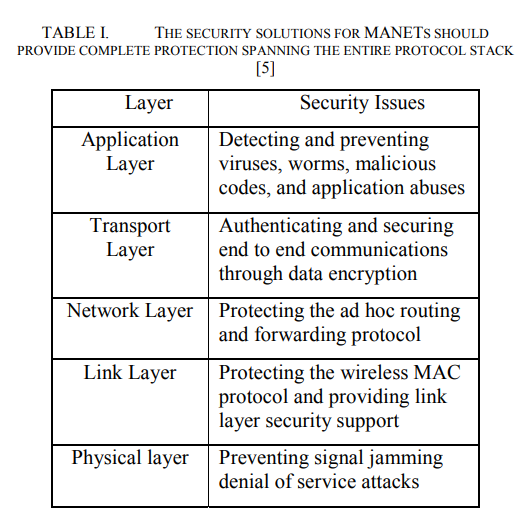
Mobile Ad hoc Networks (MANETs) have lots of applications. Due to the features of open medium, absence of infrastructure, dynamic changing network topology, cooperative algorithms, lack of centralized monitoring and management point, resource constraints and lack of a clear line of defense, these networks are vulnerable to attacks. A vital problem that must be solved in order to realize these applications is that concerning the security aspects of such networks. Solving these problems combined with the widespread availability of devices such as PDAs, laptops, small fixtures on buildings and

Machine learning methodologies in P300 speller brain-computer interface systems
Brain-Computer Interfaces (BCI) is a one kind of communication system that enables control of devices or communication with others only through brain signal activities without using motor activities. P300 Speller is a BCI paradigm that helps disabled subjects to spell words by means of their brain signal activities. This paper tries to demonstrate the performance of different machine learning algorithms based on classification accuracy. Performance has been evaluated on the data sets acquired using BC12000's P300 Speller Paradigm provided by BCI competitions II (2003) & III (2004) organizers
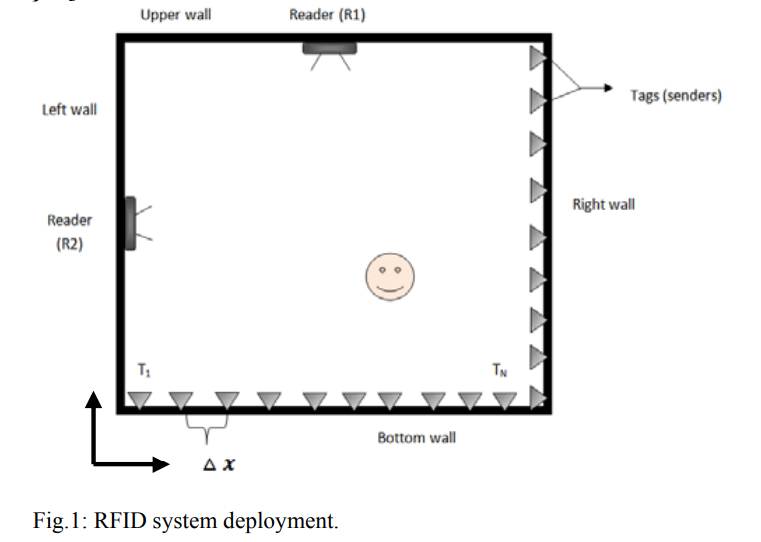
RFID-based indoors localization of tag-less objects
Object localization has become a necessary module in many radiofrequency identification (RFID) systems that require tracking features besides the conventional identification feature. A number of techniques exists in literature that uses the RFID signal information to locate the tagged objects, i.e. objects wearing RFID tags. Nevertheless, in many applications, it is required to track objects that do not carry a tag (whether intentionally or unintentionally). In this work, we propose a technique for tag-less object localization. The technique is based on reconstructing the attenuation map of
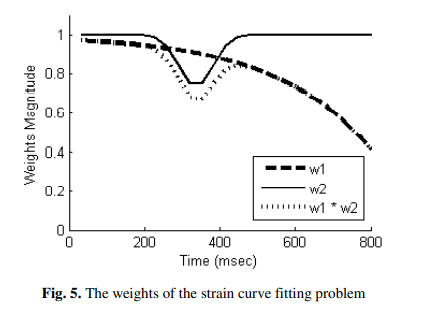
Correction of left ventricle strain signals estimated from tagged MR images
Strain measurement is a quantity used for assessing the regional function of the left ventricular (LV) of the heart. They are computed by tracking the motion of the non-invasive, virtual tags in the cardiac muscle with time. Tracking these tags gives information for each region of the cardiac muscle by quantifying its deformation during contraction (systolic period) and relaxation (diastolic period). However, these strain measurements suffer from inaccuracies caused by the degradation of the tags and the image quality. In this work, numerical simulations are used to investigate the factors
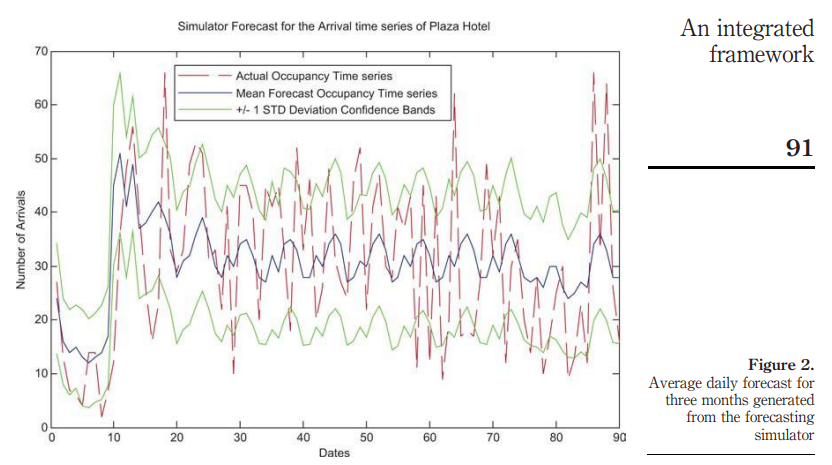
An integrated framework for advanced hotel revenue management
Purpose: This paper aims to present an integrated framework for hotel revenue room maximization. The revenue management (RM) model presented in this work treats the shortcomings in existing systems. In particular, it extends existing optimization techniques for hotel revenue management to address group reservations and uses "forecasted demand" arrivals generated from the real data. Design/methodology/approach: The proposed forecasting module attempts to model the hotel reservation process from first principles. In particular, it models hotel arrivals as an interrelated process of stochastic

Accurate analysis of cardiac tagged MRI using combined HARP and optical flow tracking
In this work, we present a new method for analyzing cardiac tagged Magnetic Resonance Imaging (tMRI). The method combines two major tracking techniques: Harmonic Phase (HARP) and Optical Flow (OF). The results of the two techniques are fused together to accurately estimate the displacement of each myocardium point. The developed methods were tested using numerical MRI phantom at different SNR levels and deformation rates. The results show that the proposed method is more accurate and reliable than the HARP and the OF methods. © 2012 IEEE.
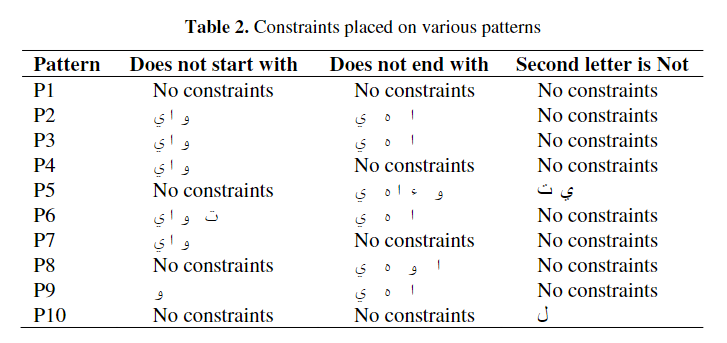
A corpus based approach for the automatic creation of Arabic broken plural dictionaries
Research has shown that Arabic broken plurals constitute approximately 10% of the content of Arabic texts. Detecting Arabic broken plurals and mapping them to their singular forms is a task that can greatly affect the performance of information retrieval, annotation or tagging tasks, and many other text mining applications. It has been reported that the most effective way of detecting broken plurals is through the use of dictionaries. However, if the target domain is a specialized one, or one for which there are no such dictionaries, building those manually becomes a tiresome, not to mention

Open issues in the sentiment analysis of Arabic social media: A case study
With the rapid increase in the volume of Arabic opinionated posts on different microblogging mediums comes an increasing demand for Arabic sentiment analysis tools. Yet, research in the area of Arabic sentiment analysis is progressing at a very slow pace compared to that being carried out in English and other languages. This paper highlights the major problems and open research issues that face sentiment analysis of Arabic social media. The paper also presents a case study the goal of which is to investigate the possibility of determining the semantic orientation of Arabic Egyptian tweets and
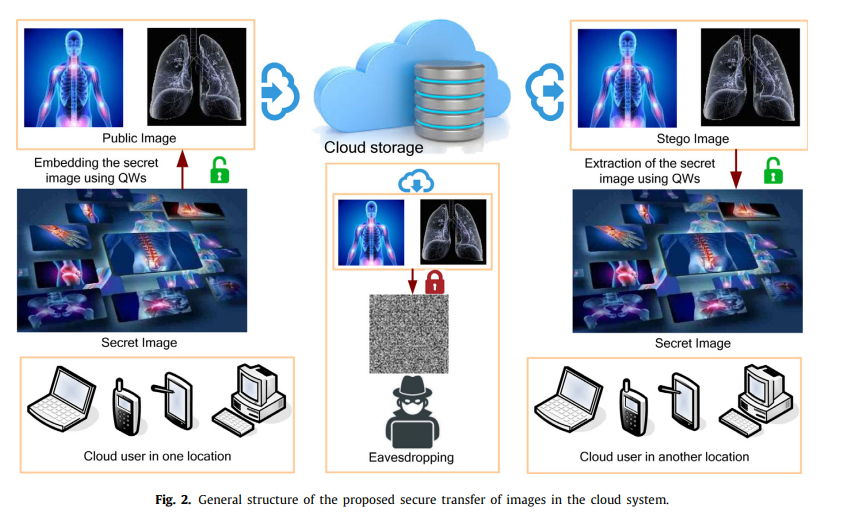
Secret images transfer in cloud system based on investigating quantum walks in steganography approaches
The central role of the cloud data warehouse is to ensure the security of confidential data that can be achieved via techniques of steganography and cryptography. Amidst the growth of quantum computation, modern data security tools may be cracked because of its structure based on mathematical computations. Quantum walk (QW) acts as a vital role in designing quantum algorithms, which is a universal computational model. Therefore, we allocate the advantages of QWs to design a QWs-based novel image steganography mechanism for cloud systems, which the embedding/extraction process for the secret
Pagination
- Previous page ‹‹
- Page 9
- Next page ››