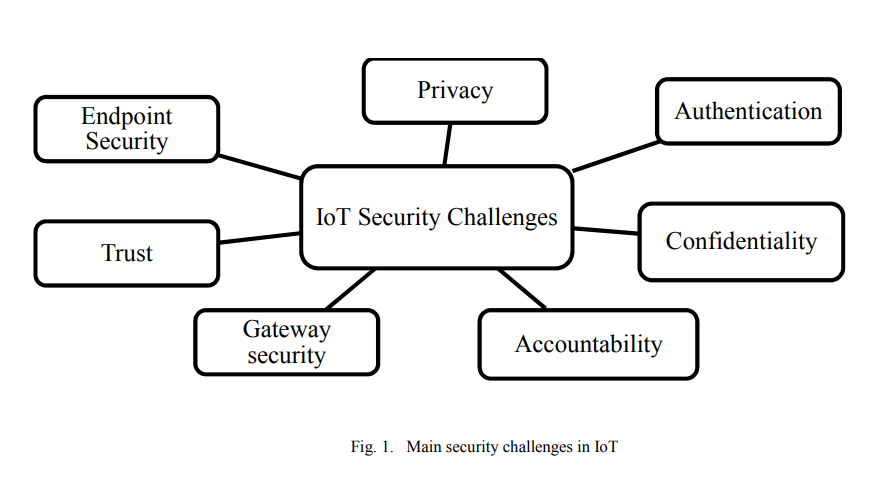
Internet of Things security framework
For the past decade, Internet of Things (IoT) had an important role in our lives. It connects a large number of embedded devices. These devices fulfill very difficult and complicated tasks, which facilitate our work. Till now the security of IoT faces many challenges such as privacy, authentication, confidentiality, trust, middleware security, mobile security and policy enforcement. In order to provide a secure environment for IoT, this paper proposes a framework for IoT devices. © 2017 IEEE.
Replica placement in peer-assisted clouds: An economic approach
We introduce NileStore, a replica placement algorithm based on an economical model for use in Peer-assisted cloud storage. The algorithm uses storage and bandwidth resources of peers to offload the cloud provider's resources. We formulate the placement problem as a linear task assignment problem where the aim is to minimize time needed for file replicas to reach a certain desired threshold. Using simulation, We reduce the probability of a file being served from the provider's servers by more than 97.5% under realistic network conditions. © 2011 IFIP International Federation for Information
Cloud-based parallel suffix array construction based on MPI
Massive amount of genomics data are being produced nowadays by Next Generation Sequencing machines. The suffix array is currently the best choice for indexing genomics data, because of its efficiency and large number of applications. In this paper, we address the problem of constructing the suffix array on computer cluster in the cloud. We present a solution that automates the establishment of a computer cluster in a cloud and automatically constructs the suffix array in a distributed fashion over the cluster nodes. This has the advantage of encapsulating all set-up details and execution of

A system for assessing the quality of Web pages
The World Wide Web has brought about an unprecedented explosion in the amount of information available on-line, largely in the form of Web pages. The fact that anyone can publish anything has ultimately led to pages with varying degrees of quality. This paper aims at investigating means for assessing the quality of a random web page and provides a quantitative approach for selecting high quality-content pages. The work was motivated by the need to locate pages that may be considered as candidates for translation. © 2013 IEEE.
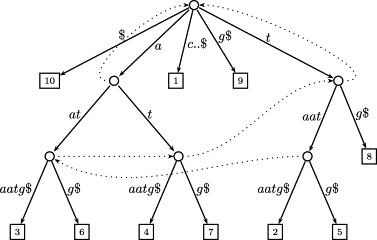
Computing the Burrows-Wheeler transform of a string and its reverse in parallel
The contribution of this article is twofold. First, we provide new theoretical insights into the relationship between a string and its reverse: If the Burrows-Wheeler transform (BWT) of a string has been computed by sorting its suffixes, then the BWT, the suffix array, and the longest common prefix array of the reverse string can be derived from it without suffix sorting. Furthermore, we show that the longest common prefix arrays of a string and its reverse are permutations of each other. Second, we provide a parallel algorithm that, given the BWT of a string, computes the BWT of its reverse

News auto-tagging using Wikipedia
This paper presents an efficient method for automatically annotating Arabic news stories with tags using Wikipedia. The idea of the system is to use Wikipedia article names, properties, and re-directs to build a pool of meaningful tags. Sophisticated and efficient matching methods are then used to detect text fragments in input news stories that correspond to entries in the constructed tag pool. Generated tags represent real life entities or concepts such as the names of popular places, known organizations, celebrities, etc. These tags can be used indirectly by a news site for indexing
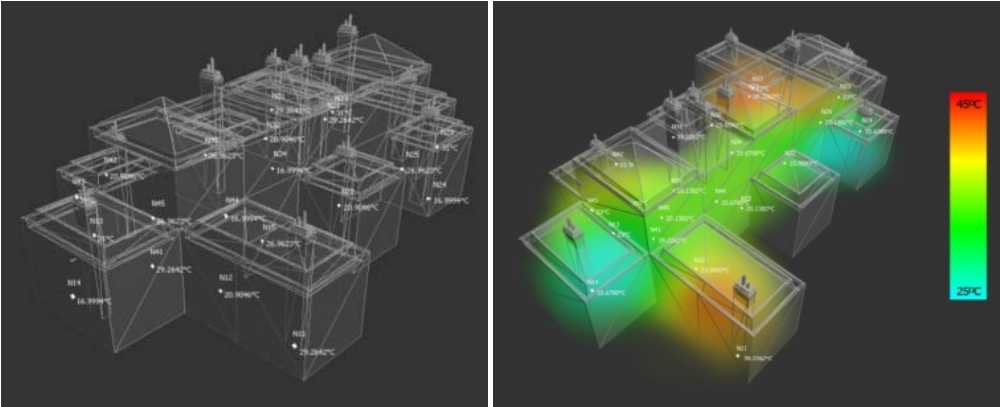
Monitoring and visualization of large WSN deployments
Recent developments in wireless sensor networks have ushered in novel ubiquitous computing applications based on distributed large-scale data acquisition and interactive interpretation. However, current WSNs suffer from lack of effective tools to support large network deployment and administration as well as unavailability of interactive visualization techniques required to explore and analyze captured sensing data, which is hindering the development of real-life WSN-based ubiquitous systems. Sensor Explorer addresses the above problems by providing modular efficient stream management engine
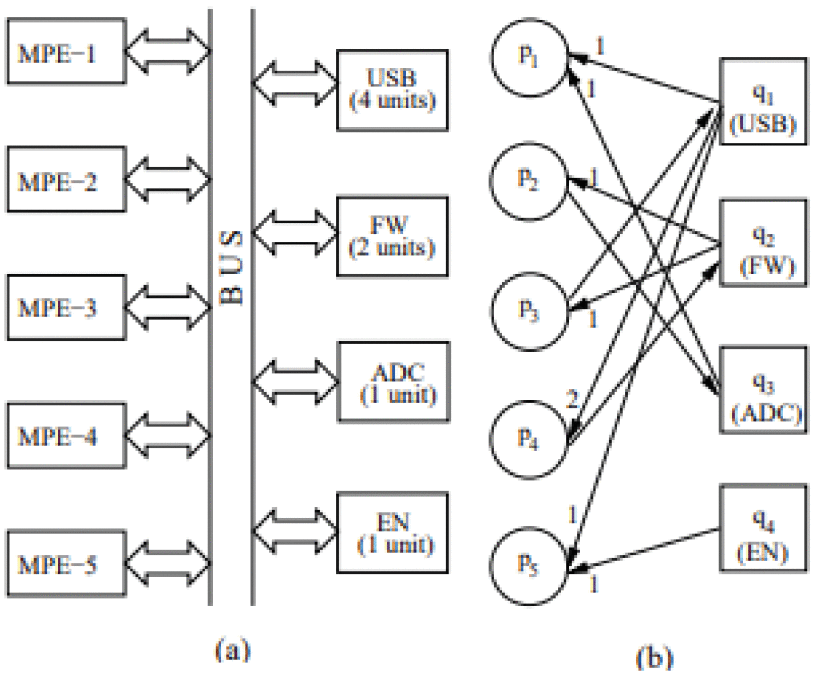
Fault-Recovery and Robust Deadlock Control of Reconfigurable Multi-Unit Resource Allocation Systems Using Siphons
A multi-unit resource allocation system usually contains several processes and a number of resources with multiple units. Due to the competition for shared resources in these systems, deadlocks may occur. Recently, researchers have shown an increased awareness in deadlock control strategies for such a kind of systems without considering the dynamic changes such as processing failures and rework by using the Petri net paradigm. This article reports a new strategy for deadlock analysis and control in reconfigurable multi-unit resource systems (MRSs). We discuss a generalized class of Petri nets
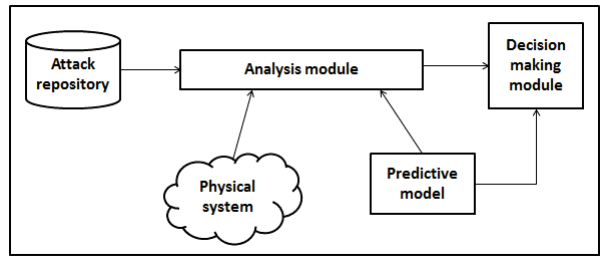
Security Perspective in RAMI 4.0
Cloud Computing, Internet of Things (IoT) are the main technologies contributing to the adoption of the fourth revolution in manufacturing, Industry 4.0 also known as smart manufacturing or digital manufacturing. Smart manufacturing facilitates and accelerates the process of manufacturing with the connection of all the systems related to the manufacturing process starting with the Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) systems, the Industrial Control Systems (ICSs) which control the production line and the Cyber Physical Systems (CPSs). Before the emerging of web applications, cloud applications

SigPloit: A New Signaling Exploitation Framework
Mobile communication networks are using signaling protocols to allow mobile users to communicate using short messages, phone calls and mobile data. Signaling protocols are also used to manage billing for operators and much more. The design flaws that signaling inherits made them vulnerable to attacks such as location tracking of subscriber, fraud, calls and SMS interception. With the high rate of these emerging attacks on telecommunication protocols there is a need to create a comprehensive penetration testing framework for signaling. In this paper, we propose a framework called Sigploit that
Pagination
- Previous page ‹‹
- Page 10
- Next page ››
