
Modeling of Nonlinear Enhanced Air Levitation System using NARX Neural Networks
the proposed paper aims to design and model an air levitation system, which is a highly nonlinear system because of its fast dynamics and low damping. The system is trained using a Nonlinear Autoregressive model with exogenous input (NARX model). An enhanced height measurement system, modified setup, and several training techniques have been used to overcome the restrictions that the non-linearity of the system imposes in the literature. The system mathematical model has been illustrated, followed by an identified model using NARX model trained on several input-output data from the physical
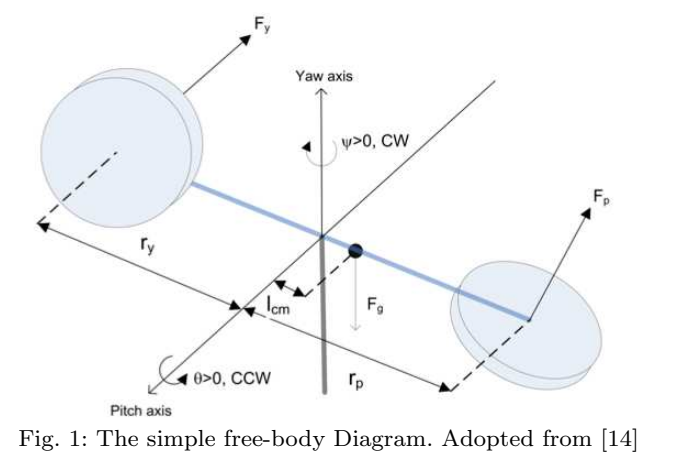
PID Controller for 2-DOFs Twin Rotor MIMO System Tuned with Particle Swarm Optimization
This paper presents the modelling and control of a 2-DOFs Twin rotor multi input multi output (MIMO) system which is a laboratory setup resembling the dynamics of a helicopter. In this paper, the system modelling process is done using the common conventional mathematical model based on Euler-Lagrange method. The transfer functions of the model are used in the different tuning methods to reach the optimal PID gain values. The study uses conventional Proportional-Integral (PI) and Proportional-Integral-Derivative (PID) controllers to obtain a robust controller for the system. Particle Swarm
Optimal Design of PID Controller for 2-DOF Drawing Robot Using Bat-Inspired Algorithm
Tuning process which is used to find the optimum values of the proportional integral derivative (PID) parameters, can be performed automatically using meta-heuristics algorithms such as BA (Bat Algorithm), PSO (Particle Swarm Optimization) and ABC (Artificial Bee Colony). This paper presented a theoretical and practical implementation of a drawing robot using BA to tune the PID controller governing the robotic arm which is a non linear system difficult to be controlled using classical control. In line with the above and in order to achieve this aim and meet high performance feedback and robust
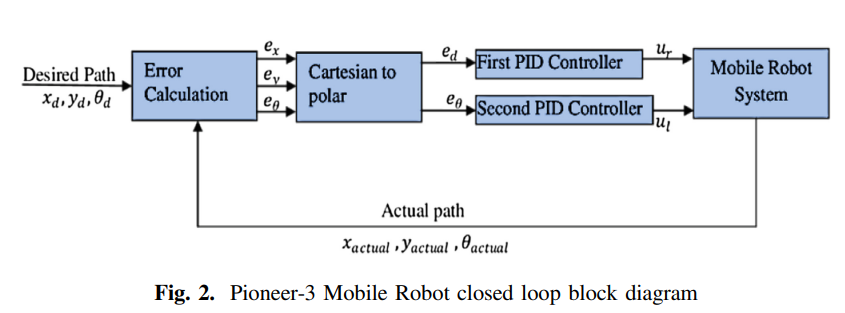
Robust Path Tracking of Mobile Robot Using Fractional Order PID Controller
This paper represents the control of the Pioneer-3 Mobile Robot as a complex non-linear system which provides an object for research nonlinear system kinematics and dynamics analysis. In this paper, the system modeling and simulation is divided into two main parts. The first part is the modeling and simulation using MATLAB and the second part is the whole mechanical design and its characteristics as a function of the motor speed and the torque depending on the system using Virtual Robot Environment Program (V-REP). The study uses Proportional–Integral–Derivative (PID) and Fractional Order PID
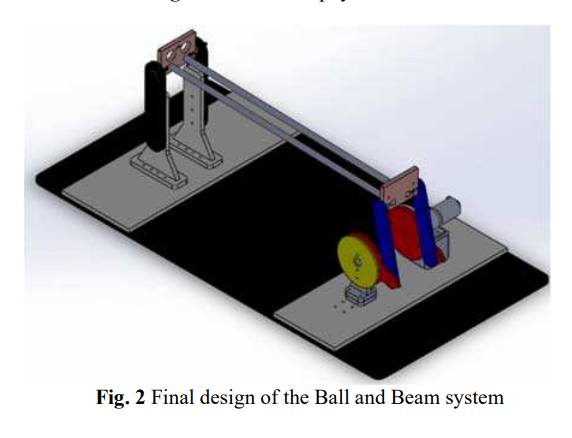
Design and Implementation of a Ball and Beam PID Control System Based on Metaheuristic Techniques
The paper introduces a comparative analysis between three meta-heuristic techniques in the optimization of Proportional-Integral-Derivative (PID) controller for a cascaded control of a ball and beam system. The meta-heuristic techniques presented in this study are Particle Swarm Optimization (PSO), Artificial Bee Colony (ABC) and Bat Algorithm Optimization (BAO). The model uses a DC motor with encoder to move the beam and a camera as a feedback for the ball position on the beam. The control theory of the system depends on two loops; the first (inner) loop is the DC motor for position control
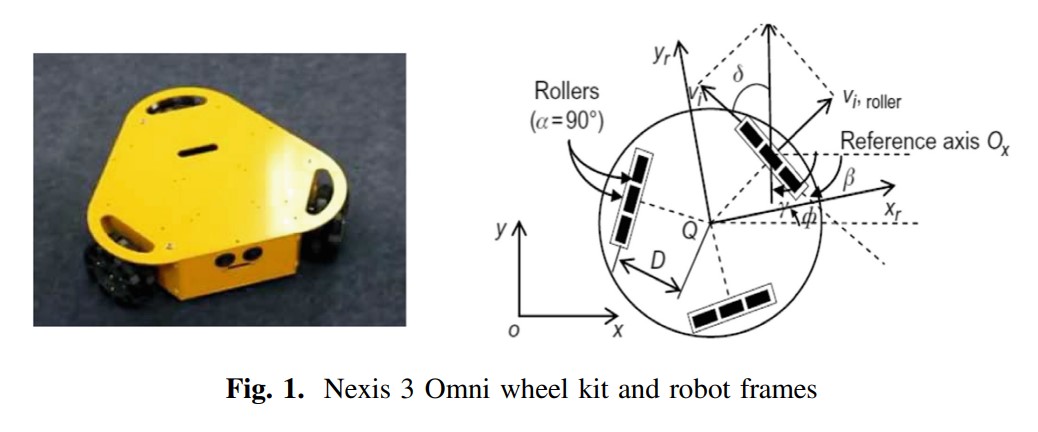
Path Planning Control for 3-Omni Fighting Robot Using PID and Fuzzy Logic Controller
This paper addresses a comparison between some control methods of three Omni wheels firefighting robot due to the variety of maneuverability. To achieve path planning for firefighting robot to reach a specific point with the shortest path, a kinematics model of omni wheel robot is applied with some control algorithms based on PID controller, Fuzzy logic controller and self-tuned PID using fuzzy logic techniques. Hardware prototype has been tested to validate the simulation results. © 2020, Springer Nature Switzerland AG.
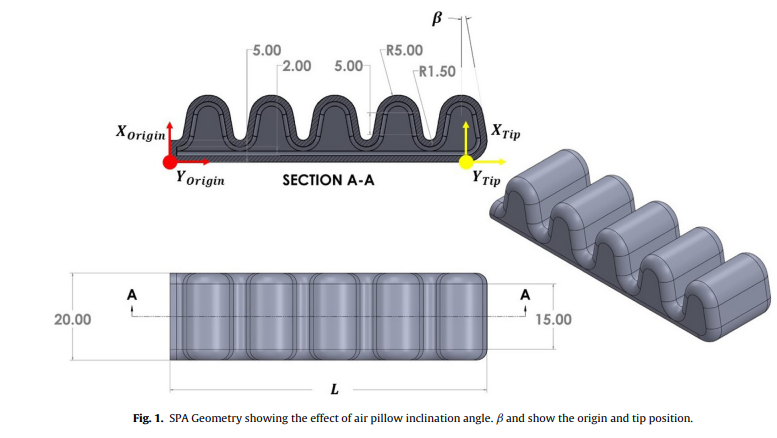
Theoretical and experimental investigation study of data driven work envelope modelling for 3D printed soft pneumatic actuators
In the last decade, soft robotics is considered one of the most widely researched fields in robotics, as it has many advantages and more versatile use than rigid robotics. Soft robots are flexible, which enable them to metaphorically complex designs, enabling them to imitate the movement of living things. In this article, the use of regression models with finite element analysis (FEA) data is compared with neural network (NN) models trained on visual feedback data. The effect of the soft pneumatic actuator (SPA) air pillow inclination angle (β) under positive and vacuum pressure on the

Design and implementation of variable inclined air pillow soft pneumatic actuator suitable for bioimpedance applications
The technological revolution has caused the modernization of human–machine relationship changing our approach in problem solving our society issues and deviated the science of robotic all together. An example for one of the most important pawn in this revolution is soft robotics, the soft robots are robots that are made of deformable materials that provide an alternative approach to rigid robots. The soft pneumatic actuator (SPA) is one of the most widely used and studied form of this type of robotics. In this study, a new geometrical parameter of the SPAs is introduced by studying the effect
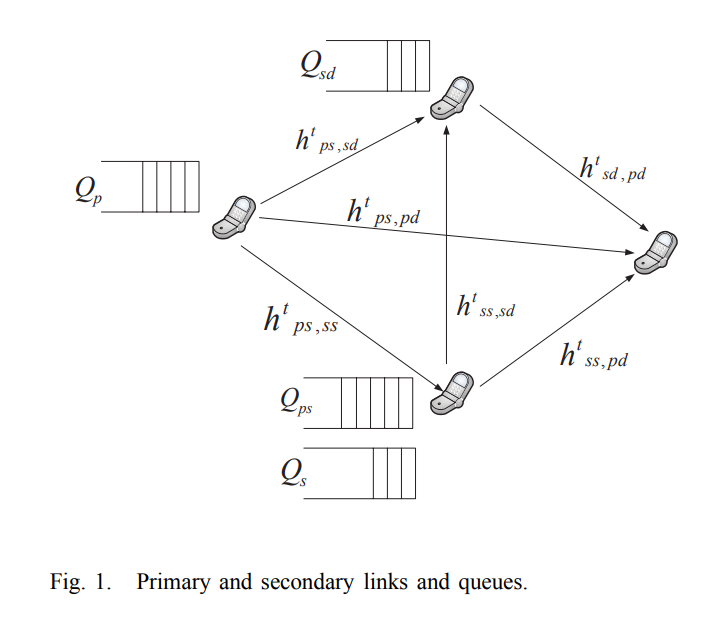
Transmit and receive cooperative cognition: Protocol design and stability analysis
In this paper, we investigate the stability of a cooperative cognitive system. We propose a cooperative secondary transmitter-receiver system (CSTR), where, the secondary transmitter (ST) and the secondary receiver (SR) increase the spectrum availability for the ST packets by relaying the unsuccessfully transmitted packets of the primary transmitter (PT). We assume receiving nodes with multipacket reception capability (MPR). We provide two inner bounds and two outer bounds on the stability region of the considered system. © 2013 ICST - The Institute for Computer Sciences, Social Informatics
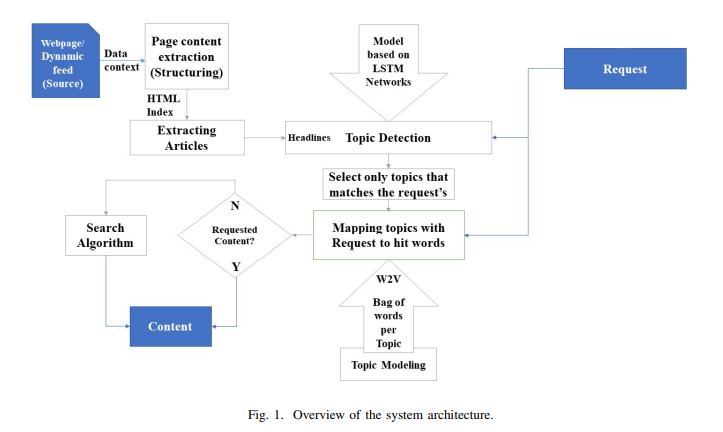
Towards Intelligent Web Context-Based Content On-Demand Extraction Using Deep Learning
Information extraction and reasoning from massive high-dimensional data at dynamic contexts, is very demanding and yet is very hard to obtain in real-time basis. However, such process capability and efficiency might be affected and limited by the available computational resources and the consequent power consumption. Conventional search mechanisms are often incapable of real-time fetching a predefined content from data source, without concerning the increased number of connected devices that contribute to the same source. In this work, we propose and present a concept for an efficient approach
Pagination
- Previous page ‹‹
- Page 47
- Next page ››
