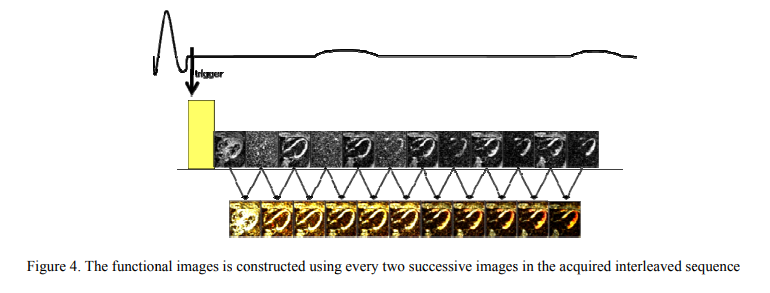
Strain correction in interleaved strain-encoded (SENC) cardiac MR
The strain encoding (SENC) technique directly encodes regional strain of the heart into the acquired MR images and produces two images with two different tunings so that longitudinal strain, on the short-axis view, or circumferential strain on the long-axis view, are measured. Interleaving acquisition is used to shorten the acquisition time of the two tuned images by 50%, but it suffers from errors in the strain calculations due to inter-tunings motion of the heart. In this work, we propose a method to correct for the inter-tunings motion by estimating the motion-induced shift in the spatial
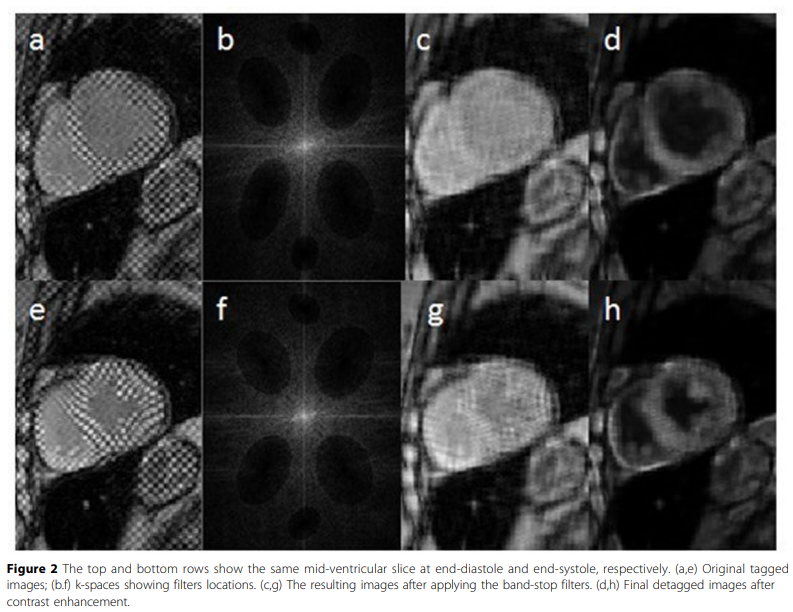
Evaluation of the cardiac global function from tagged magnetic resonance images
Tagged Magnetic Resonance (MR) images are considered the gold standard for evaluating the cardiac regional function. Nevertheless, the low myocardium-to-blood contrast in tagged MR images prevents accurate segmentation of the myocardium, and hence, hinders the quantitative assessment of the global function of the heart. In this work, a method for enhancing the myocardium-to-blood contrast in tagged MR images is proposed. First, the tag pattern in each input tagged MR image is removed using technique based on the image texture and the frequency components of the tag pattern to produce two
Estimation of the myocardium rotation from standard cine Magnetic Resonance Imaging sequences
Myocardium rotation and torsion are important indicators of the cardiac function. Currently, tagged Magnetic Resonance Imaging (tMRI) sequences are analyzed to estimate these parameters. Unfortunately, tMRI is not widely used in clinical practice because it prolongs the scanning time and requires sophisticated analysis software. In this work, we present a method for estimating the myocardium rotation from standard cine MRI sequences. The method is based on identifying special features, i.e. landmarks, of the intensity pattern around the myocardium borders at each timeframe. Each set of
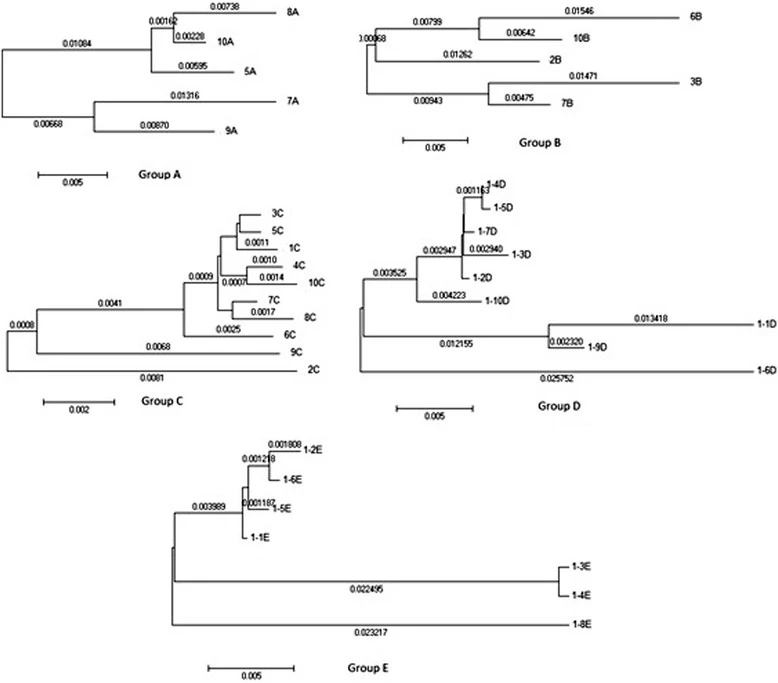
New insight into HCV E1/E2 region of genotype 4a
Introduction: Hepatitis C virus (HCV) genome contains two envelope proteins (E1 and E2) responsible for the virus entry into the cell. There is a substantial lack of sequences covering the full length of E1/E2 region for genotype 4. Our study aims at providing new sequences as well as characterizing the genetic divergence of the E1/E2 region of HCV 4a using our new sequences along with all publicly available datasets. Methods: The genomic segments covering the whole E1/E2 region were isolated from Egyptian HCV patients and sequenced. The resulting 36 sequences 36 were analyzed using sequence
Molecular prognostic profile of egyptian HCC cases infected with hepatitis C virus
Background: Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) is a common and aggressive malignancy. Despite of the improvements in its treatment, HCC prognosis remains poor due to its recurrence after resection. This study provides complete genetic profile for Egyptian HCC. Genome-wide analyses were performed to identify the predictive signatures. Patients and Methods: Liver tissue was collected from 31 patients with diagnosis of HCC and gene expression levels in the tumours and their adjacent non-neoplastic tissues samples were studied by analyzing changes by microarray then correlate these with the clinico
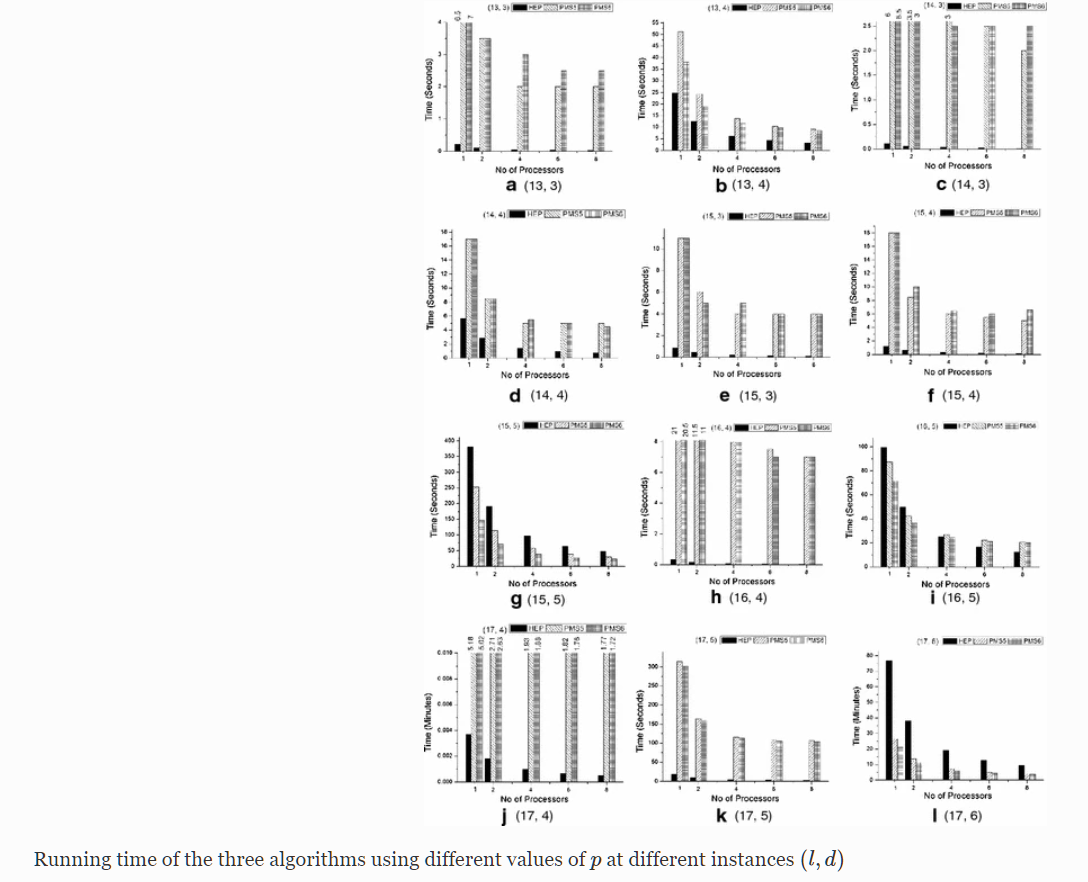
Parallelizing exact motif finding algorithms on multi-core
The motif finding problem is one of the important and challenging problems in bioinformatics. A variety of sequential algorithms have been proposed to find exact motifs, but the running time is still not suitable due to high computational complexity of finding motifs. In this paper we parallelize three efficient sequential algorithms which are HEPPMSprune, PMS5 and PMS6. We implement the algorithms on a Dual Quad-Core machine using openMP to measure the performance of each algorithm. Our experiment on simulated data show that: (1) the parallel PMS6 is faster than the other algorithms in case
Cardiac magnetic resonance image classification and retrieval based on the image acquisition technique
Magnetic resonance imaging allows a number of imaging techniques and protocols that can be used to capture the different aspects of the cardiac function and structure. The produced amount of data is huge and its classification and/or retrieval based on its visual content are necessary for educational and training purposes. In this work, we propose a method for classification and retrieving cardiac magnetic resonance images based on the type of the acquisition technique. Preliminary results are obtained from two data sets of 3175 images acquired using five different cardiac imaging techniques
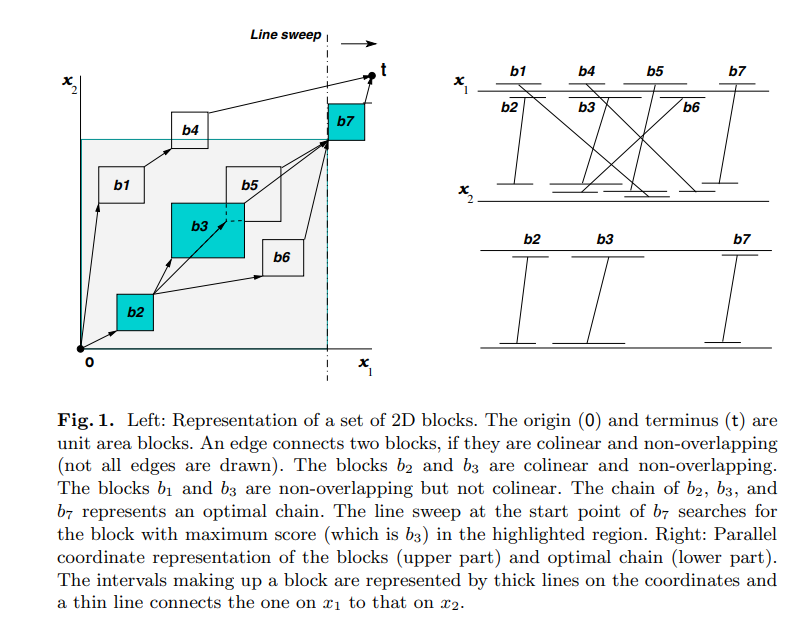
Parallel chaining algorithms
Given a set of weighted hyper-rectangles in a k-dimensional space, the chaining problem is to identify a set of colinear and non-overlapping hyper-rectangles of total maximal weight. This problem is used in a number of applications in bioinformatics, string processing, and VLSI design. In this paper, we present parallel versions of the chaining algorithm for bioinformatics applications, running on multi-core and computer cluster architectures. Furthermore, we present experimental results of our implementations on both architectures. © 2010 Springer-Verlag.
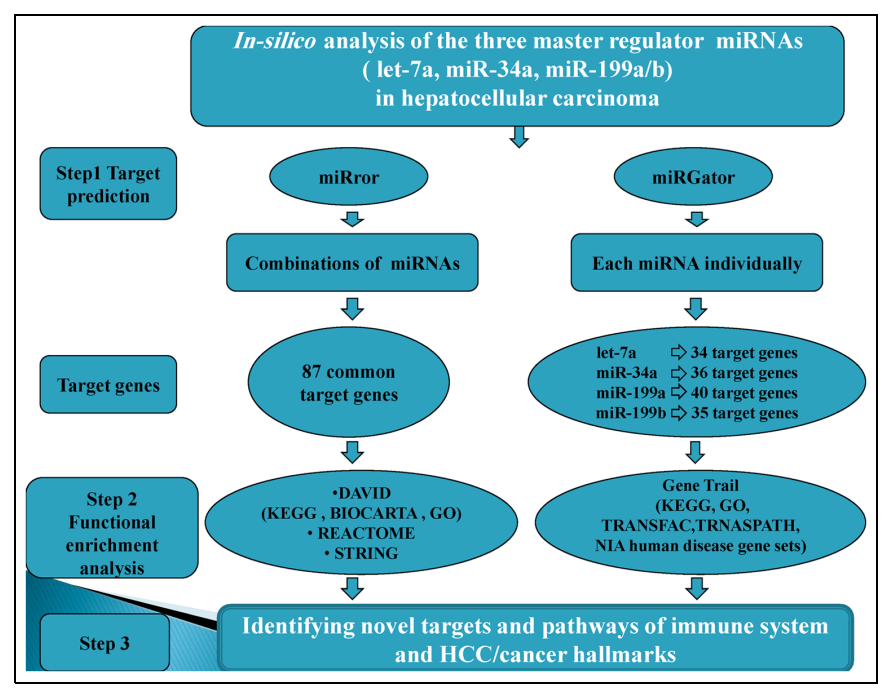
Bioinformatics functional analysis of let-7a, miR-34a, and miR-199a/b reveals novel insights into immune system pathways and cancer hallmarks for hepatocellular carcinoma
Let-7a, miR-34a, and miR-199 a/b have gained a great attention as master regulators for cellular processes. In particular, these three micro-RNAs act as potential onco-suppressors for hepatocellular carcinoma. Bioinformatics can reveal the functionality of these micro-RNAs through target prediction and functional annotation analysis. In the current study, in silico analysis using innovative servers (miRror Suite, DAVID, miRGator V3.0, GeneTrail) has demonstrated the combinatorial and the individual target genes of these micro-RNAs and further explored their roles in hepatocellular carcinoma
Modeling of ultrasound hyperthermia treatment of breast tumors
Ultrasound hyperthermia has become one of the new therapeutic modalities for breast cancer treatment, since ultrasound appears to selectively affect malignant cells without causing any deleterious effects to the surrounding normal tissues. The main objective of this study is to numerically simulate the interaction of therapeutic ultrasound with a multi- tissue type system, and to develop an analytical model for calculating the temperature rise in these tissues due to ultrasound. First, the Finite-Element Method has been used to compute the radiated power density produced by a circular
Pagination
- Previous page ‹‹
- Page 5
- Next page ››
