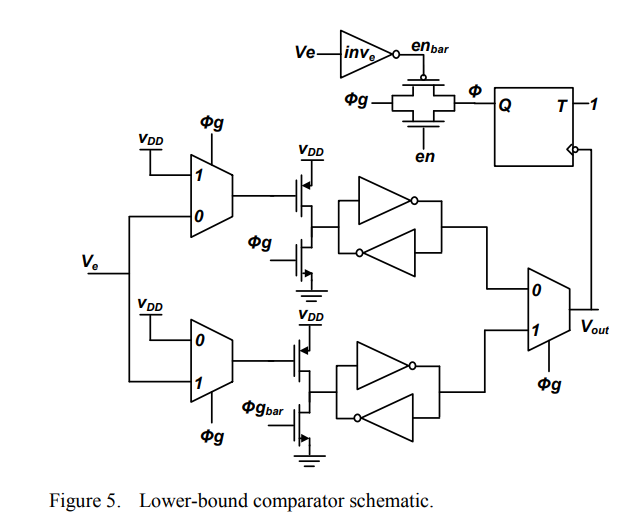
Gain-band self-clocked comparator for DC-DC converters hysteretic control
A novel digital comparator topology is presented. The proposed digital comparator cell uses transistors' ratio to program a fixed comparison level. A double-bound hysteretic control comparator, for DC-DC converters, is built using the proposed digital comparator cell. The hysteretic-band width variation, due to process effects, decreases with increased preamplifier stage gain and constitutes a fixed ratio of the hysteretic-band width. The proposed comparator does not require offset cancellation circuits, which reduces power consumption as well as the die area and increases the comparison speed
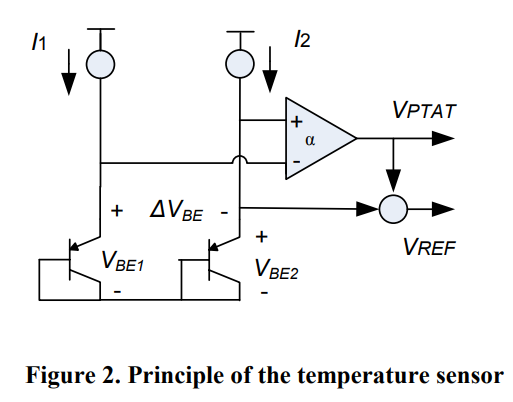
Counter based CMOS temperature sensor for low frequency applications
A simple temperature sensor in Bi-CMOS technology is proposed for applications with low frequency temperature variations in addition to a complete analysis of each block in the system. Most CMOS temperature sensors are based on the temperature characteristics of parasitic bipolar transistors. Two important factors need to be met in the design of the sensor: the first is the accuracy of the sensor, and the second is the power consumption of the temperature sensor that needs to be reduced. A simplified counter approach is used here instead of the commonly used complex decimation filter

A 12Gbps all digital low power SerDes transceiver for on-chip networking
In this paper, a new self-timed signaling technique for reliable low-power on-chip SerDes (Serialization and DeSerialization) links is presented. The transmitter serializes 8 parallel bits at 1.5GHz, and multiplexes the 12Gbps serial data stream with a 24GHz clock on a single line using three level signaling. This new signaling technique enables the receiver to recover the clock from the data with a simple phase detector circuitry. Moreover, this technique is insensitive to jitter accumulated during signal propagation or at the receiver input because the clock signal is extracted from the
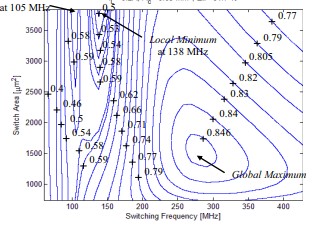
Slow-switching-limit loss removal in SC DC-DC converters using adiabatic charging
A novel technique to remove the slow-switching-limit (SSL) loss in switched-capacitor (SC) dc-dc converters is presented. A small series inductor is cascaded with an SC converter causing adiabatic charging of the converter's energy-transfer capacitors. In this work, the theory and necessary conditions for SSL loss elimination through an inductive output filter are derived. The new topology enables high efficiency for on-die dc-dc converters while maintaining reasonable energy density. A 2:1 SC converter is built in 65-nm CMOS process to validate the analysis methods and asses the proposed
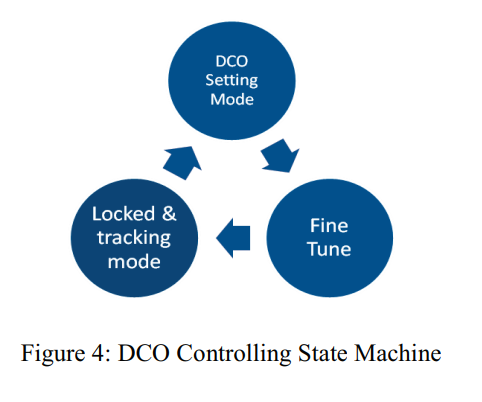
A novel power gated digitally controlled oscillator
In this paper a novel power gated digitally controlled oscillator (DCO) is presented. The DCO is suitable for integration in various systems such as clock generation circuits, clock and data recovery, and clocking schemes for high speed links. Simulations of the proposed DCO on 65nm TSMC technology show frequency range of 2.5 GHz to 6.8 GHz across all corners. The proposed DCO consumes only 1.7 mW at 3 GHz and 3.2 mW at 6.8 GHz with estimated layout area of 70 *70 m 2. The phase noise of the free running DCO is 92 dBc/Hz measured at 1 MHz offset from a 3.4 GHz center frequency. © 2011 IEEE.
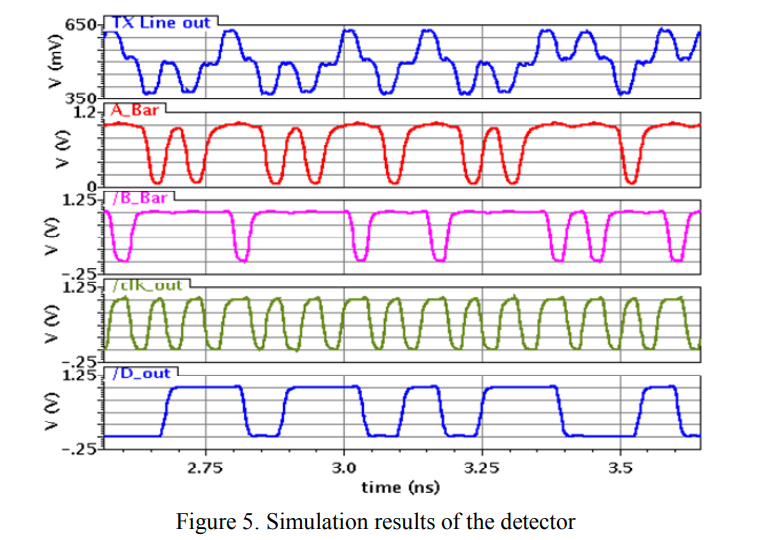
A 16Gbps low power self-timed SerDes transceiver for multi-core communication
This paper presents a modified design for a self-timed SerDes transceiver that was recently published [1]. The new architecture overcomes the main problems that arise in [1], while offering the same advantages. Resistive termination is used instead of source matching to eliminate the need for Manchester coding in [1], this resistive termination increased the data rate to be 16Gbps compared to 12Gbps in [1]. Moreover, resistive termination removed the limitation on the minimum operating frequency that existed in [1], solving a lot of problems at the slow process corners. A single ended
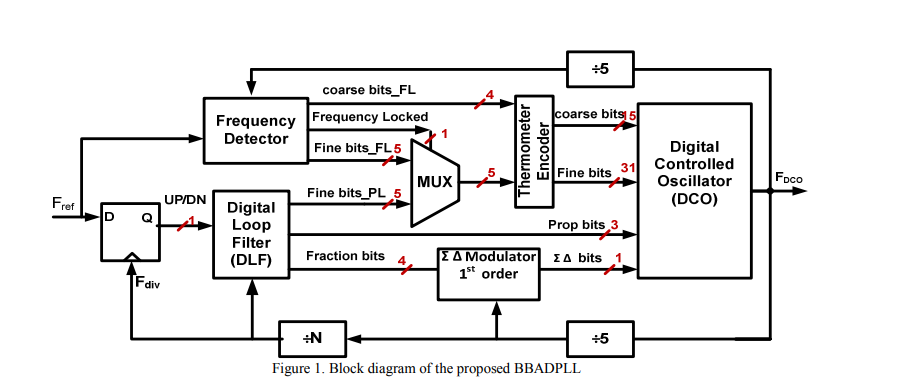
A 5-10GHz low power bang-bang all digital PLL based on programmable digital loop filter
This paper presents the design and the implementation of a low power bang-bang all digital phase locked loop (BBADPLL). The design of the proposed architecture is based on the programmable coefficients of the digital loop filter (DLF) that manages the tradeoffs between stability and jitter of a closed loop. A proposed simple digital controlled oscillator (DCO) based on three stages ring oscillator provides a wide frequency range, and proven to be of lower area and power compared to arrayed DCO. The proposed design results in a significant reduction in the area and power compared to other time
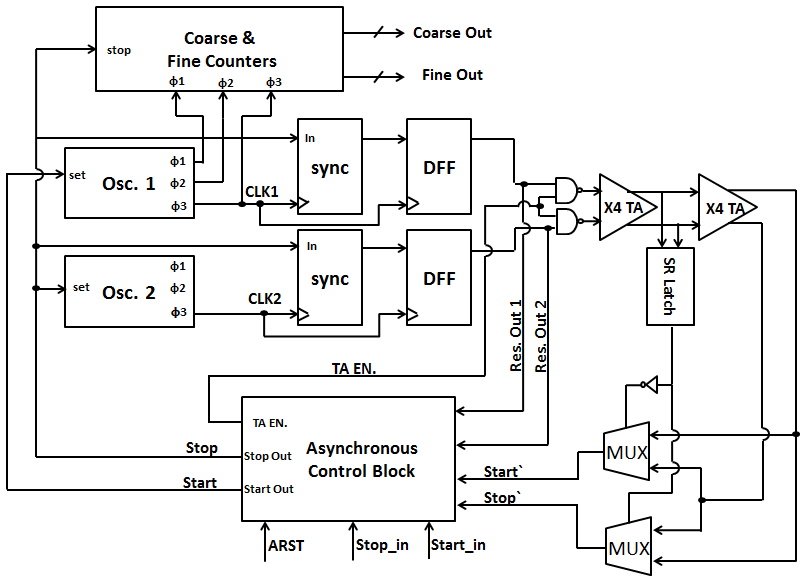
A novel 10-Bit high-throughput two-stage TDC with reduced power and improved linearity
This paper introduces a new architecture that improves the throughput of the two-stage Time to Digital Converter (TDC). An oscillator-based TDC is used for conversion. The time residue from the first stage is generated directly after the stop signal is asserted and saved in the form of phase-shift between two oscillating signals. Instead of using two stages, an asynchronous control block is implemented to reuse the same hardware block for both the first and second conversion stages. This technique not only reduces power and area, but also eliminates the TDC nonlinearity due to the mismatch
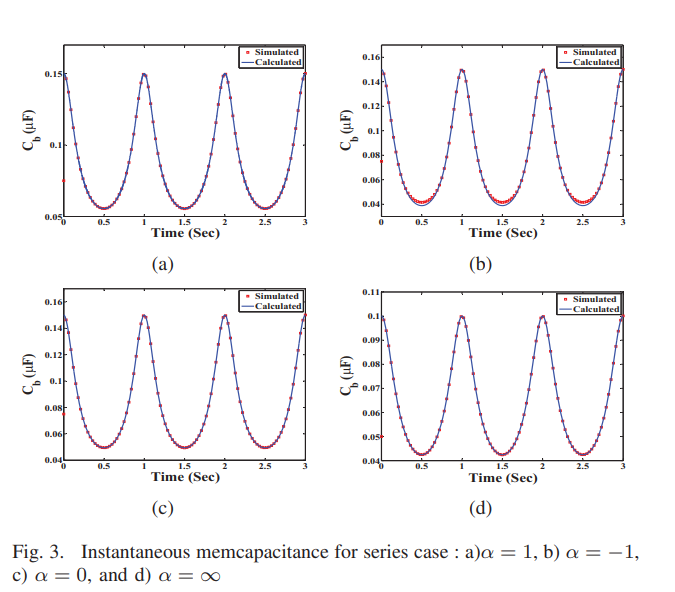
On the mathematical modeling of series and parallel memcapacitors
Recently, Memristive elements such as memristor, memcapacitor and meminductors have become very attractive components in many applications, due to its unique behavior which can not be obtained using the other conventional elements. This paper discusses the analytical analysis of two memcapacitors connected in series and in parallel taking the effect of mismatch in mobility factor and polarity of each one. The obtained formulas of instantaneous memcapacitance for each memcapacitor are derived and four special cases are analyzed in more details. The proposed special cases are validated using
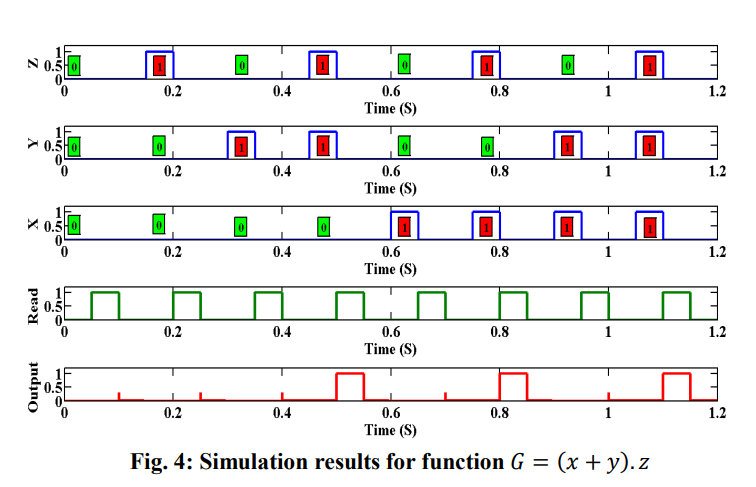
Memristor-MOS hybrid circuit redundant multiplier
This paper introduces a step forward towards memristor-MOS hybrid circuit to achieve any combinational function. The proposed design is based on reducing the area by replacing the complete pull-down network with just one memristor and one comparator. The concept is then verified using an example of a simple function. Also, a proposed architecture for memristor based redundant multiplier circuit is introduced and verified using the SPICE simulation. Therefore, any redundant functions can be implemented using the same concept. © 2014 IEEE.
Pagination
- Previous page ‹‹
- Page 21
- Next page ››
