Multi-phase oscillator for higher-order PSK applications
Multi-phase oscillator is an essential block in digital communication systems especially phase shift keying PSK based systems. In this paper, a procedure for designing a multi-phase oscillator with any required phase shift is proposed, unlike the previous oscillator which generates equal phase shifts. This oscillator circuit is built using fractional-order elements to generate any distribution of phase shift. The general characteristics equation is studied where the condition for oscillation and oscillation frequency are derived. Finally, different examples are introduced with their
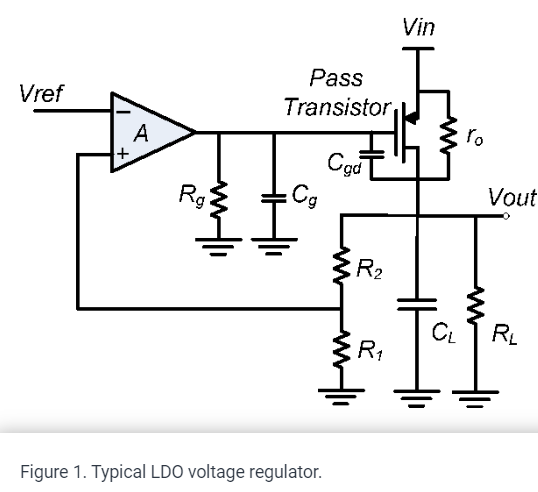
Parallel feedback compensation for LDO voltage regulators
A novel low dropout (LDO) voltage regulator compensation technique is demonstrated. A parallel feedback path is used to insert a zero at approximately three times the output pole. The parallel feedback consists of passive elements only and occupies small area. The proposed technique completely eliminates the output pole at different load conditions and results in high LDO bandwidth, which achieves fast output tracking of the input reference and fast recovery of sudden load changes. Moreover, the output pole elimination at different load conditions enables the potential scaling of the error
FPGA realization of ALU for mobile GPU
Arithmetic Logic Unit (ALU) is the most important component of processors. All arithmetic and logical computations are performed inside the ALU. This paper presents the design and the implementation of the ALU. The design is based on Approximated Precision Shader and Look-Up Table (LUT) multiplier. The lookup table, Wallace tree, and Carry Look-ahead Adder (CLA) are used in combination to speed up the multiplier operation. The proposed ALU is designed using Verilog and verified using Xilinx Virtex-5 XC5VLX30 FPGA. © 2016 IEEE.
FPGA realization of a speech encryption system based on a generalized modified chaotic transition map and bit permutation
This paper proposes a generalized modified chaotic transition map with three independent parameters. A hardware speech encryption scheme utilizing this map along with a bit permutation network is presented. While the transition map’s generalization introduces additional parameters, the modification enhances its chaotic properties and overcomes the finite range of the control parameter and dynamical degradation problems. The modification also presents a simplification for the hardware realization of the exponentiation operation in the map’s equation because the modified output range allows
FPGA Speech Encryption Realization Based on Variable S-Box and Memristor Chaotic Circuit
This paper introduces a new encryption/decryption scheme based on a dynamic substitution box concept. Values of the proposed S-Box are different for each sample depending on the behavior of a memristor-based chaotic system. MATLAB simulations and FPGA implementation for the circuit are presented with throughput 4.266 Gbit/s. Also, FPGA realization for encryption/decryption scheme is proposed. Entropy, MSE, correlation coefficient tests are applied on two different input files to examine the efficiency of this cryptosystem. © 2018 IEEE.
FPGA realization of speech encryption based on modified chaotic logistic map
This paper presents an FPGA design and implementation of a chaotic speech encryption and decryption system based on bit permutations. Different encryption schemes are realized and compared. In addition, various testing methods including entropy, mean squared error, and correlation coefficients are used to analyze the efficiency of the system. The techniques for area and delay minimization are used. Carry look-ahead adder, multi-operand adder and booth multiplier are used to improve the performance of the encryption schemes design. A comparison between the different encryption architectures and
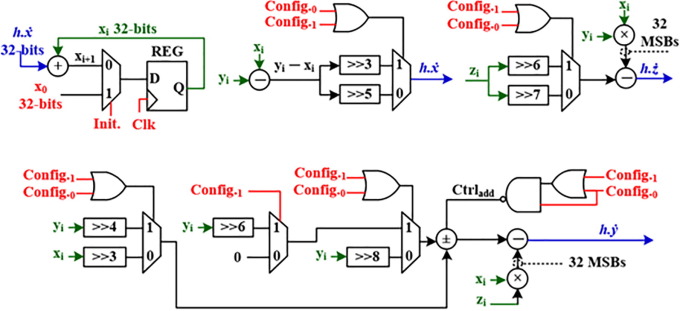
Reconfigurable chaotic pseudo random number generator based on FPGA
This paper presents an FPGA Pseudo Random Number Generator (PRNG) that is based on the Lorenz and Lü chaotic systems. These two systems are used to generate four different 3D chaotic attractors. One attractor is generated from Lorenz while the other three attractors are generated from Lü. The output attractor of the proposed PRNG can be reconfigured during real time operation using an efficient hardwired shifting and multiplexing scheme. Furthermore, in order to exploit the proposed reconfiguration feature, the proposed PRNG has been embedded in an FPGA cascaded encryption processor that
Chaos-based hardware speech encryption scheme using modified tent map and bit permutation
This paper proposes a speech encryption scheme based on a generalized modified chaotic tent map and bit permutation and presents its hardware realization. The generalization scales the output range and increases the key space. The modification controls the bounds on the output range through a parameter such that chaotic output exists for almost all values of the parameter. The security and efficiency of the speech encryption scheme are validated through the randomness of the encrypted signal, the key sensitivity and the hardware resources utilization. The proposed scheme utilizes less FPGA
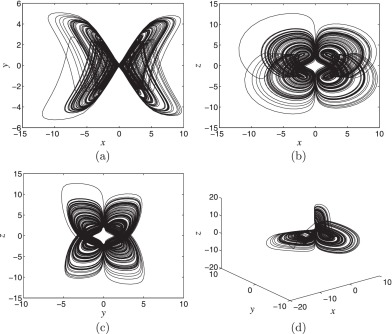
Four-wing attractors in a novel chaotic system with hyperbolic sine nonlinearity
Chaotic systems generating multi-wing attractors have received considerable attention in the literature. In this work, we propose a novel three-dimensional chaotic system with hyperbolic sine nonlinearity. It is worth noting that the system is elegant and includes only one parameter. Despite its simple structure, the new system displays double-wing and four-wing chaotic attractors. By studying dynamics of the system, coexistence of limit cycles or chaotic attractors is discovered. The capable of the synchronization of new chaotic system is verified by using an adaptive control. Furthermore, an
Controllable OTA Slew-rate for CMOS Image Sensor
In this work, a proposed circuit is implemented using tsmc 0.18um technology of area 16642 um2 with supply voltage equals 5V. A proposed implementation of a controllable Operational Transconductance Amplifier (OTA) slew rate for CMOS image sensor (CIS) is proposed. The slew rate is controlled by switching between various bias circuits for the OTA. The biasing circuit controls the value of OTA biased current, which allows controlling the amplifier's characteristics. As the flicker noise in the main contributor in reducing the quality of image sensors performance. The proposed circuit allows
Pagination
- Previous page ‹‹
- Page 12
- Next page ››
