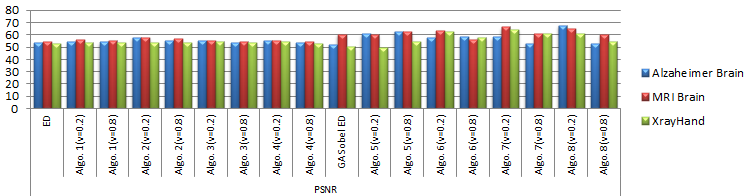
Radiographic images fractional edge detection based on genetic algorithm
Recently, fractional edge detection algorithms have gained focus of many researchers. Most of them concern on the fractional masks implementation without optimization of threshold levels of the algorithm for each image. One of the main problems of the edge detection techniques is the choice of optimal threshold for each image. In this paper, the genetic algorithm has been used to get the optimal threshold levels for each image to enhance the edge detection of the fractional masks. A fully automatic way to cluster an image using K-means principle has been applied to different fractional edge
Implementation of a fractional-order electronically reconfigurable lung impedance emulator of the human respiratory tree
The fractional-order lung impedance model of the human respiratory tree is implemented in this paper, using Operational Transconductance Amplifiers. The employment of such active element offers electronic adjustment of the impedance characteristics in terms of both elements values and orders. As the MOS transistors in OTAs are biased in the weak inversion region, the power dissipation and the dc bias voltage of operation are also minimized. In addition, the partial fraction expansion tool has been utilized, in order to achieve reduction of the spread of the required time-constants and scaling
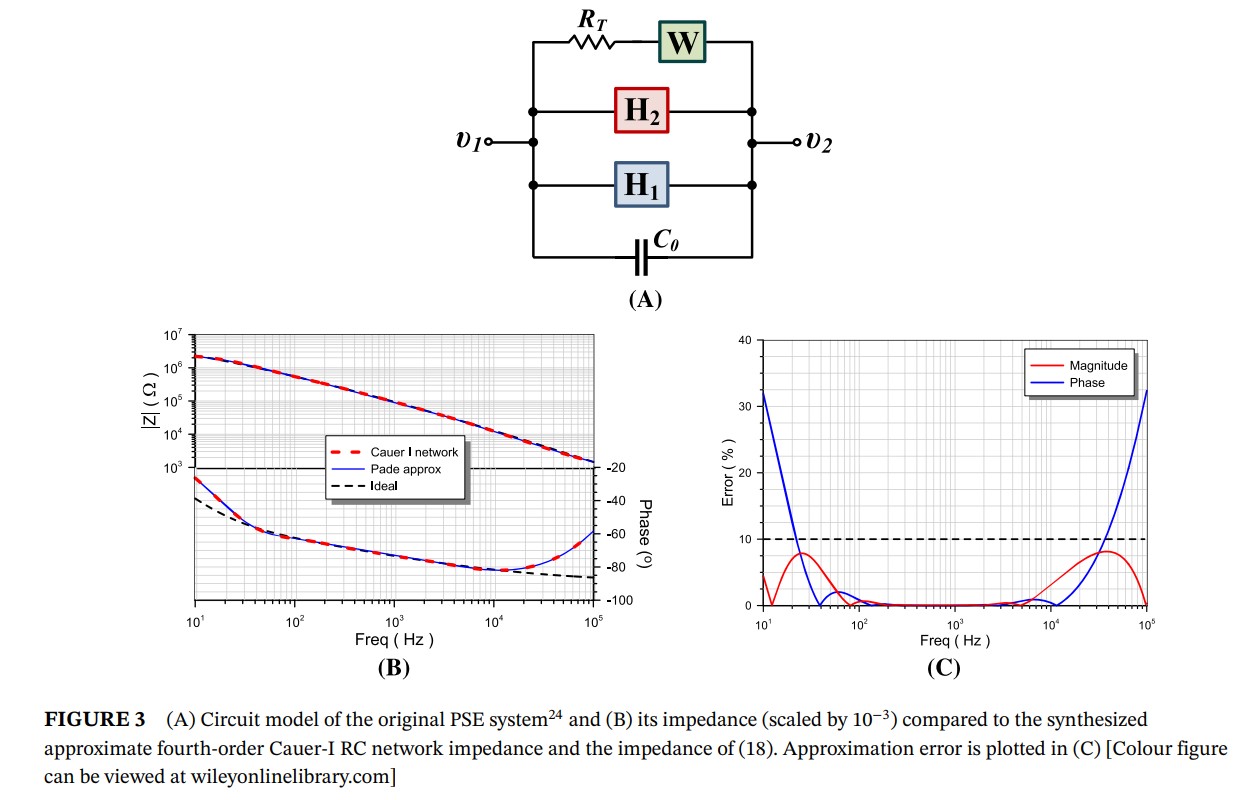
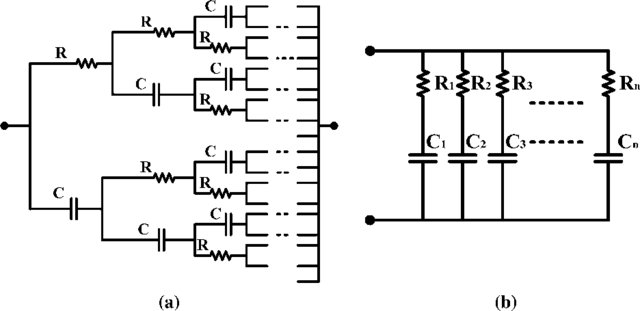
Passive approximations of double-exponent fractional-order impedance functions
Double-exponent fractional-order impedance functions are important for modeling a wide range of biochemical materials and biological tissues. Through appropriate selection of the two exponents (fractional orders), the well-known Havriliak–Negami, Cole–Cole, Cole–Davidson, and Debye relaxation models can be obtained as special cases. Here we show that an integer-order Padé-based approximation of the Havriliak–Negami function is possible to obtain and can be realized using appropriately configured Cauer/Foster resistor-capacitor (RC) networks. Two application examples are subsequently examined
Using Meta-heuristic Optimization to Extract Bio-impedance Parameters from an Oscillator Circuit
This paper introduces a method for extracting the Cole-impedance model parameters using a meta-heuristic optimization technique. The method is based on a single proposed resistor controlled oscillator (SRCO) where the unknown bio-impedance is embedded. At two different oscillation frequencies, the start-up oscillation condition is recorded. Then the corresponding nonlinear equations are solved using the flower pollination optimization (FPA) technique to find the optimum impedance parameters that minimize an objective error function. Experimental results are provided, and comparisons with model
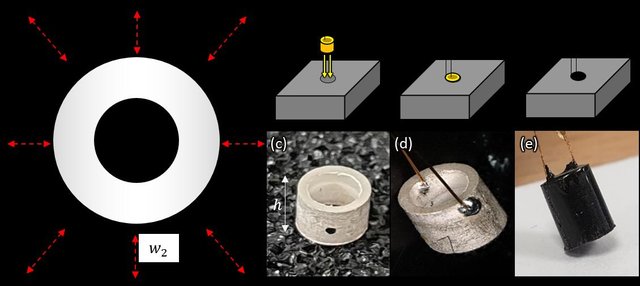
Ultrasound intra body multi node communication system for bioelectronic medicine
The coming years may see the advent of distributed implantable devices to support bioelectronic medicinal treatments. Communication between implantable components and between deep implants and the outside world can be challenging. Percutaneous wired connectivity is undesirable and both radiofrequency and optical methods are limited by tissue absorption and power safety limits. As such, there is a significant potential niche for ultrasound communications in this domain. In this paper, we present the design and testing of a reliable and efficient ultrasonic communication telemetry scheme using
Hybrid rough-bijective soft set classification system
In today’s medical world, the patient’s data with symptoms and diseases are expanding rapidly, so that analysis of all factors with updated knowledge about symptoms and corresponding new treatment is merely not possible by medical experts. Hence, the essential for an intelligent system to reflect the different issues and recognize an appropriate model between the different parameters is evident. In recent decades, rough set theory (RST) has been broadly applied in various fields such as medicine, business, education, engineering and multimedia. In this study, a hybrid intelligent system that
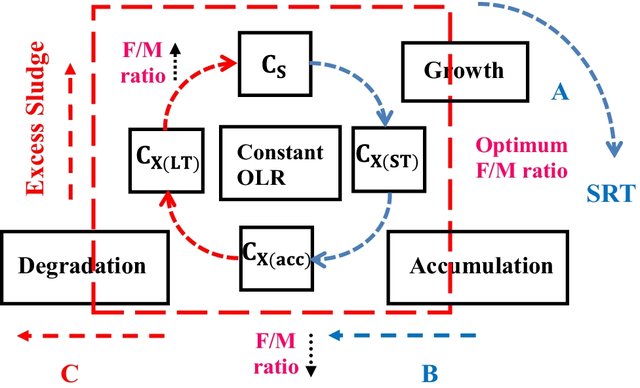
Two-dimensional steady-state analysis of selected wastewater state variables using asm3
Performance of activated sludge wastewater treatment plants are mainly dependent on bacterial growth, which is limited by many factors. These factors include availability of suitable substrate, limiting nutrients, environmental conditions, and energy. In activated sludge model no. 3 (ASM3), constituents in wastewater are divided into two main categories: carbonaceous compounds and nitrogenous compounds, which are further subdivided depending on their solubility and biodegradability. These compounds are not mutually independent; hence, the fate of one compound in the biological processes is
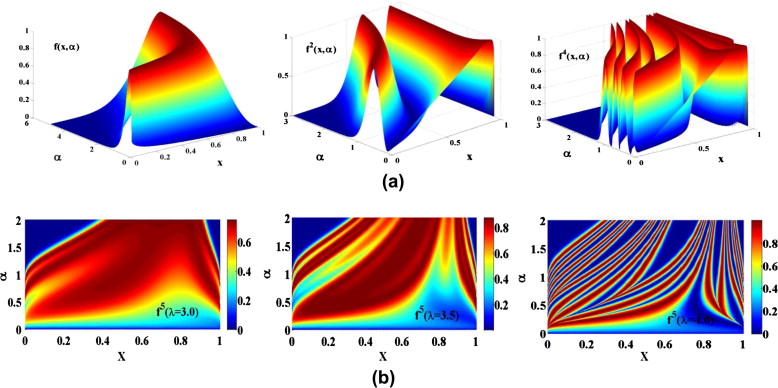
On some generalized discrete logistic maps
Recently, conventional logistic maps have been used in different vital applications like modeling and security. However, unfortunately the conventional logistic maps can tolerate only one changeable parameter. In this paper, three different generalized logistic maps are introduced with arbitrary powers which can be reduced to the conventional logistic map. The added parameter (arbitrary power) increases the degree of freedom of each map and gives us a versatile response that can fit many applications. Therefore, the conventional logistic map is considered only a special case from each proposed
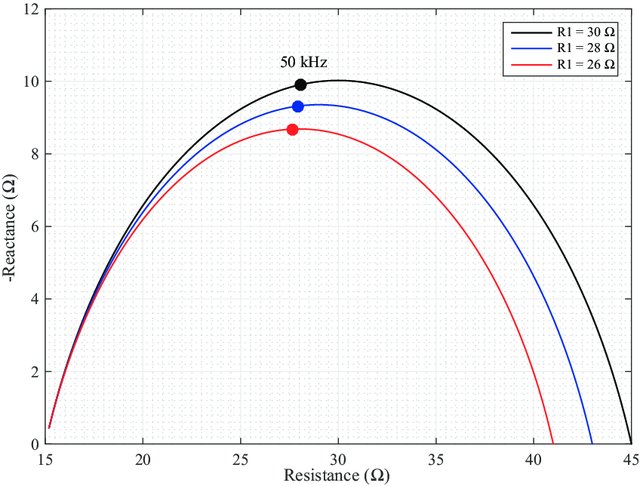
Variability of Cole-model bioimpedance parameters using magnitude-only measurements of apples from a two-electrode configuration
Electrical impedance measurements have been widely researched to monitor physiological changes in fruits and vegetables in a nondestructive manner. Recently, the parameters of the Cole bioimpedance model (R0, R1, C, and α), an equivalent circuit that is widely used to represent the electrical impedance of biological tissues, were extracted using techniques without direct impedance measurements. In this study, the variability of the Cole parameters extracted from magnitude-only measurements (from 200 Hz to 1 MHz) of apples in a two-electrode setup was examined to understand the impact of
Two-Port Network Analysis of Equal Fractional-order Wireless Power Transfer Circuit
Wireless power transfer (WPT) has been widely employed in many applications. Its advantages have added more safety and ease in various medical, industrial, and electrical applications. This paper investigates the two-port network concept in the analysis of the fractional-Order WPT circuit. A general expression for the WPT efficiency as a function of two-port network parameters is derived. It is represented in terms of the transmission matrix parameters of a generalized Two-Port network. The analysis is performed on both Series-Series (SS) and Series-Parallel (SP) topologies. The best
Pagination
- Previous page ‹‹
- Page 43
- Next page ››
