Optimal Proportional Integral Derivative (PID) Controller Design for Smart Irrigation Mobile Robot with Soil Moisture Sensor
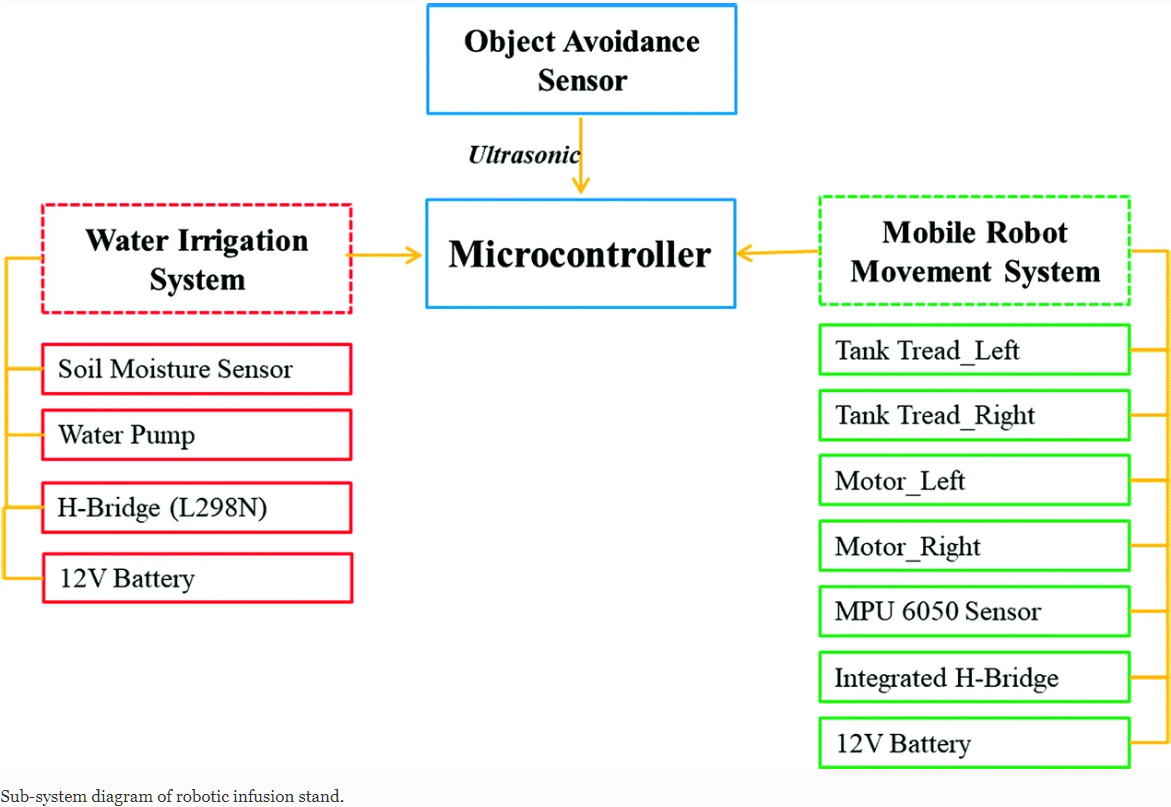
Uncertainty on the condition of the weather always give a major headache to the agricultural industry as the cultivated plant that is grown on a large scale commercially rely on the condition of the weather. Therefore, to reduce the interdependency on the weather itself, a recommendation to develop a prototypic mobile robot for smart irrigation is submitted. Smart irrigation system is an essential tool from yield point of view and scarcity of the water. This smart irrigation system adopts a soil moisture sensor to measure the moisture content of the soil and automatically provide a signal to switches the water pump when the power is on. This mobile robot uses a tracked vehicle as the chassis of the robot whereby two parallel forces of motion are controlled to create a linear and rotation motion of the wheel. Besides, ultrasonic sensor is also assembled on this prototypic design to avoid any object or obstacles during the movement of the mobile robot. The novelty of this study is to demonstrate that the smart irrigation mobile robot can be used, not only to provide water to the crops but also, to reduce water usage. In this research, 2-Degree of Freedom Proportional Integral Derivative (2-DOF PID) controller is proposed for smart irrigation mobile robot after comparison between optimal 1-Degree of Freedom Proportional Integral Derivative (1-DOF PID) to acquire the best controller. Further investigation of controller effort, disturbance rejection and reference tracking are implemented to validate the capability of the proposal within the parameter of the system itself. © 2020, Springer Nature Switzerland AG.