Integration of a 2-D periodic nanopattern into thin-film polycrystalline silicon solar cells by nanoimprint lithography
The integration of 2-D periodic nanopattern defined by nanoimprint lithography and dry etching into aluminum-induced crystallization-based polycrystalline silicon thin-film solar cells is investigated experimentally. Compared with the unpatterned cell, an increase of 6% in the light absorption has been achieved thanks to the nanopattern, which, in turn, increased the short-circuit current from 20.6 to 23.8 mA/cm2. The efficiency, on the other hand, has limitedly increased from 6.4% to 6.7%. We show using the transfer length method that the surface topography modification caused by the
Implementation of PID Controller with PSO Tuning for Autonomous Vehicle
In the use of automatic control and its optimization methods, this research discusses how Proportional Integral Derivative (PID) controller is used to provide a smooth auto-parking for an electrical autonomous car. Different tuning methods are shown, discussed, and applied to the system looking forward to enhancing its performance. Time domain specifications are used as a criterion of comparison between tuning methods in order to select the best tuning method to the system with a proper cost function. Results show that Particle Swarm Optimization (PSO) method gives the best results according
Fractional-order bio-impedance modeling for interdisciplinary applications: A review
Bio-impedance circuit modeling is a popular and effective non-invasive technique used in medicine and biology to fit the measured spectral impedance data of living or non-living tissues. The variations in impedance magnitude and/or phase at different frequencies reflect implicit biophysical and biochemical changes. Bio-impedance is also used for sensing environmental changes and its use in the agriculture industry is rapidly increasing. In this paper, we review and compare among the fractional-order circuit models that best fit bio-impedance data and the different methods for identifying the
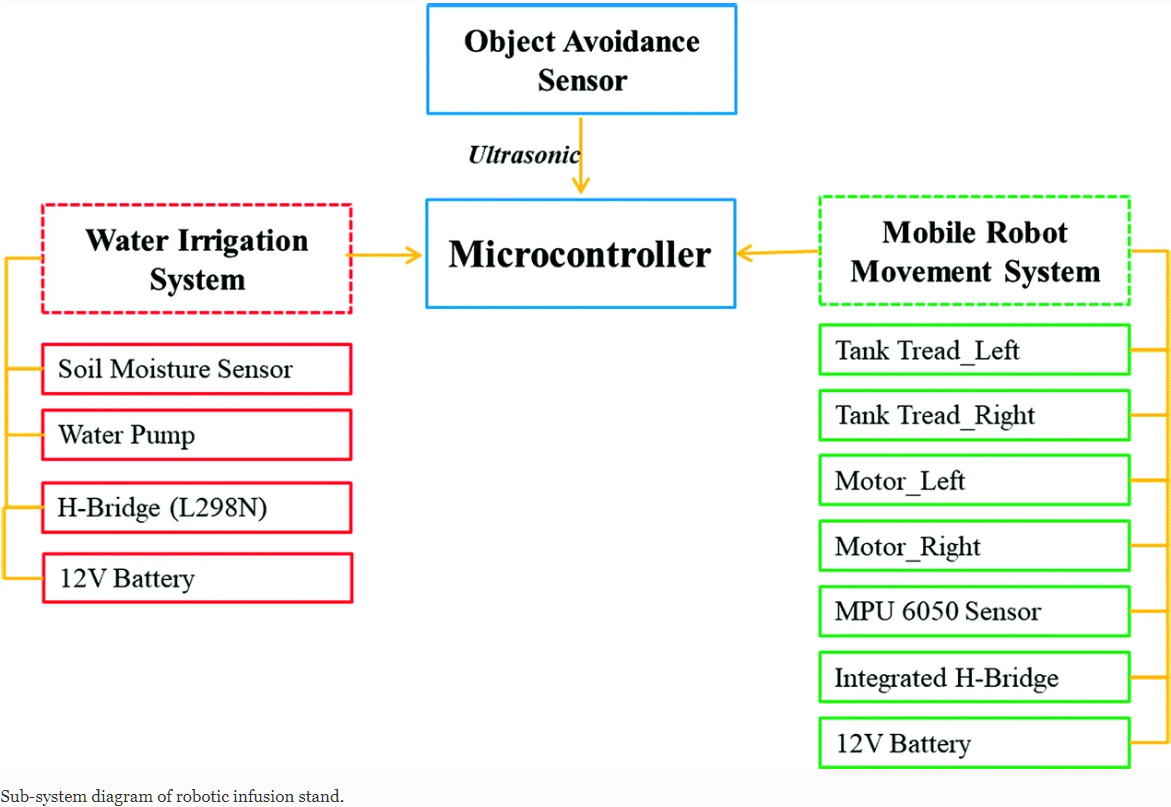
Optimal Proportional Integral Derivative (PID) Controller Design for Smart Irrigation Mobile Robot with Soil Moisture Sensor
Uncertainty on the condition of the weather always give a major headache to the agricultural industry as the cultivated plant that is grown on a large scale commercially rely on the condition of the weather. Therefore, to reduce the interdependency on the weather itself, a recommendation to develop a prototypic mobile robot for smart irrigation is submitted. Smart irrigation system is an essential tool from yield point of view and scarcity of the water. This smart irrigation system adopts a soil moisture sensor to measure the moisture content of the soil and automatically provide a signal to
Pagination
- Previous page ‹‹
- Page 61
