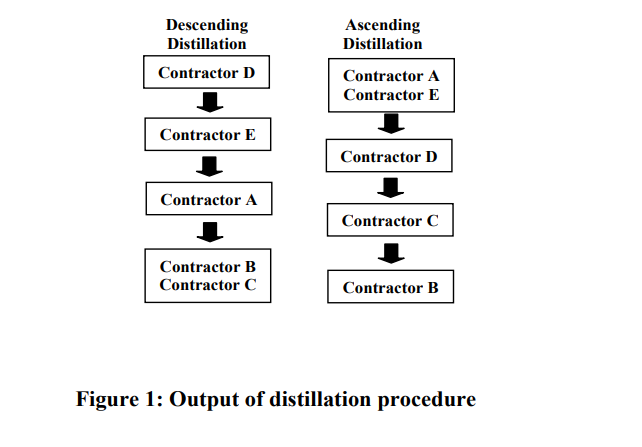
An application of ELECTRE III to contractor selection
Contractor selection is carried out in order to choose a competent and capable contractor to do the work. To help in this selection, baselines are established to ensure that the contractors have the required skills, resources, and abilities to execute the project. Contractor selection is a multiple criteria decision making wherein several criteria are required to be evaluated simultaneously. This paper proposes a decisionmaking model for contractor selection utilizing ELECTRE III modeling. The steps of ELECTRE III model include; estimation of concordance indices, estimation of discordance
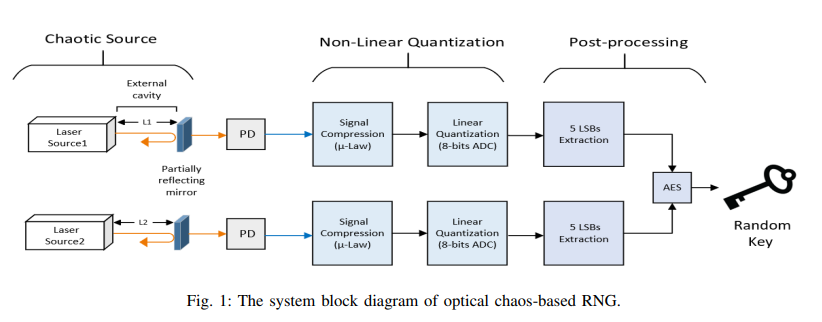
Chaos-Based RNG using Semiconductor Lasers with Parameters Variation Tolerance
Random numbers play an essential role in guaranteeing secrecy in most cryptographic systems. A chaotic optical signal is exploited to achieve high-speed random numbers. It could be generated by using one or more semiconductor lasers with external optical feedback. However, this system faces two major issues, high peak to average power ratio (PAPR) and parameter variations. These issues highly affected the randomness of the generated bitstreams. In this paper, we use a non-linear compression technique to compand the generated signal before it is quantized to avoid the effects of the PAPR. Also
Arithmetic optimization approach for parameters identification of different PV diode models with FOPI-MPPT
The Maximum Power Point Tracker (MPPT) provides the most efficient use of a Photo-voltaic system independent of irradiance or temperature fluctuations. This paper introduces the modeling and control of a photo-voltaic system operating at MPPT using the arithmetic optimization algorithm (AOA). The single and double Photo-voltaic models are investigated. Their optimal unknown parameters are extracted using AOA based on commercial Photo-voltaic datasheets. A comparison is performed between these optimal parameters extracted by AOA and other optimization techniques presented in the literature
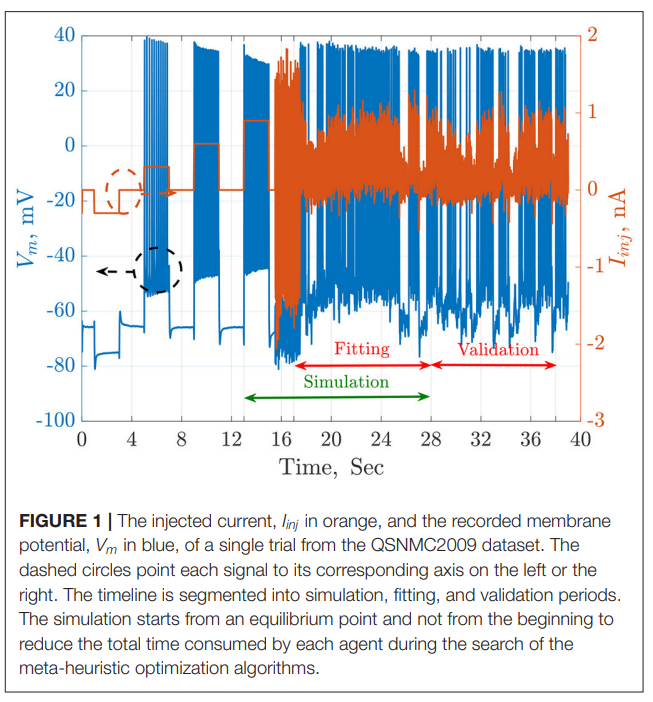
Parameter Estimation of Two Spiking Neuron Models With Meta-Heuristic Optimization Algorithms
The automatic fitting of spiking neuron models to experimental data is a challenging problem. The integrate and fire model and Hodgkin–Huxley (HH) models represent the two complexity extremes of spiking neural models. Between these two extremes lies two and three differential-equation-based models. In this work, we investigate the problem of parameter estimation of two simple neuron models with a sharp reset in order to fit the spike timing of electro-physiological recordings based on two problem formulations. Five optimization algorithms are investigated; three of them have not been used to
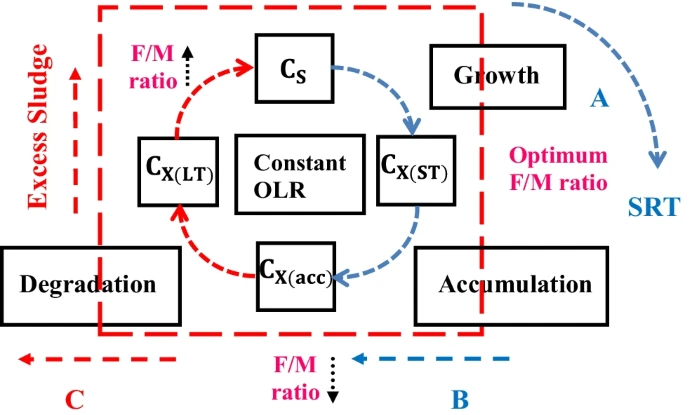
Modified fractional-order model for biomass degradation in an up-flow anaerobic sludge blanket reactor at Zenein Wastewater Treatment Plant
This paper presents a modified fractional-order model (FOM) for microorganism stimulation in an up-flow anaerobic sludge blanket (UASB) reactor treating low-strength wastewater. This study aimed to examine the famine period of methanogens due to biomass accumulation in the UASB reactor over long time periods at a constant organic loading rate (OLR). This modified model can investigate the substrate biodegradation in a UASB reactor while considering substrate diffusion into biological granules during the feast and famine periods of methanogens. The Grünwald-Letnikov numerical technique was used
Electronically Controlled Power-Law Filters Realizations
A generalized structure that is capable of implementing power-law filters derived from 1st and 2nd-order mother filter functions is presented in this work. This is achieved thanks to the employment of Operational Transconductance Amplifiers (OTAs) as active elements, because of the electronic tuning capability of their transconductance parameter. Appropriate design examples are provided and the performance of the introduced structure is evaluated through simulation results using the Cadence Integrated Circuits (IC) design suite and Metal Oxide Semiconductor (MOS) transistors models available
On Inverse Full State Hybrid Function Projective Synchronization For Continuous-time Chaotic Dynamical Systems with Arbitrary Dimensions
Referring to continuous-time chaotic dynamical systems, this paper investigates the inverse full state hybrid function projective synchronization (IFSHFPS) of non-identical systems characterized by different dimensions. By taking a master system of dimension n and a slave system of dimension m, the method enables each master system state to be synchronized with a linear combination of slave system states, where the scaling factor of the linear combination can be any arbitrary differentiable function. The approach, based on the Lyapunov stability theory and stability of linear continuous-time
Discrete fractional-order Caputo method to overcome trapping in local optima: Manta Ray Foraging Optimizer as a case study
Enhancing the exploration and exploitation phases of the metaheuristic (MH) optimization algorithms is the key to avoiding local optima. The Manta ray foraging optimizer is a recently proposed MH optimizer. The MRFO showed a good performance in the simple optimization problems. However, it is trapped into the local optimum in the more elaborated ones due to the original algorithm's low capability in exploiting the optimal solutions and its convergence. From this principle, in this work, a novel variant of the Manta ray foraging optimizer has been proposed for global optimization problems
Fractional-Order and Power-Law Shelving Filters: Analysis and Design Examples
Low-pass and high-pass non-integer order shelving filter designs, which are suitable for acoustic applications, are presented in this work. A first design is based on a standard fractional-order bilinear transfer function, while a second one is based on the transposition of the integer-order transfer function into its power-law counterpart. Both transfer functions are approximated using the Oustaloup approximation tool, while the implementation in the case of the power-law filters is performed through the employment of the concept of driving-point impedance synthesis. An attractive benefit is
Pagination
- Page 1
- Next page ››

