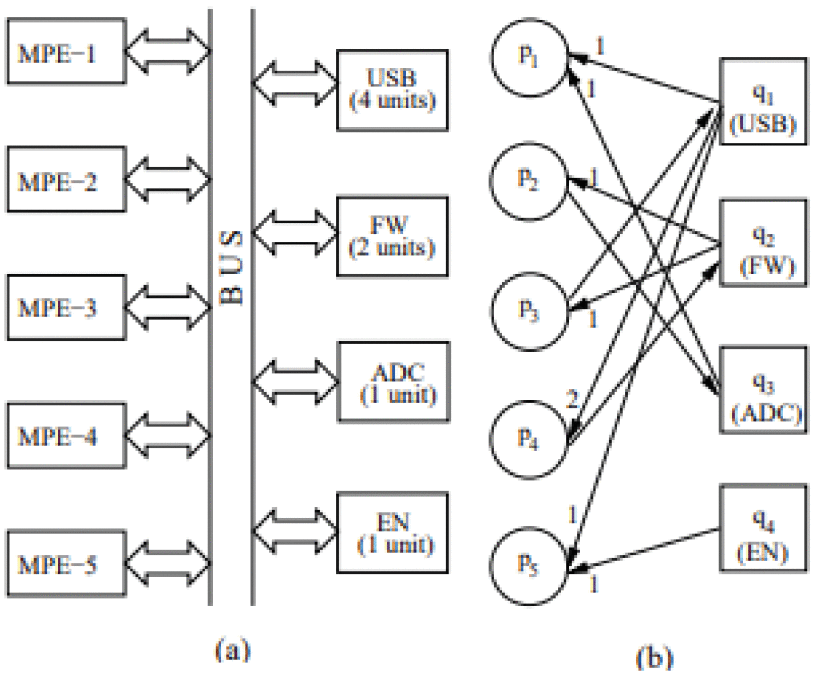
Fault-Recovery and Robust Deadlock Control of Reconfigurable Multi-Unit Resource Allocation Systems Using Siphons
A multi-unit resource allocation system usually contains several processes and a number of resources with multiple units. Due to the competition for shared resources in these systems, deadlocks may occur. Recently, researchers have shown an increased awareness in deadlock control strategies for such a kind of systems without considering the dynamic changes such as processing failures and rework by using the Petri net paradigm. This article reports a new strategy for deadlock analysis and control in reconfigurable multi-unit resource systems (MRSs). We discuss a generalized class of Petri nets
Convergence study of IPv6 tunneling techniques
IPv4 address exhaustion pushed IETF to create IPv6, the improved substitute of IPv4. The Internet complexity and its enormous size prolong the transition from IPv4 to IPv6 process. This means that both versions will necessarily co-exist. Meanwhile, tunneling appears as a solution trend. The tunneling is a transition technique that is considered temporary till all ISPs would support IPv6. At this paper, we compare the routing convergence of two tunnel types, 6to4 and Manually Configured versus the conventional IPv4 and IPv6 protocols. We analyze the network resources consumed during cold start
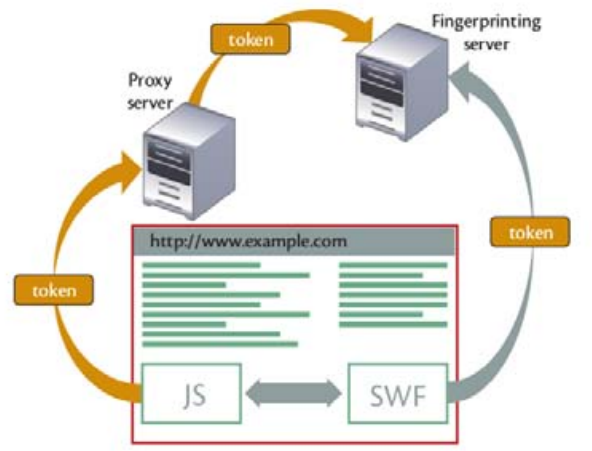
Browsers fingerprinting motives, methods, and countermeasures
With the continuous and aggressive competition in advertising businesses, uncontrollably desires have emerged to identify and classify consumers. It is proven that companies must have a clear definition of its target market. Based on this we have seen different ways to identify, analyze, and track consumers, either voluntarily or without their consent. Browser fingerprinting techniques have evolved from being privacy-friendly to privacy intrusive to serve these demands. This also has pushed privacy concerned people to save no effort to advance countermeasures. In this paper we introduce
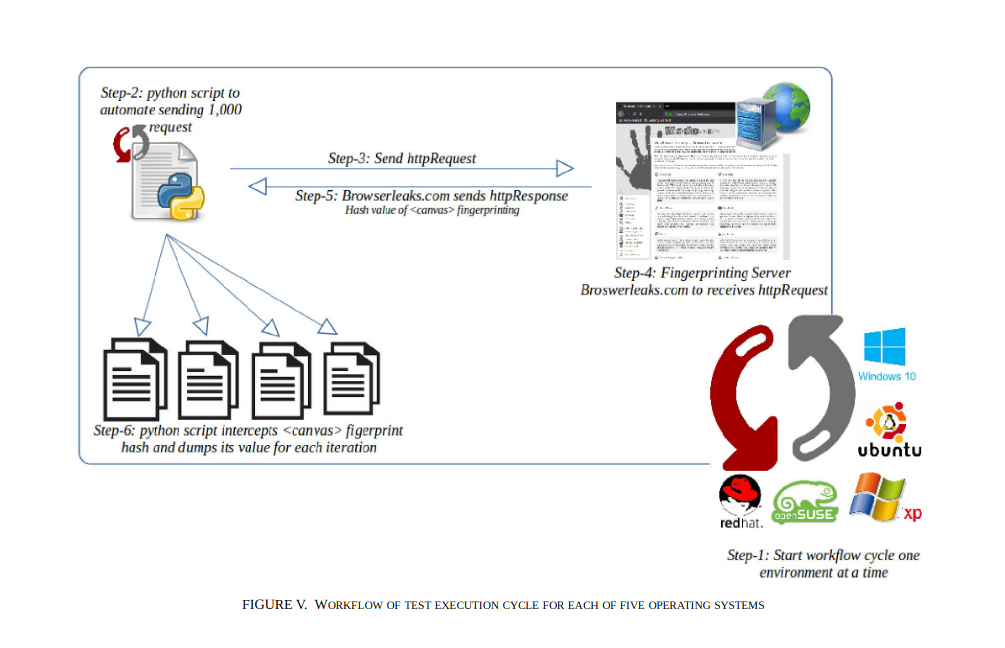
NONYM!ZER: Mitigation Framework for Browser Fingerprinting
Not only recent compelled cookies regulations have radically restrained their threats but also increased people awareness has played a fundamental part. This has placed huge pressure on enterprises to find alternatives to bridge this gap and satisfy business demands. Since then fingerprinting has gained enormous popularity. In this paper, we introduce 'nonym!zer' as a mitigation framework for browser fingerprinting. It helps to hinder or impede browser fingerprinting on desktop browsers that web servers use such as WebGL or Canvas technologies. © 2019 IEEE.
Cloud computing security: Challenges & future trends
Cloud computing is one of the most trendy terminologies. Cloud providers aim to satisfy clients' requirements for computing resources such as services, applications, networks, storage and servers. They offer the possibility of leasing these resources rather than buying them. Many popular companies, such as Amazon, Google and Microsoft, began to enhance their services and apply the technology of cloud computing to provide cloud environment for their customers. Although there are lots of advantages in using a cloud-based system, some issues must be handled before organisations and individuals
Code Smells and Detection Techniques: A Survey
Design and code smells are characteristics in the software source code that might indicate a deeper design problem. Code smells can lead to costly maintenance and quality problems, to remove these code smells, the software engineers should follow the best practices, which are the set of correct techniques which improve the software quality. Refactoring is an adequate technique to fix code smells, software refactoring modifies the internal code structure without changing its functionality and suggests the best redesign changes to be performed. Developers who apply correct refactoring sequences
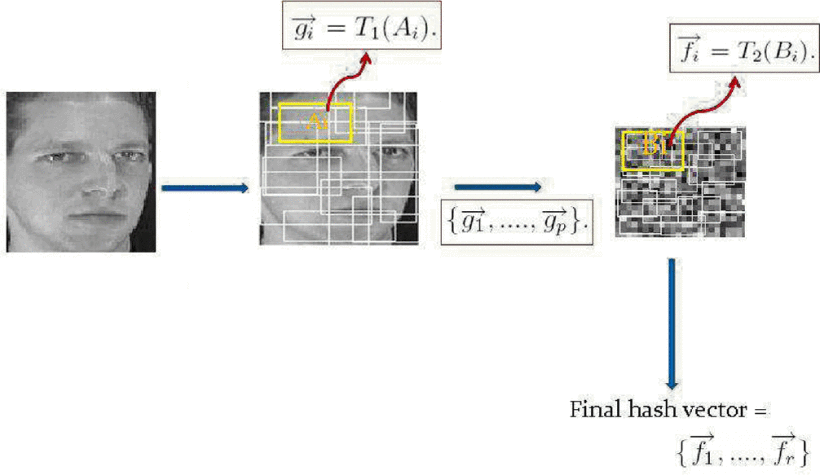
A secure face verification system based on robust hashing and cryptography
Face verification has been widely studied during the past two decades. One of the challenges is the rising concern about the security and privacy of the template database. In this paper, we propose a secure face verification system which employs a user dependent one way transformation based on a two stage hashing algorithm.We first hash the face image using a two stages robust image hashing technique, then the result hash vector is encrypted using Advanced Encryption Standard (AES). Both the hashing and the encryption/decryption keys are generated from the user claimed ID, using a modified

SigPloit: A New Signaling Exploitation Framework
Mobile communication networks are using signaling protocols to allow mobile users to communicate using short messages, phone calls and mobile data. Signaling protocols are also used to manage billing for operators and much more. The design flaws that signaling inherits made them vulnerable to attacks such as location tracking of subscriber, fraud, calls and SMS interception. With the high rate of these emerging attacks on telecommunication protocols there is a need to create a comprehensive penetration testing framework for signaling. In this paper, we propose a framework called Sigploit that
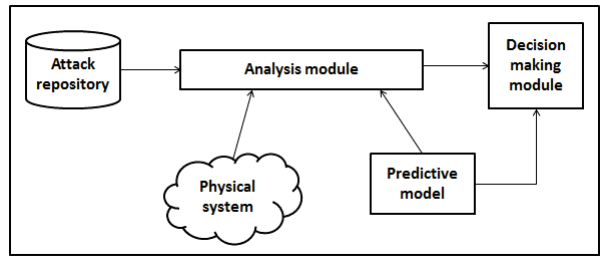
Security Perspective in RAMI 4.0
Cloud Computing, Internet of Things (IoT) are the main technologies contributing to the adoption of the fourth revolution in manufacturing, Industry 4.0 also known as smart manufacturing or digital manufacturing. Smart manufacturing facilitates and accelerates the process of manufacturing with the connection of all the systems related to the manufacturing process starting with the Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) systems, the Industrial Control Systems (ICSs) which control the production line and the Cyber Physical Systems (CPSs). Before the emerging of web applications, cloud applications
Replica placement in peer-assisted clouds: An economic approach
We introduce NileStore, a replica placement algorithm based on an economical model for use in Peer-assisted cloud storage. The algorithm uses storage and bandwidth resources of peers to offload the cloud provider's resources. We formulate the placement problem as a linear task assignment problem where the aim is to minimize time needed for file replicas to reach a certain desired threshold. Using simulation, We reduce the probability of a file being served from the provider's servers by more than 97.5% under realistic network conditions. © 2011 IFIP International Federation for Information
Pagination
- Previous page ‹‹
- Page 28
- Next page ››
