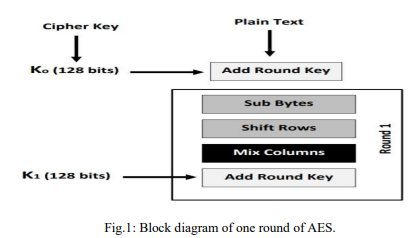
Generation of the chaotic keys on the fly for AES encryption system
This paper proposes a safe and effective method to generate the subkeys that are used in the Advanced Encryption Standard (AES) algorithm for data encryption applications. The suggested method relies upon the Pseudo-Random Number Generator (PRNG) that is created from the improved Lorenz chaotic system. The output of PRNG is exploited as a key schedule for generating AES subkeys where the output is characterized by having an infinite periodic length. This method can be used in high-speed applications since no hardware multipliers are utilized so it gives the best hardware performance
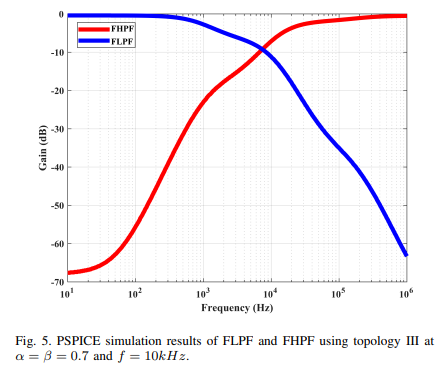
Generalized α+β-order Filter Based on Single CCII
Different generalized filters topologies are proposed in the fractional-order domain. Three voltage-mode topologies and one current-mode topology are used to realize several types of fractional-order filters by applying different admittances combinations. The proposed topologies are designed using a single second-generation current conveyor (CCII-) and two fractional-order capacitors, which add more degrees of freedom for the design. The generalized Fractional Transfer Function (FTF) for each proposed topology is investigated where the fractional-order low-pass, band-pass, high-pass, and notch
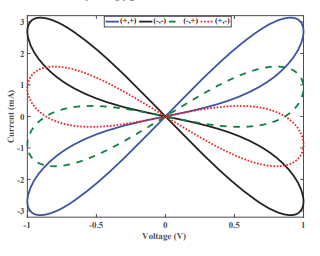
Fractional-order Memristor Emulator with Multiple Pinched Points
The paper proposes voltage-controlled first-and second-order memristor emulators. The emulators are designed using an operational-transconductance amplifier (OTA) and voltage multiplier blocks plus a fractional-order capacitor. The presented second-order emulator provides two pinched points controlled by order of the employed fractional-order capacitor. Numerical and PSPICE simulation results using AD844 and AD633 are introduced for different cases to validate the theoretical findings. The experimental verification is presented, showing the design flexibility and controllability based on the
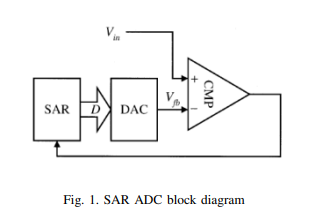
A 26.24uW 9.26-ENOB Dynamic RAM Based SAR ADC for Biomedical Applications
This work introduces a new successive approximation register circuit (SAR) for SAR analog to digital converter (ADC) based on Dynamic Random Access Memory (DRAM) cells. Based on the proposed DRAM based SAR ADC and a differential capacitive DAC, a 10-bit 2V ADC is designed in 0.18um CMOS technology. The proposed SAR is compared to traditional SAR to verify that the proposed SAR decreases the power of SAR ADC for biomedical applications. The power consumption for the proposed SAR ADC is found to be 26.24uW with ENOB equal to 9.26, and the maximum sampling frequency is 1MHz. For the traditional
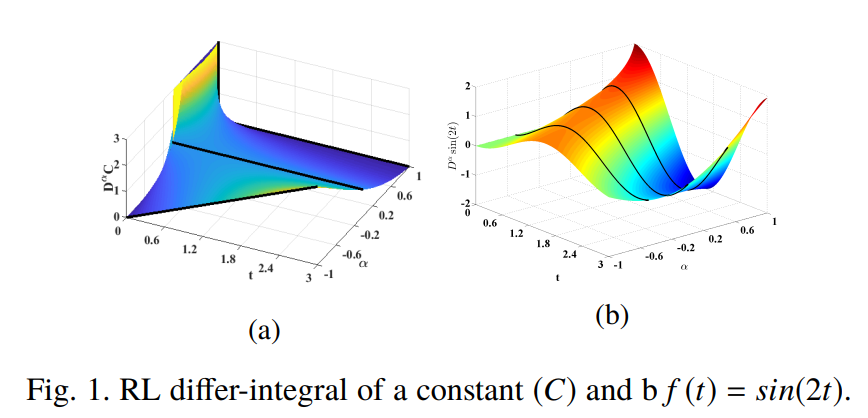
Fractional calculus definitions, approximations, and engineering applications
The basic idea behind fractional calculus is that it considers derivatives and integrals of non-integer orders giving extra degrees of freedom and tuning knobs for modeling complex and memory dependent systems with compact descriptions. This paper reviews fractional calculus history, theory, and its applications in electrical engineering. The basic definitions of fractional calculus are presented together with some examples. Integer order transfer function approximations and constant phase elements (CPEs) emulators are overviewed due to their importance in implementing fractional-order
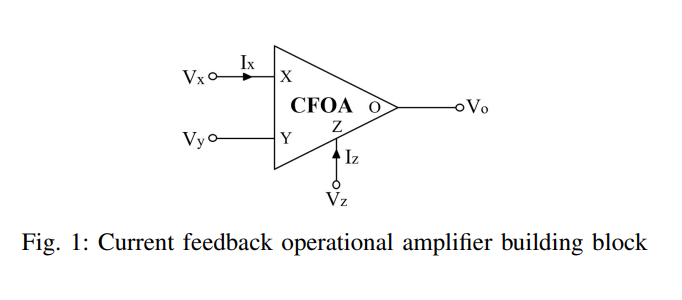
On the realization of Current-Mode Fractional-order Simulated Inductors
The objective of this work is to revisit the design criteria of current-mode simulated inductors in order to realize their fractional-order versions. Numerical simulations and SPICE circuits simulations are carried out on these generalized fractional-order simulated inductors. As well, fractional-order low pass filters based on the proposed circuits are realized and validated. © 2019 IEEE.

Chaos synchronisation of continuous systems via scalar signal
By analyzing the issue of chaos synchronization in the literature, it can be noticed the lack of a general approach, which would enable any type of synchronization to be achieved. Similarly, there is the lack of a unified method for synchronizing both continuous-time and discrete-time systems via a scalar signal. This paper and the companion one [1] aim to bridge these two gaps by presenting a novel general unified framework to synchronize chaotic systems via a scalar signal. The framework, based on the concept of observer, enables any type of synchronization defined to date to be achieved for
Pagination
- Previous page ‹‹
- Page 42
- Next page ››

