Hardware Optimized FPGA Implementations of High-Speed True Random Bit Generators Based on Switching-Type Chaotic Oscillators
One of the important applications of chaotic oscillators is their employment as sources of entropy for True Random Bit Generators (TRBGs). In this work, we introduce high-speed TRBGs realized on a modular Field Programmable Gate Array (FPGA) hardware platform using two different switching-type chaotic oscillators. While both oscillators are autonomous, one is 3-D and the other is 4-D. This enables us to investigate and compare the advantages/disadvantages of higher dimensional chaotic oscillators on the throughput, hardware requirements and security of the generated bit-streams. For that
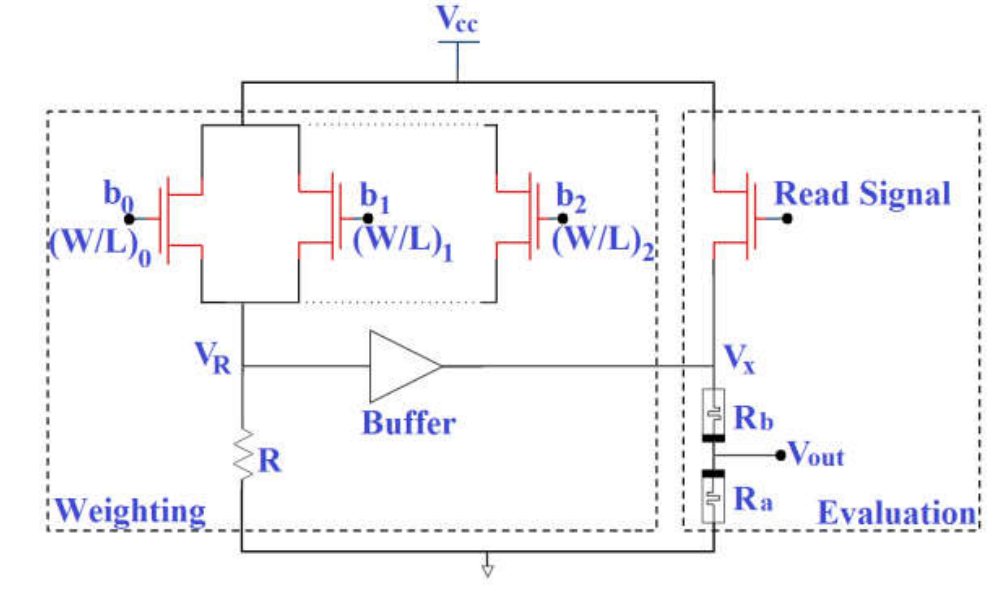
Memristor-based data converter circuits
This paper introduces data converter circuit based on memristors. A proposed Digital to Analog Converter (DAC) circuit based on non-overlapped input signals, which is suitable for common source connected transistors. Analytical formulas are introduced to relate the digital input with the analog output including the transistors dimension. In addition, PSpice simulations are performed to validate the theoretical analysis for several cases. Moreover, a modified circuit for 2-bit digital to analog converter is introduced where the input can be overlapped. One of the advantages of these designs
High-Frequency Capacitorless Fractional-Order CPE and FI Emulator
A fractional-order capacitor and inductor emulator, implemented using MOS transistors, instead of passive capacitors, is introduced in this paper. This is achieved using current mirrors as active elements, without passive resistors, and therefore reducing the circuit complexity and resulting in both a resistorless and capacitorless topology. The emulator has been designed by combining fractional-order differentiator or integrator topologies with a voltage-to-current converter. An important benefit from the design flexibility point of view is that the same topology could be used for emulating a
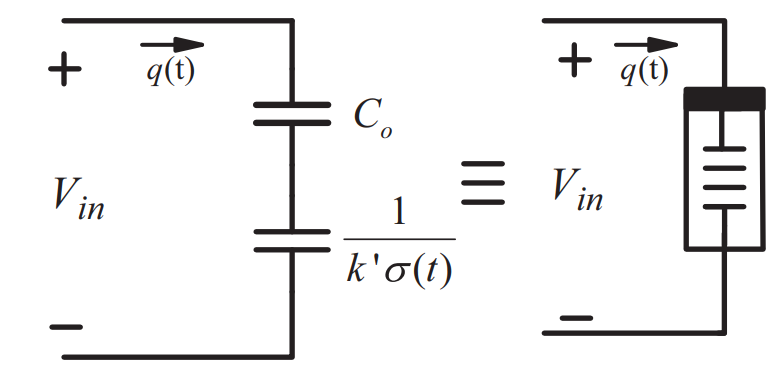
Memcapacitor response under step and sinusoidal voltage excitations
Recently, mem-elements have become fundamental in the circuit theory through promising potential applications based on the built-in memory-properties of these elements. In this paper, the mathematical analysis of the memcapacitor model is derived and the effect of different voltage excitation signals is studied for the linear dopant model. General closed form expressions and analyses are presented to describe the memcapacitor behavior under DC step and sinusoidal voltage excitations. Furthermore, the step and sinusoidal responses are used to analyze the memcapacitor response under any periodic
Synthesis of a family of differential cross-coupled oscillators and design application
A new class of differential oscillators comprising ten possible circuits is introduced in this work. Half of the members of this family are LC-based oscillators and the other half are RC-based ones. While all oscillators are second-order, a maximum of four resistors was imposed as a restriction on possible oscillators that belong to the proposed architecture. Only two of the found oscillators are canonical but all members of the this family have unique and attractive design features. Experimental results using discrete components verify the operation of selected circuits designed for short
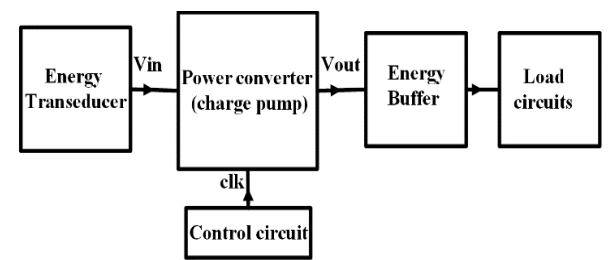
Memcapacitor based charge pump
This paper proposes a charge pump based on a charge controlled memcapacitor. The operation of the charge pump is investigated along with the mathematical analysis of the memcapacitor. Different implementations of charge pump are summarized. The proposed charge pump has the capability of driving low input voltage in range of 200mv and the capability of operating at the low frequencies which makes it suitable for biomedical applications. © 2017 IEEE.
Symmetric encryption algorithms using chaotic and non-chaotic generators: A review
This paper summarizes the symmetric image encryption results of 27 different algorithms, which include substitution-only, permutation-only or both phases. The cores of these algorithms are based on several discrete chaotic maps (Arnold's cat map and a combination of three generalized maps), one continuous chaotic system (Lorenz) and two non-chaotic generators (fractals and chess-based algorithms). Each algorithm has been analyzed by the correlation coefficients between pixels (horizontal, vertical and diagonal), differential attack measures, Mean Square Error (MSE), entropy, sensitivity
Memristor FPGA IP core implementation for analog and digital applications
Exploring the nonlinear dynamics of the memristors is essential to be adequately used in the applications. Realizing memristor on FPGAs as an intellectual property (IP) core offers a flexible platform to realize different models. In the literature, few implementations have been proposed for simple and limited memristor model. In this brief, two discrete and continuous versatile memristor models alongside their FPGA realizations are proposed. These models can generate different pinched hysteric behaviors, such as symmetric, asymmetric pinched hysteresis, and multi-state switching behavior. In
Hardware Speech Encryption Using a Chaotic Generator, Dynamic Shift and Bit Permutation
This paper proposes a speech encryption and decryption system, its hardware architecture design and FPGA implementation. The system utilizes Nosé Hoover chaotic generator and/or dynamic shift and bit permutation. The effect of different blocks in the proposed encryption scheme is studied and the security of the system is validated through perceptual and statistical tests. The complete encryption scheme is simulated using Xilinx ISE 14.5 and realized on FPGA Xilinx Kintex 7, presenting the experimental results on the oscilloscope. The efficiency is also validated through hardware resources
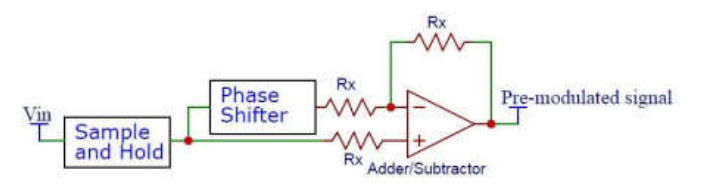
Memristor-based pulse width modulator circuit
This paper discusses the use of the memristor in one of the most important modulation techniques in communication field namely the pulse-width modulation. A fundamental two designs for memristor-based lead and trail PWM are discussed with mathematical analysis and PSPICE simulation results which show a great matching with the analytical formulation. Moreover, a third design which combine those two designs to generate a more accurate memristor-based center PWM is discussed with the appropriate analysis, numerical and PSPICE simulation results. The simulation results matches the theoretical
Pagination
- Previous page ‹‹
- Page 53
- Next page ››
