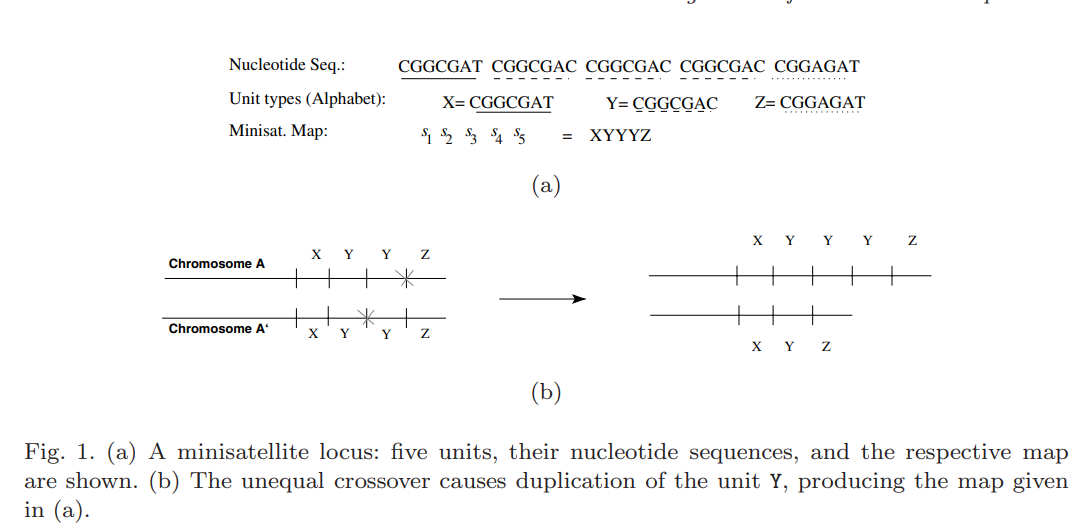
Alignment of minisatellite maps based on run-length encoding scheme
Subsequent duplication events are responsible for the evolution of the minisatellite maps. Alignment of two minisatellite maps should therefore take these duplication events into account, in addition to the well-known edit operations. All algorithms for computing an optimal alignment of two maps, including the one presented here, first deduce the costs of optimal duplication scenarios for all substrings of the given maps. Then, they incorporate the pre-computed costs in the alignment recurrence. However, all previous algorithms addressing this problem are dependent on the number of distinct
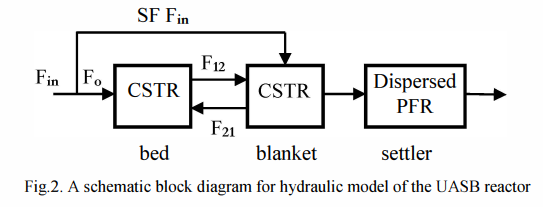
Mathematical modeling of Upflow Anaerobic Sludge Blanket reactor in domestic wastewater treatment
This paper introduces a dynamic model to adequately describe an Upflow Anaerobic Sludge Blanket (UASB) reactor. Some available models of a UASB reactor are discussed in order to modify their drawbacks and propose a new improved model with less complexity and more reliability. The developed model is a combination of two recent models introduced in Sweden. According to this model, a UASB rector is divided hydraulically into three compartments with integration of a kinetic model. Simulations are performed to investigate the validity of the developed model which indicates a good agreement with
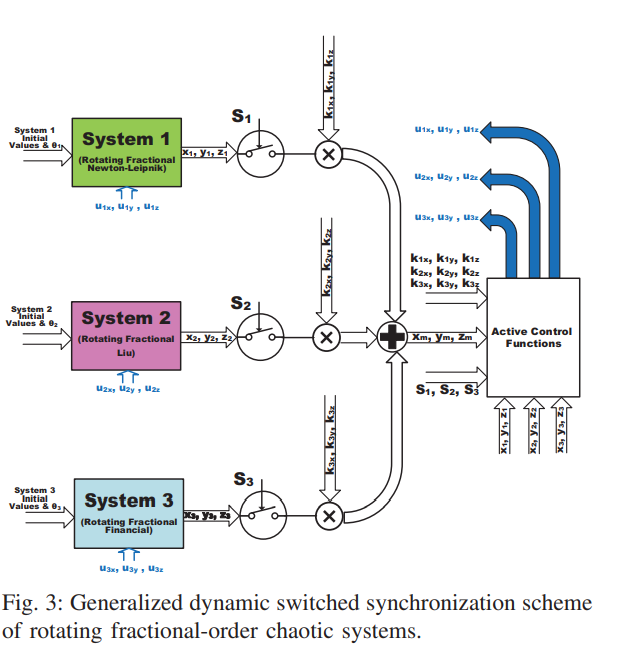
All-Dynamic Synchronization of Rotating Fractional-Order Chaotic Systems
This paper proposes generalized controllable strange attractors through dynamic rotation of fractional-order chaotic systems. Dynamic rotation angle enables the generation of multi-scroll and multi-wing attractors from single and double-scroll ones. The rotating systems are integrated with a generalized dynamic switched synchronization scheme. Dynamic control switches determine whether each system plays the role of master or slave. Based on dynamic scaling factors, the master can be one system or a combination of several ones with new strange attractors. The rotating fractional-order systems
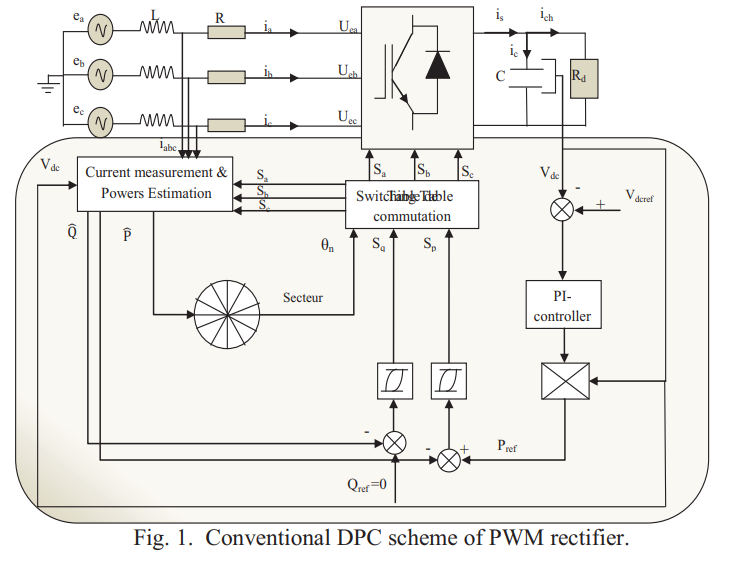
Direct Power Control of a three-phase PWM-Rectifier based on Petri nets for the selection of Switching States
This article proposes a new simple scheme for direct power control of a PWM rectifier without a switch table and voltage sensor. The selection of the switching state of the converter is based on the transition of a Petri net, using the instantaneous active and reactive power tracking errors and the angular position of the network line voltage estimated as variables of Controller input based on Petri nets. Simulation and experimental results demonstrated better performance and verified the validity of the new command with the Petri nets applied to the bridge rectifier connected to the
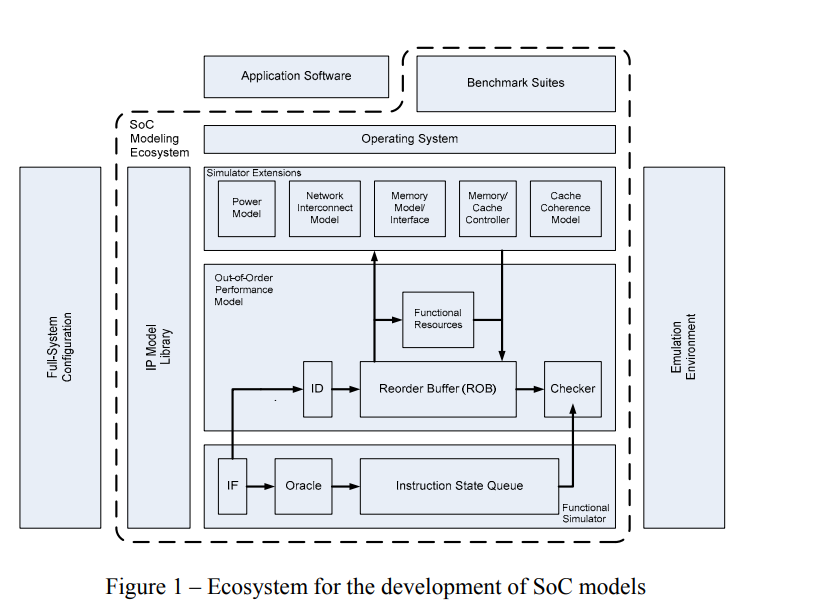
Ecosystems for the development of multi-core and many-core SoC models
Multi-core and many-core Systems-on-Chip (SoC) are growing more complex than ever. Consequently, developing system models for such SoCs to guide and validate architectural and implementation decisions is becoming a daunting task. It consumes a huge amount of time and effort just to get the model up and running. Although these system models can be fairly abstracted, they still require the setup of a complicated platform to model a homogeneous or a heterogeneous mix of processing cores, a network-on-chip, cache memories, input-output interfaces as well as several other functional units. The
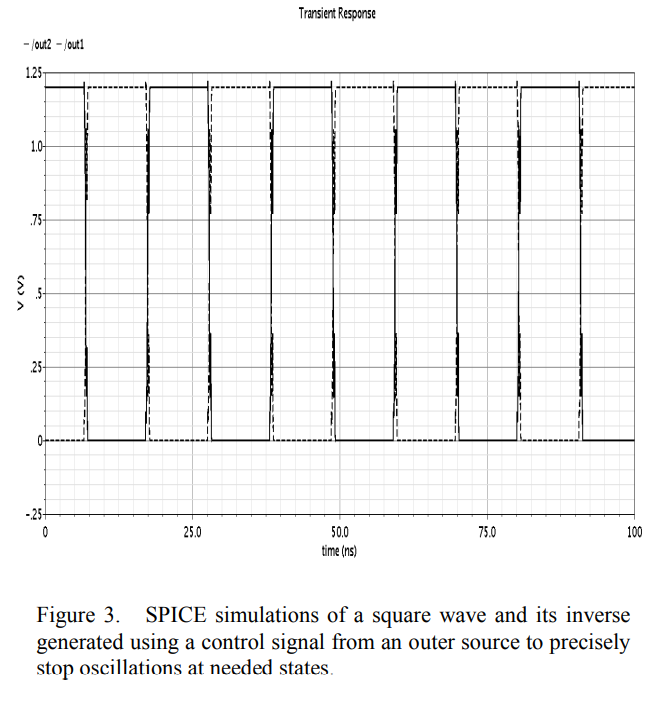
Low power clock generator using charge recycling
A major portion of the power consumed in today's systems is due to the clock distribution network. Solutions attempted to reduce clocking power result in low efficiency systems or systems with high complexity control schemes. In this work, a low power clock generator is introduced that can reduce switching power of the clock by almost 75%. This circuit uses the charge recycling concept to achieve such power reduction while utilizing a simple control technique. ©2010 IEEE.
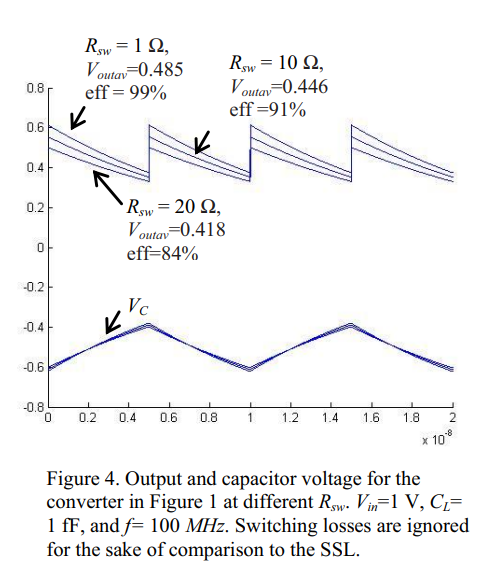
On the accuracy of commonly used loss models in SCVRs
[No abstract available]
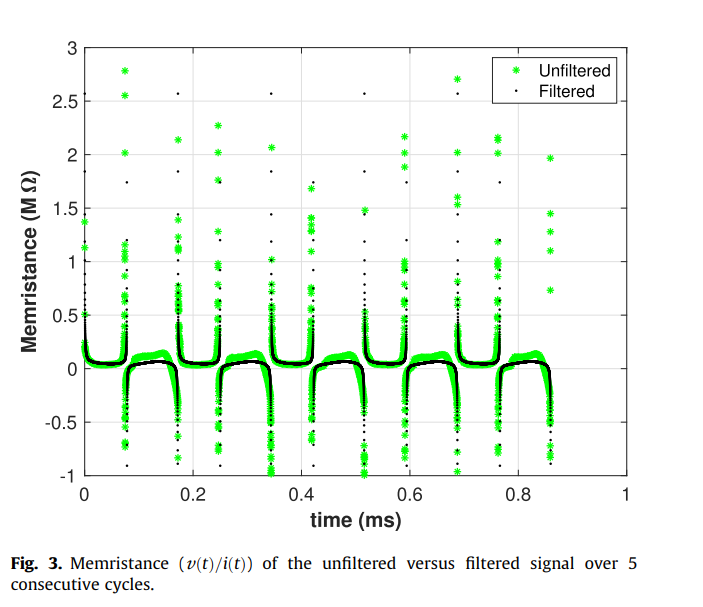
On the mechanism of creating pinched hysteresis loops using a commercial memristor device
In this short communication we analyze the impact of signal harmonics on the formation of the pinched hysteresis loop using a commercial memristor device. We show that by using only the fundamental frequency and the second harmonic components, extracted from the measured electrical current signal, a distortion-less pinched hysteresis loop is re-created. This loop is then used to simulate memristor-based AND/OR gates without any loss in digital functionality. This verifies that the generation of a pinched hysteresis loop requires a nonlinear frequency doubling mechanism to create a second
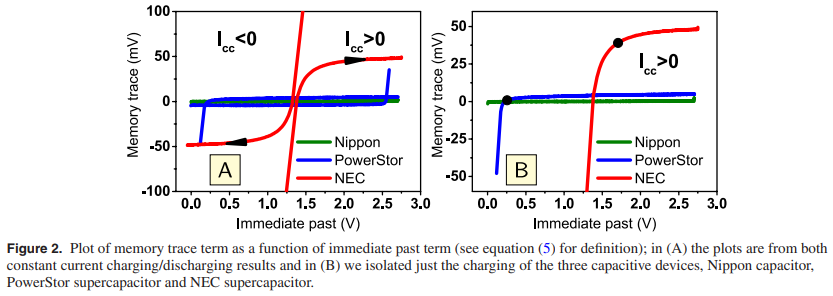
Quantification of memory in fractional-order capacitors
In this study we quantify and interpret the inherent memory in fractional-order capacitors when subjected to constant current charging/discharging waveforms. This is done via a finite difference approximation of the fractional order rate equation I(t) = Cαdαv(t)/dtα (0 le; α ≤ 1) relating current to voltage in these devices. It is found that as the fractional exponent α decreases, the weight of the voltage memory trace that results from the contribution of past voltage activity increases, and thus the measured response of the device at any time is increasingly correlated to its past. Ideal
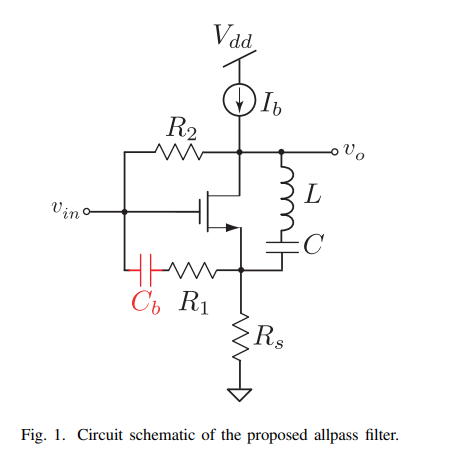
8-GHz low-power voltage-mode second-order allpass filter in 65-nm CMOS
In this paper, a CMOS wide-band low-power second-order voltage-mode allpass filter design is proposed as a true time delay element. The proposed allpass filter core design consists of a single transistor, three resistors, one capacitor and one inductor. As a time delay element, the proposed circuit exhibits a group delay of 34 ps within a bandwidth of 8 GHz while consuming only 926 μW from a 1-V supply voltage. The proposed filter was designed in 65-nm CMOS technology and verified through post-layout simulation results. © 2019 IEEE.
Pagination
- Previous page ‹‹
- Page 23
- Next page ››
