Analysis of Tapered Timoshenko and Euler-Bernoulli Beams on an Elastic Foundation with Moving Loads
This research studies the vibration analysis of Euler-Bernoulli and Timoshenko beams utilizing the differential quadrature method (DQM) which has wide applications in the field of basic vibration of different components, for example, pillars, plates, round and hollow shells, and tanks. The free vibration of uniform and nonuniform beams laying on elastic Pasternak foundation will be studied under three sets of boundary conditions, that is, mixing between being simply upheld and fixed while utilizing the DQM. The natural frequencies and deflection values were produced through the examination of
Two-dimensional heat conduction in a rigid thermal conductor within the dual-phase-lag model by one-sided Fourier transform
An exact analytical solution in closed form is obtained for a two-dimensional initial-boundary-value problem of heat wave propagation in a thick slab of an anisotropic rigid thermal conductor within the dual-phase-lag model. One-sided Fourier transform technique is used to obtain a formal solution. The method requires an essential change of the dependent variable in order to guarantee a suitable asymptotic time behavior of the unknown function. The solution satisfies prescribed boundary temperatures and zero initial conditions. Numerical results are presented to put in evidence the effect of
Analytic and numeric analysis for deformation of non-prismatic beams resting on elastic foundations
Background: The buckling load as well as the natural frequency under axial load for non-prismatic beam is a changeling problem. Determination of buckling load, natural frequency, and elastic deflection is very important in civil applications. The current paper used both perturbation method (PM), analytic method, and differential quadrature method (DQM), numerical method, to find buckling load and natural frequency with different end supports. The deflection of the beam resting on an elastic foundation under transverse distributed and axial loads is also obtained. Both PM and DQM are used for
Comparative Analysis of Various Machine Learning Techniques for Epileptic Seizures Detection and Prediction Using EEG Data
Epileptic seizures occur as a result of functional brain dysfunction and can affect the health of the patient. Prediction of epileptic seizures before the onset is beneficial for the prevention of seizures through medication. Electroencephalograms (EEG) signals are used to predict epileptic seizures using machine learning techniques and feature extractions. Nevertheless, the pre-processing of EEG signals for noise removal and extraction of features are two significant problems that have an adverse effect on both anticipation time and true positive prediction performance. Considering this, the
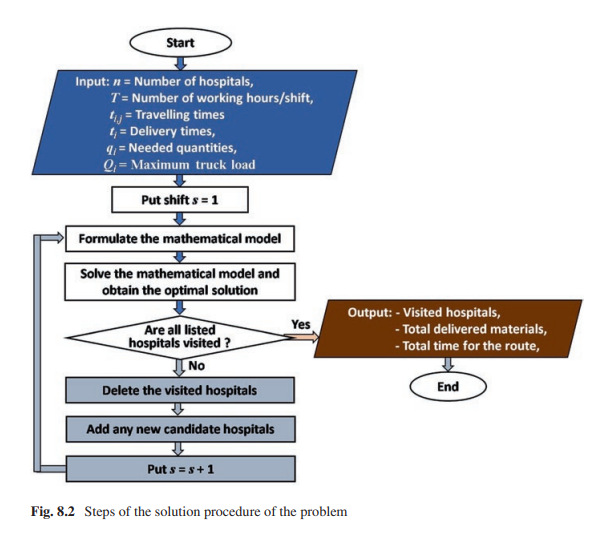
Optimum distribution of protective materials for COVID−19 with a discrete binary gaining-sharing knowledge-based optimization algorithm
Many application problems are formulated as nonlinear binary programming models which are hard to be solved using exact algorithms especially in large dimensions. One of these practical applications is to optimally distribute protective materials for the newly emerged COVID-19. It is defined for a decision-maker who wants to choose a subset of candidate hospitals comprising the maximization of the distributed quantities of protective materials to a set of chosen hospitals within a specific time shift. A nonlinear binary mathematical programming model for the problem is introduced with a real
Optimum Location of Field Hospitals for COVID-19: A Nonlinear Binary Metaheuristic Algorithm
Determining the optimum location of facilities is critical in many fields, particularly in healthcare. This study proposes the application of a suitable location model for field hospitals during the novel coronavirus 2019 (COVID-19) pandemic. The used model is the most appropriate among the threemost common locationmodels utilized to solve healthcare problems (the set covering model, the maximal covering model, and the P-median model). The proposed nonlinear binary constrained model is a slight modification of the maximal covering model with a set of nonlinear constraints. The model is used to
Comparative study of fractional filters for Alzheimer disease detection on MRI images
This paper presents a comparative study of four fractional order filters used for edge detection. The noise performance of these filters is analyzed upon the addition of random Gaussian noise, as well as the addition of salt and pepper noise. The peak signal to noise ratio (PSNR) of the detected images is numerically compared. The mean square error (MSE) of the detected images as well as the execution time are also adopted as evaluation methods for comparison. The visual comparison of the filters capability in medical image edge detection is presented, that can help in the diagnosis of
Centralized Multi-agent Mobile Robots SLAM and Navigation for COVID-19 Field Hospitals
In this paper we focus on the proof of concept prototype of fully autonomous centralized Multi-Robot System (MRS) consisting of a Hexapod walking robot and a six wheeled mobile robot. Recently, there has been an increasing demand for such systems as they can be involved in several tasks such as collaborative search and rescue, surveillance, monitoring, and disinfecting Field hospitals. To name a few, COVID-19 pandemic showed the weak points in the medical sector around the world, including those in the most advanced nations that had to go through hard decisions due to the lack of medical
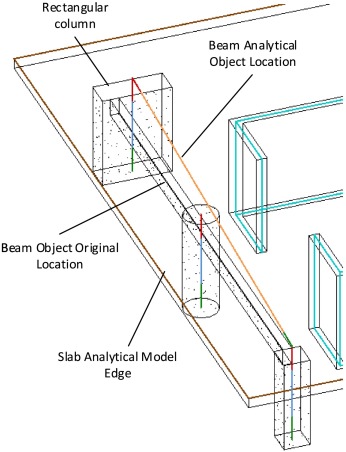
Geometrically accurate structural analysis models in BIM-centered software
Current BIM models impose restrictions on the geometry of building members in their analytical models, where components are fitted to wireframe representations. This unnecessary reduction in geometrical representation drives the loss of structural details and may lead to defective structural analysis. The present paper addresses the current shortcomings in the semantics of analytical models within BIM environments and recommends enhancements. An explanation is given of a BIM-centered structural analysis system based on coupling finite elements for vertical and horizontal elements, and boundary
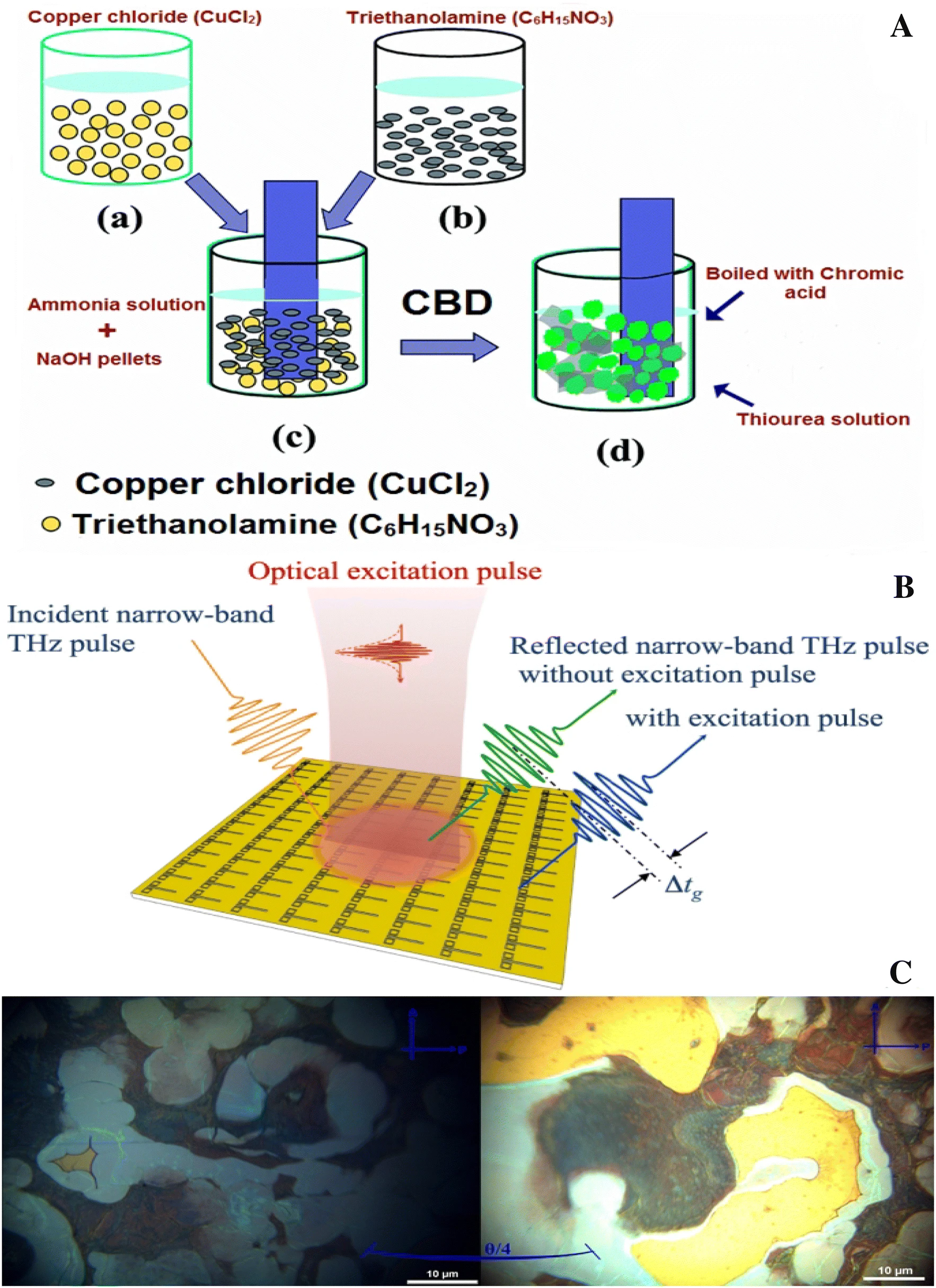
Growth dynamics of CBD-assisted CuS nanostructured thin-film: optical, dielectric and novel switchable device applications
The microcrystal structure of copper sulfide (CuS) nano-structured ultra-thin film was prepared on glass substrate from aqueous ammonia solution and sodium hydroxide at 60 °C using a simple and cost-effective chemical bath deposition (CBD). The powder X-ray diffraction method was used to characterize the hexagonal structure of the prepared CuS thin-film. While, surface morphology and surface topology were investigated by scanning electron microscopy (SEM) and atomic force microscopy (AFM). The optical properties were investigated by using UV–visible absorption spectrum. The electronic
Pagination
- Previous page ‹‹
- Page 11
- Next page ››
