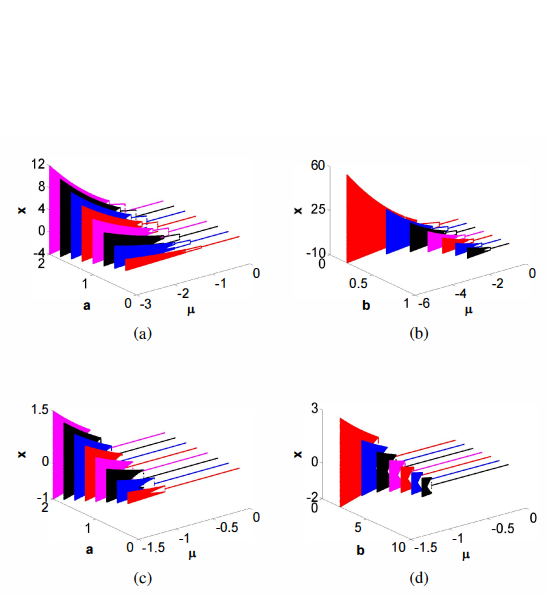
Design of a generalized bidirectional tent map suitable for encryption applications
The discrete tent map is one of the most famous discrete chaotic maps that has widely-spread applications. This paper investigates a set of four generalized tent maps where the conventional map is a special case. The proposed maps have extra degrees of freedom which provide different chaotic characteristics and increase the design flexibility required for many applications. Mathematical analyses for generalized positive and mostly positive tent maps include: bifurcation diagrams relative to all parameters, effective range of parameters, bifurcation points. The maximum Lyapunov exponent (MLE)
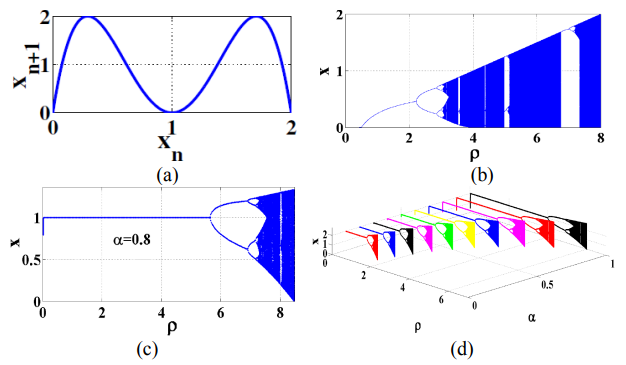
Biomedical image encryption based on double-humped and fractional logistic maps
This paper presents a secured highly sensitive image encryption system suitable for biomedical applications. The pseudo random number generator of the presented system is based on two discrete logistic maps. The employed maps are: the double humped logistic map as well as the fractional order logistic map. The mixing of the map parameters and the initial conditions x0, offers a great variety for constructing more efficient encryption keys. Different analyses are introduced to measure the performance of the proposed encryption system such as: histogram analysis, correlation coefficients, MAE
Controlled Picard Method for Solving Nonlinear Fractional Reaction–Diffusion Models in Porous Catalysts
This paper discusses the diffusion and reaction behaviors of catalyst pellets in the fractional-order domain as well as the case of nth-order reactions. Two generic models are studied to calculate the concentration of reactant in a porous catalyst in the case of a spherical geometric pellet and a flat-plate particle with different examples. A controlled Picard analytical method is introduced to obtain an approximated solution for these systems in both linear and nonlinear cases. This method can cover a wider range of problems due to the extra auxiliary parameter, which enhances the convergence
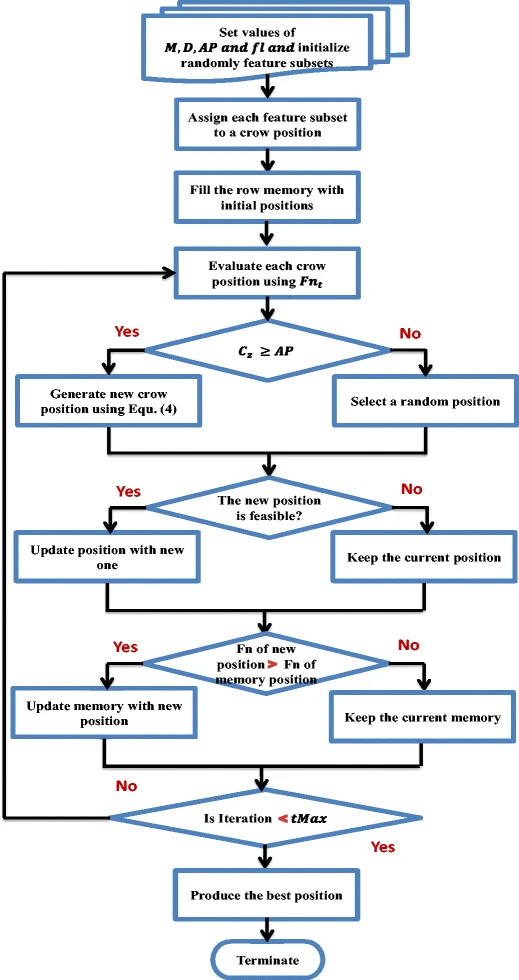
Feature selection via a novel chaotic crow search algorithm
Crow search algorithm (CSA) is a new natural inspired algorithm proposed by Askarzadeh in 2016. The main inspiration of CSA came from crow search mechanism for hiding their food. Like most of the optimization algorithms, CSA suffers from low convergence rate and entrapment in local optima. In this paper, a novel meta-heuristic optimizer, namely chaotic crow search algorithm (CCSA), is proposed to overcome these problems. The proposed CCSA is applied to optimize feature selection problem for 20 benchmark datasets. Ten chaotic maps are employed during the optimization process of CSA. The
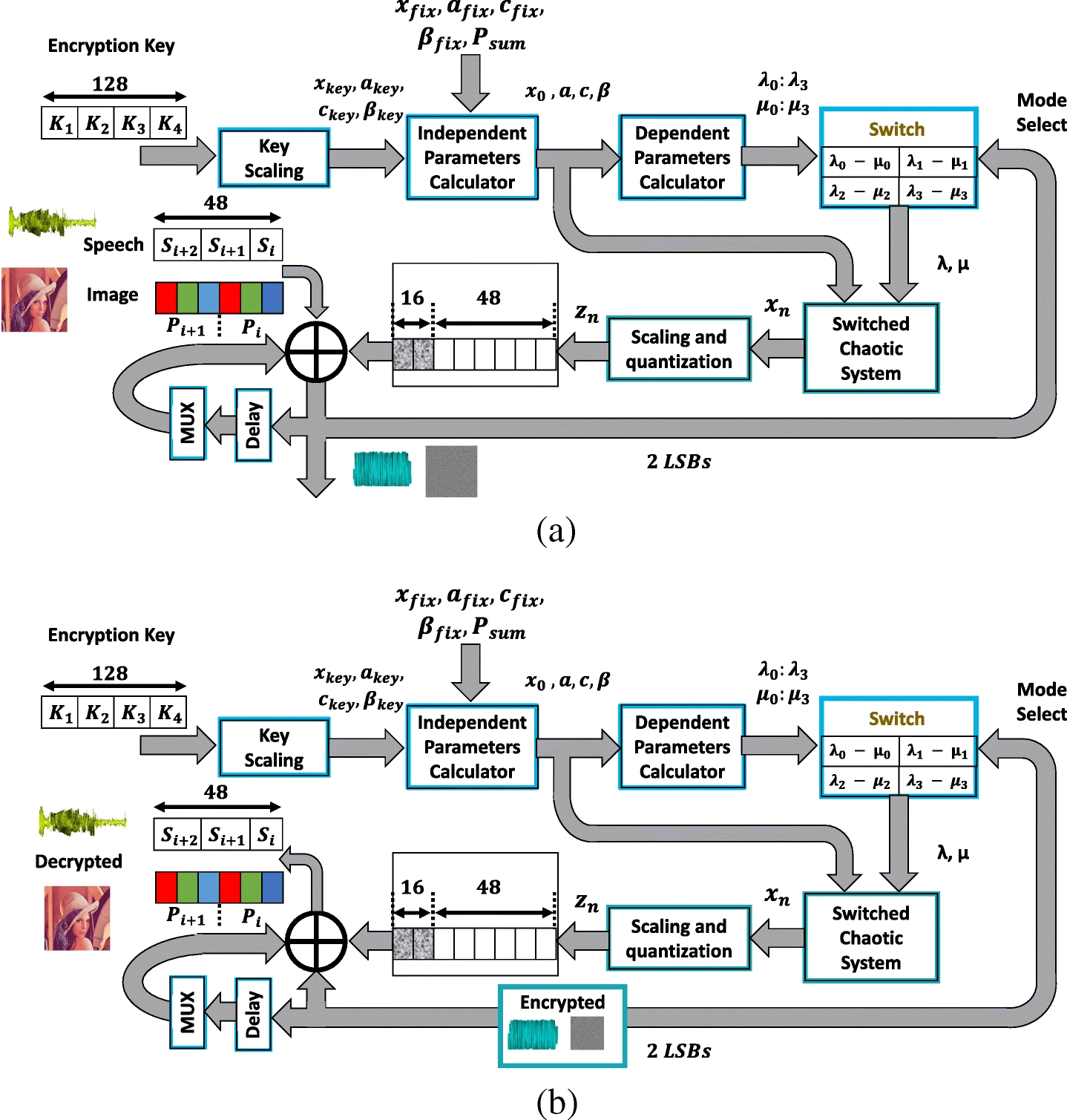
A switched chaotic encryption scheme using multi-mode generalized modified transition map
This paper presents a multi-mode generalized modified transition chaotic map and a switched chaotic encryption scheme based on it. Eight different modes of operation can be selected based on the map graph (concave or convex), the range modification procedure (shrinking or widening) and the sign of one of its independent parameters. The generalization and modification preserve the controllability and continuous chaotic behavior properties, respectively. For the same encryption key and map equation, multi-mode operation occurs through switching between four alternatives of the dependent
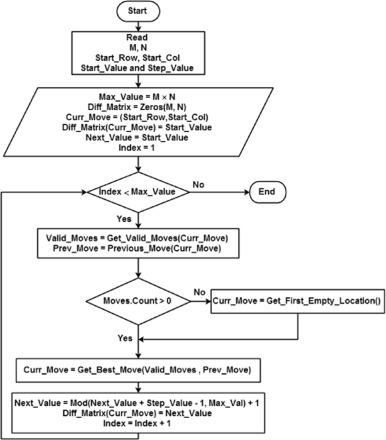
Novel permutation measures for image encryption algorithms
This paper proposes two measures for the evaluation of permutation techniques used in image encryption. First, a general mathematical framework for describing the permutation phase used in image encryption is presented. Using this framework, six different permutation techniques, based on chaotic and non-chaotic generators, are described. The two new measures are, then, introduced to evaluate the effectiveness of permutation techniques. These measures are (1) Percentage of Adjacent Pixels Count (PAPC) and (2) Distance Between Adjacent Pixels (DBAP). The proposed measures are used to evaluate
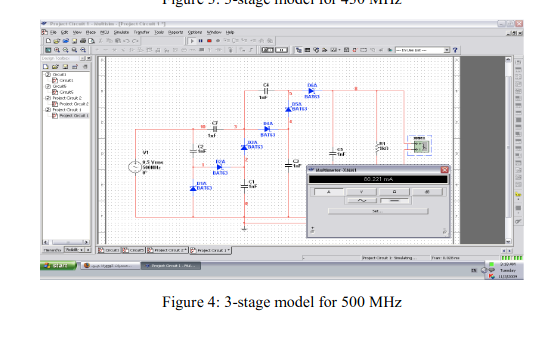
Novel radio frequency energy harvesting model
Energy and Environment, both are the main concern for every researcher allover the world. Alternative energy sources that are environmental friendly became the challenge to satisfy world needs. Oil and Gas are no more the main source of Energy, consequently the demand of an everlasting cheap source of energy that is environmental friendly, is the main goal recently. During the last decade, power consumption has decreased opening the field for energy harvesting to become a real time solution for providing different sources of electrical power. Energy Harvesting is a new technology that is going
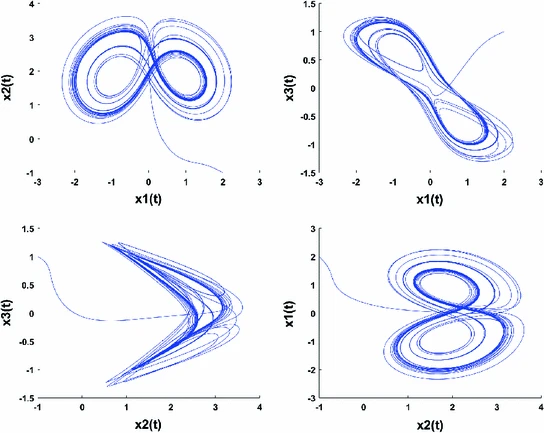
A study on coexistence of different types of synchronization between different dimensional fractional chaotic systems
In this study, robust approaches are proposed to investigate the problem of the coexistence of various types of synchronization between different dimensional fractional chaotic systems. Based on stability theory of linear fractional order systems, the co-existence of full state hybrid function projective synchronization (FSHFPS), inverse generalized synchronization (IGS), inverse full state hybrid projective synchronization (IFSHPS) and generalized synchronization (GS) is demonstrated. Using integer-order Lyapunov stability theory and fractional Lyapunov method, the co-existence of FSHFPS

A study on coexistence of different types of synchronization between different dimensional fractional chaotic systems
In this study, robust approaches are proposed to investigate the problem of the coexistence of various types of synchronization between different dimensional fractional chaotic systems. Based on stability theory of linear fractional order systems, the co-existence of full state hybrid function projective synchronization (FSHFPS), inverse generalized synchronization (IGS), inverse full state hybrid projective synchronization (IFSHPS) and generalized synchronization (GS) is demonstrated. Using integer-order Lyapunov stability theory and fractional Lyapunov method, the co-existence of FSHFPS
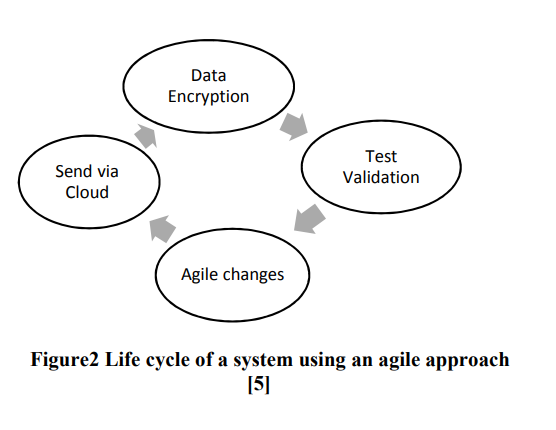
IoT Agile Framework Enhancement
Internet of Things (IoT) is considered as a trend nowadays. Devices connected to the internet interact with surrounding; this poses strong challenges in handling big data with a certain level of security. In this paper IoT devices will be divided in to two categories high vulnerability devices and low vulnerability devices. The classification depends on the ease of attacks. In order to ensure the security of IoT devices, an agile approach is used to secure high vulnerability devices as first step and then low vulnerability devices by applying encryption algorithms. © 2018 IEEE.
Pagination
- Previous page ‹‹
- Page 38
- Next page ››
