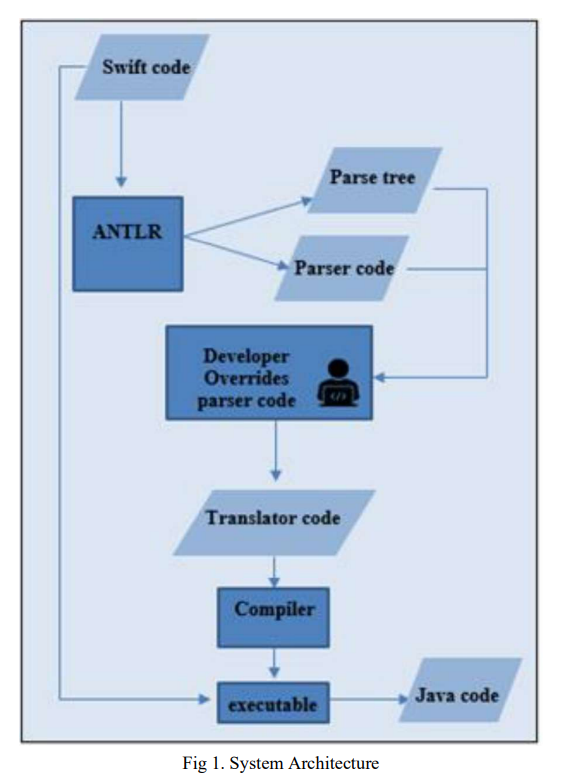
Trans-Compiler based Mobile Applications code converter: Swift to java
Numerous commercial tools like Xamarin, React Native and PhoneGap utilize the concept of cross-platform mobile applications development that builds applications once and runs it everywhere opposed to native mobile app development that writes in a specific programming language for every platform. These commercial tools are not very efficient for native developers as mobile applications must be written in specific language and they need the usage of specific frameworks. In this paper, a suggested approach in TCAIOSC tool to convert mobile applications from Android to iOS is used to develop the
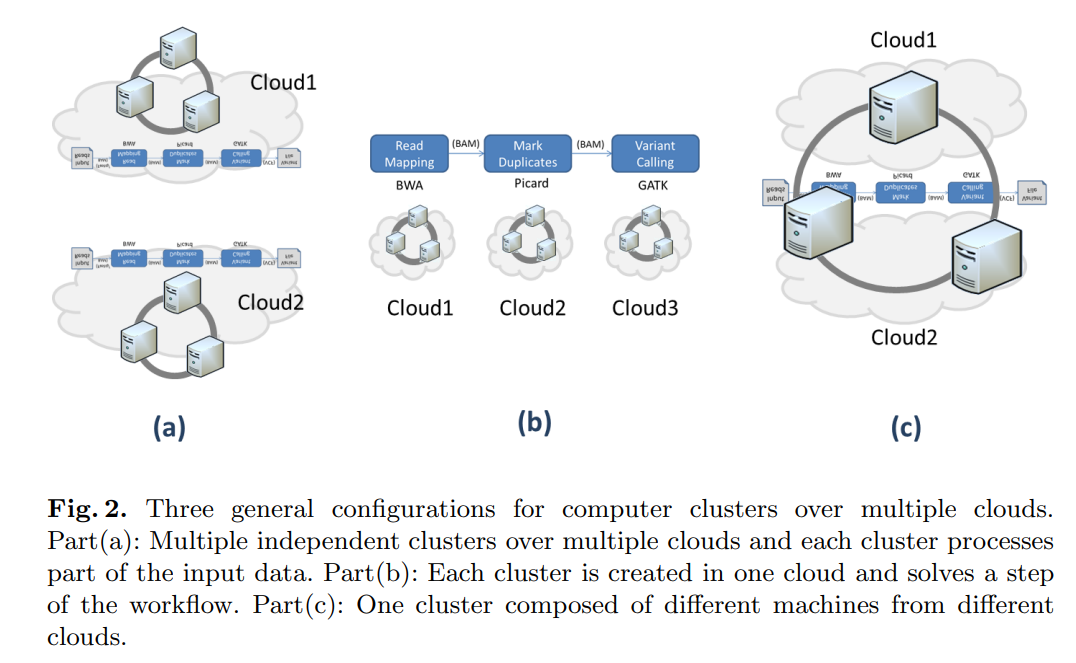
Supporting bioinformatics applications with hybrid multi-cloud services
Cloud computing provides a promising solution to the big data problem associated with next generation sequencing applications. The increasing number of cloud service providers, who compete in terms of performance and price, is a clear indication of a growing market with high demand. However, current cloud computing based applications in bioinformatics do not profit from this progress, because they are still limited to just one cloud service provider. In this paper, we present different use case scenarios using hybrid services and resources from multiple cloud providers for bioinformatics
A dynamic system development method for startups migrate to c loud
Cloud computing has become the most convenient environment for startups to run, build and deploy their products. Most startups work on availing platforms as a solution for problems related to education, health, traffic and others. Many of these platforms are mobile applications. With platforms as a service (PaaS), startups can provision their applications and gain access to a suite of IT infrastructure as their business needs. But, startups face many business and technical challenges to adapt rapidly to cloud computing. This paper helps startups to build a migration strategy. It discusses
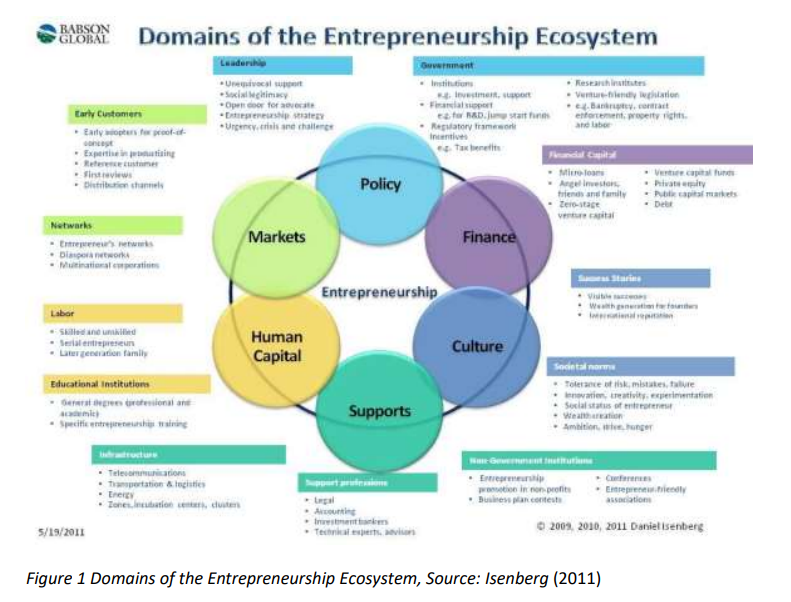
Entrepreneurial ecosystems: Global practices and reflection on the egyptian context
Following the Egyptian revolution that had taken place in 2011, many social and economic norms changed. The Egyptian economy witnessed a severe deterioration. In 2016, the Egyptian pound lost almost 60% of its value overnight. Egyptian government and foreign development agencies rallied to find a remedy to the economic downturn. With no jobs, young Egyptians started experimenting with the possibility of entrepreneurship. This acted as a pretext to the massive transformations taking place in the Egyptian ecosystem. The objective of this paper is to identify how Egypt should shape its
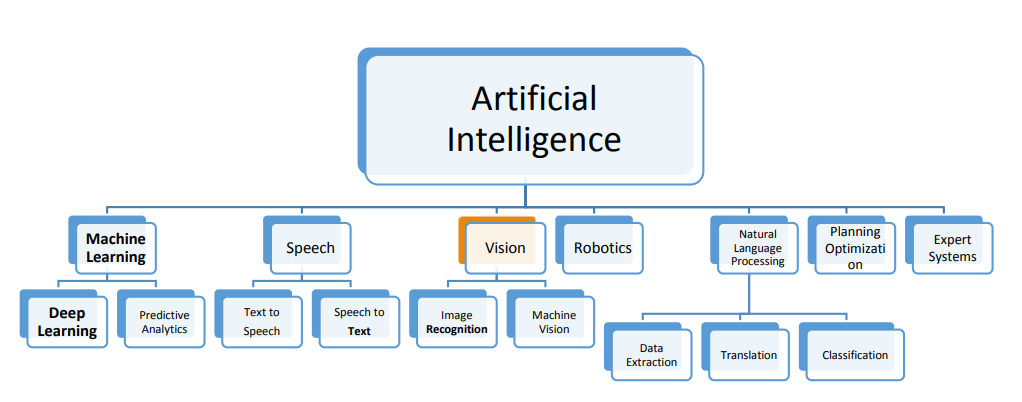
Artificial intelligence for retail industry in Egypt: Challenges and opportunities
In the era of digital transformation, a mass disruption in the global industries have been detected. Big data, the Internet of Things (IoT) and Artificial Intelligence (AI) are just examples of technologies that are holding such digital disruptive power. On the other hand, retailing is a high-intensity competition and disruptive industry driving the global economy and the second largest globally in employment after the agriculture. AI has large potential to contribute to global economic activity and the biggest sector gains would be in retail. AI is the engine that is poised to drive the

Labour productivity in building construction: A field study
This paper describes a field study conducted over a period of 11-months on labour productivity observed during the construction of a new university campus in Cairo, Egypt. The campus is being built on 127 acres and the field study was conducted during the construction of two main buildings; each of 20,000 m 2 built up area. The study utilized work sampling (WS), craftsman questionnaire (CQ), and foreman delay survey (FDS) methods to analyze labour productivity of three indicative and labour-intensive trades, namely formwork, masonry work, and HVAC duct installation. The results were also
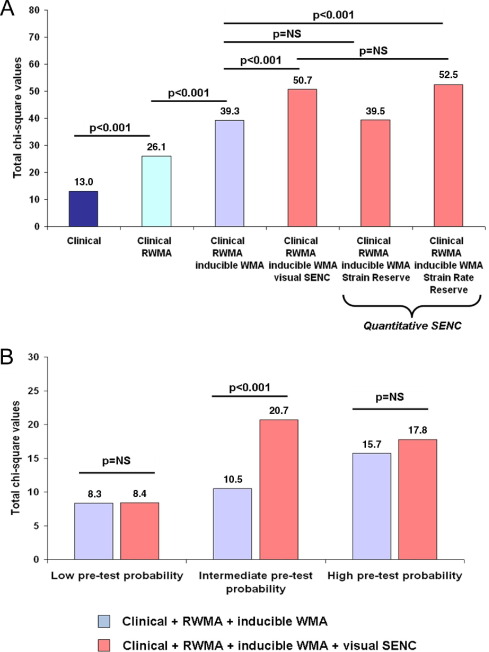
Strain-encoded cardiac magnetic resonance during high-dose dobutamine stress testing for the estimation of cardiac outcomes: Comparison to Clinical Parameters and Conventional Wall Motion Readings
Objectives: The purpose of this study was to determine the prognostic value of strain-encoded magnetic resonance imaging (SENC) during high-dose dobutamine stress cardiac magnetic resonance imaging (DS-MRI) compared with conventional wall motion readings. Background: Detection of inducible ischemia by DS-MRI on the basis of assessing cine images is subjective and depends on the experience of the readers, which may influence not only the diagnostic classification but also the risk stratification of patients with ischemic heart disease. Methods: In all, 320 consecutive patients with suspected or
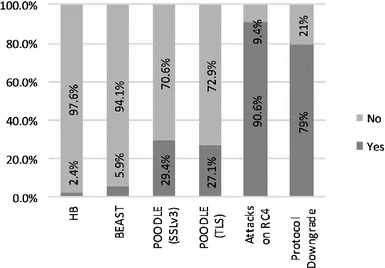
Stock exchange threat modeling, EGX as a case study
Cyber crime is a growing threat affecting all business sectors. Stock Exchanges, a financial services sector, are not far from it. Trading stocks via Internet exposes the process to cyber threats that might take advantage of a system defect to breach security and cause possible harm. Online Trading websites are protected by various security systems. Digital Certificate, which is based on Secure Socket Layer (SSL) protocol, is an example. This research examines implementation of Digital Certificate in online trading servers. This evaluation helps to identify security weaknesses and take actions
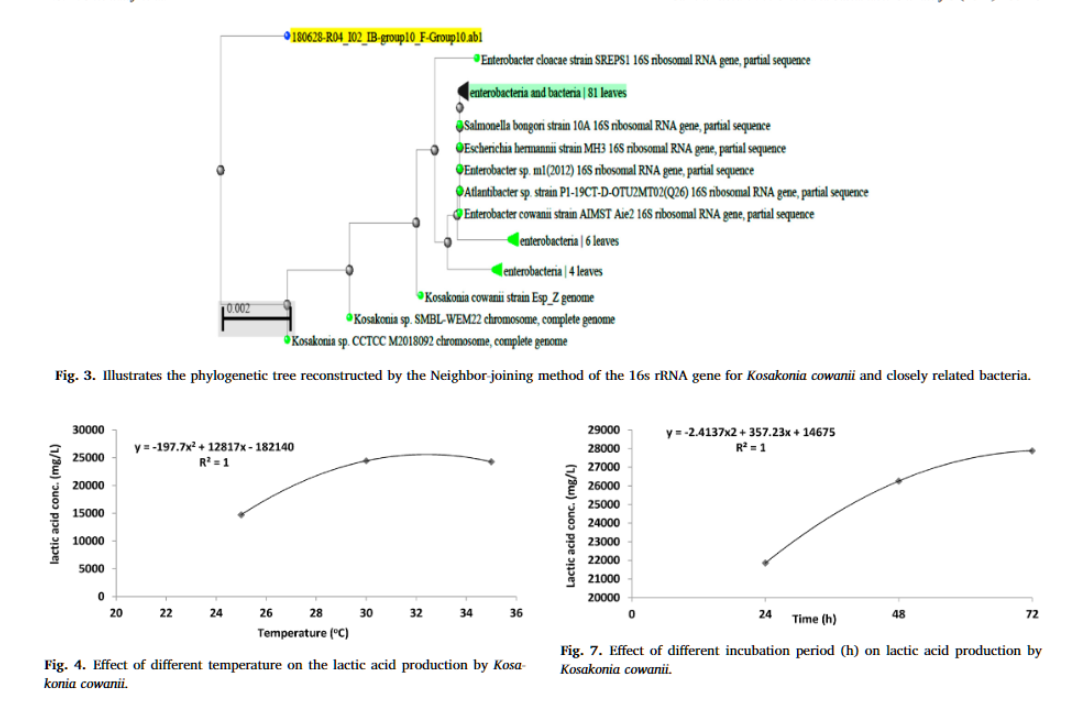
Optimization of lactic acid production from agro-industrial wastes produced by Kosakonia cowanii
Lactic acid is used for the preparation of poly-lactic acid. The objective of this research was to produce lactic acid from agro-industrial wastes as cheap, renewable substrates, and also reduce the pollution burden on the environment. Sixteen bacterial isolates were isolated from agro-industrial wastes. The chemical hydrolysis of agro-industrial wastes was achieved with hydrochloric acid, sulfuric acid, and sodium hydroxide. The highest yield of lactic acid produced was identified using 16S rRNA. The optimum conditions for lactic acid production were determined. Calcium lactate, produced from
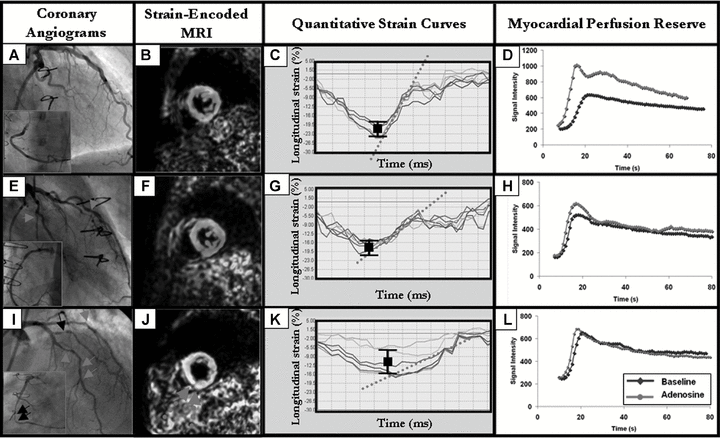
Strain-encoded cardiac magnetic resonance for the evaluation of chronic allograft vasculopathy in transplant recipients
The aim of our study was to investigate the ability of Strain-Encoded magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) to detect cardiac allograft vasculopathy (CAV) in heart transplantation (HTx)-recipients. In consecutive subjects (n = 69), who underwent cardiac catheterization, MRI was performed for quantification of myocardial strain and perfusion reserve. Based on angiographic findings subjects were classified: group A including patients with normal vessels; group B, patients with stenosis
Pagination
- Previous page ‹‹
- Page 6
- Next page ››
