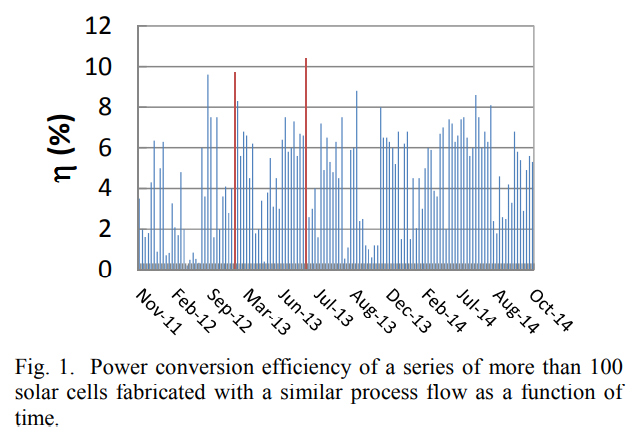
Process variability in Cu2ZnSnSe4 solar cell devices: Electrical and structural investigations
We have fabricated 9.7% efficient Cu2ZnSnSe4/CdS/ZnO solar cells by H2Se selenization of sequentially sputtered metal layers. Despite the good efficiency obtained, process control appears to be difficult. In the present contribution we compare the electrical and physical properties of two devices with nominal same fabrication procedure, but 1% and 9.7% power conversion efficiency respectively. We identify the problem of the lower performing device to be the segregation of ZnSe phases at the backside of the sample. This ZnSe seems to be the reason for the strong bias dependent photocurrent

3D surface reconstruction of retinal vascular structures
We propose in this paper, a three-dimensional surface reconstruction of a retinal vascular network from a pair of 2D retinal images. Our approach attempts to address the above challenges by incorporating an epipolar geometry estimation and adaptive surface modelling in a 3D reconstruction, using three steps: segmentation, 3D skeleton reconstruction and 3D surface modelling of vascular structures. The intrinsic calibration matrices are found via the solution of simplified Kruppa equations. A simple essential matrix based on a self-calibration method has been used for the 'fundus camera-eye'
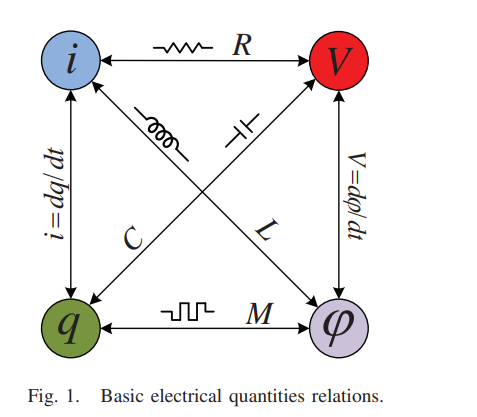
Review of the missing mechanical element: Memdamper
In this paper, the analogy between electrical and mechanical quantities is reviewed. Based on this analogy, there is a missing link between displacement and momentum. This missing link corresponds to the link between the charge and flux which represents the memristor. This link is still missing between the mechanical quantities. In this work, we shed the light on this missing mechanical element. We introduce the mathematical relation which links displacement and momentum. Two main types of missing relations are discussed. © 2015 IEEE.
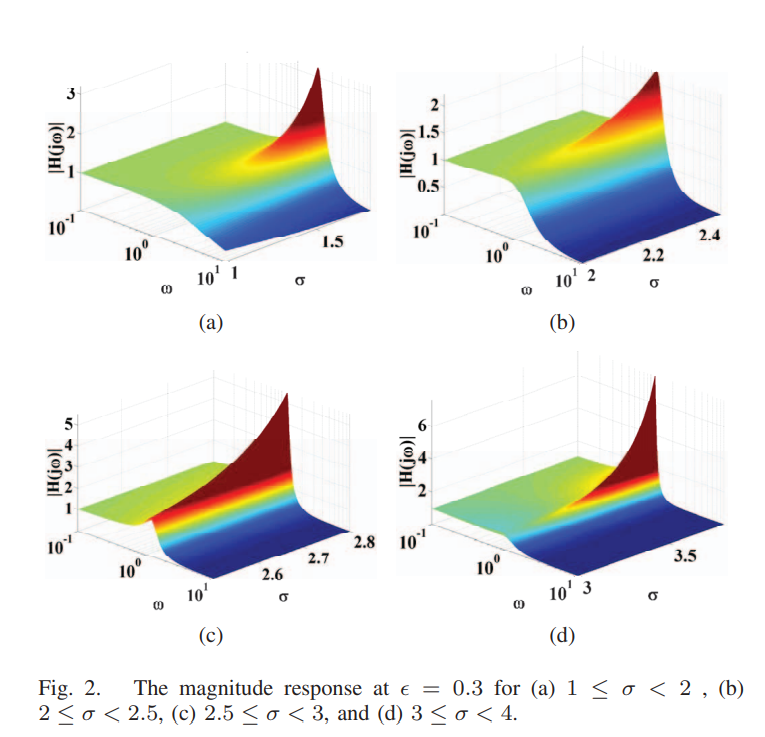
Low pass filter design based on fractional power chebyshev polynomial
This paper introduces the design procedure for the low pass filter based on Chebyschev polynomials of fractional power of any order. The filter order is considered in intervals of width two. Only the first two intervals are considered along with their pole locus produced by varying the filter order and the magnitude response. A general formula for constructing the filter from its s-plane poles is suggested. Numerical analysis and circuit simulations using MATLAB and Advanced Design System (ADS) based on the proposed design procedure are presented. Good matching between the circuit simulation
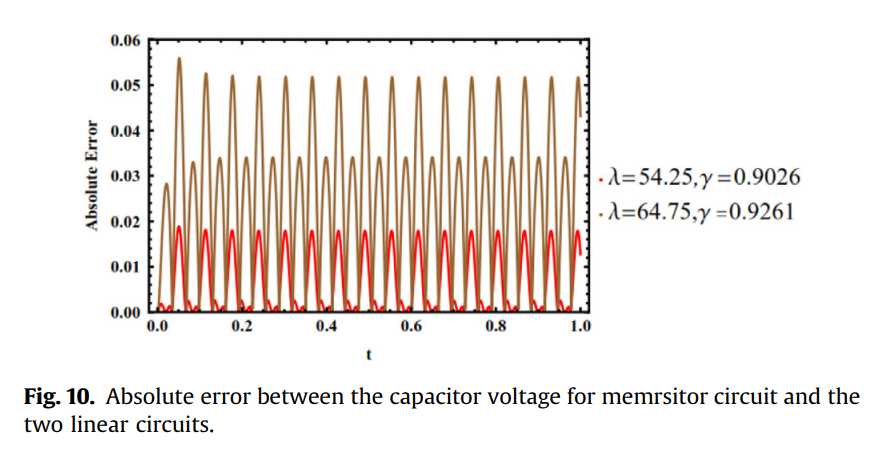
An optimal linear system approximation of nonlinear fractional-order memristor-capacitor charging circuit
The analysis of nonlinear fractional-order circuits is a challenging problem. This is due to the lack of nonlinear circuit theorems and designs particularly in the presence of memristive elements. The response of a series connection of a simple resistor with fractional order capacitor and its analytical formulation in both charging and discharging phases is considered. The numerical simulation of fractional order HP memristor in series with a fractional order capacitor is also discussed. It is a demonstration of a simple nonlinear fractional-order memristive circuit in both charging and
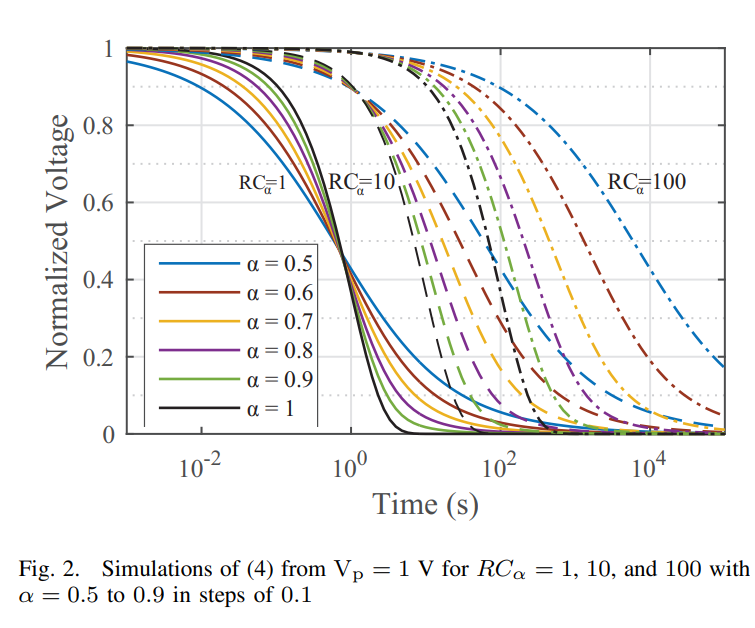
Analysis of a rectifier circuit realized with a fractional-order capacitor
An analysis of a traditional rectifier circuit when a fractional-order capacitor with order 0 < α < 1 replaces the integer-order smoothing capacitor (α = 1) is presented. Exploring the change in discharging behaviour that results from this replacement and the impacts on ripple voltage, nominal DC voltage, current, and power expressions used to describe the performance of this class of circuits. Further, the assumptions made for the analysis of the traditional circuit are explored from the fractional perspective to determine if they are still valid. © 2016 IEEE.
Double-sided bifurcations in tent maps: Analysis and applications
The tent map is a piece-wise linear one-dimensional discrete map which could be implemented easily. In this paper, a signed system parameter is allowed leading to the appearance of bidirectional bifurcations. A set of proposed tent maps with different sign variations and a signed parameter are investigated where the conventional map is a special case. The proposed maps exhibit period doubling as a route to chaos with wider and alternating sign output ranges that could fit multiple applications. Based on the maximum achievable output range corresponding to maximum chaotic behavior, the
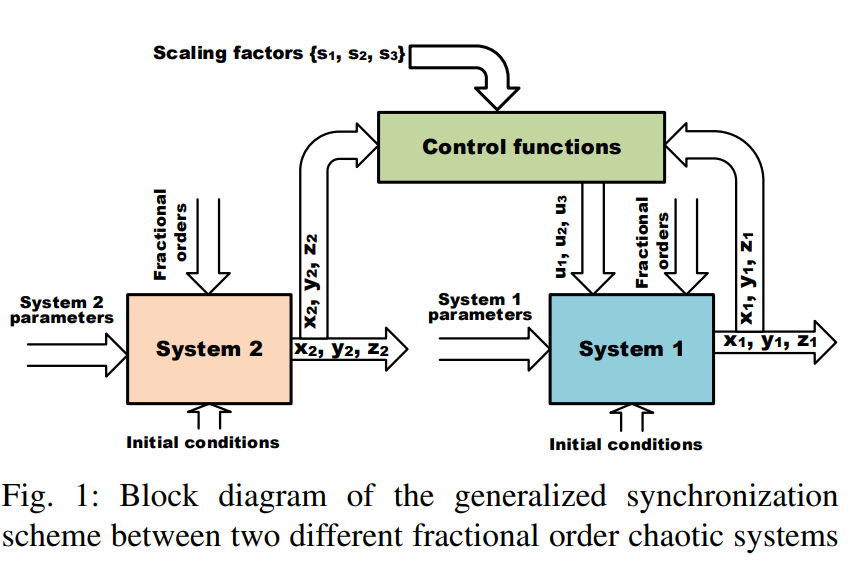
Generalized synchronization involving a linear combination of fractional-order chaotic systems
In this paper, a generalized scheme for synchronizing a fractional order chaotic system with another one or with a linear combination of two other fractional order chaotic systems is presented. Static (time-independent) or dynamic (time-dependent) synchronization that could generate multiple scaled versions of the response is discussed for some fractional order continuous chaotic systems based on differential equations. Non-Standard finite difference method suitable for fractional order chaotic systems is used to solve each system and get the responses. Analysis in the generalized fractional
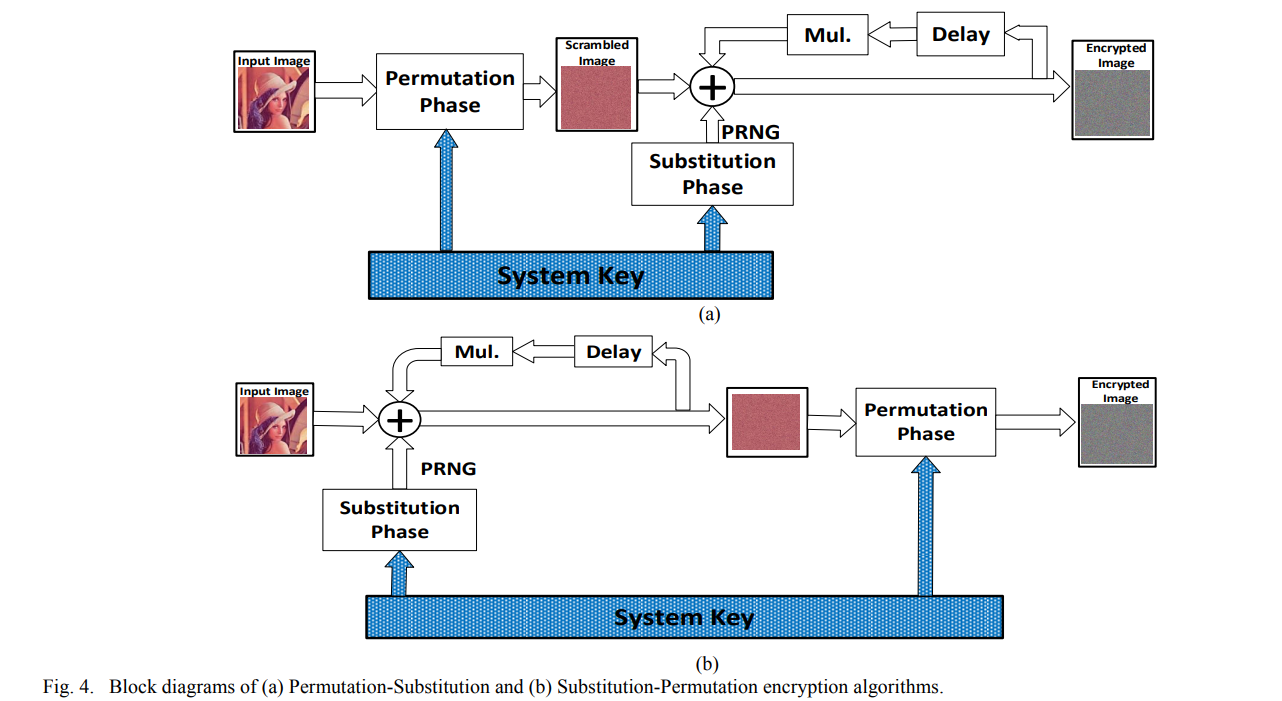
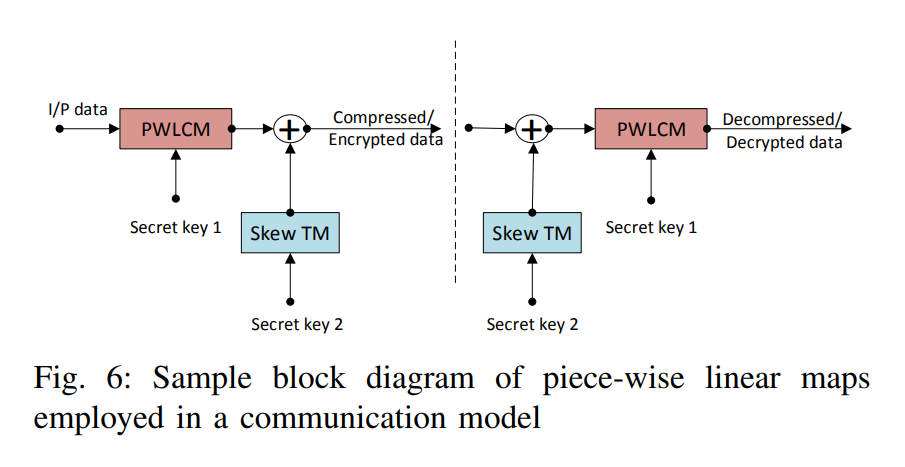
Image encryption algorithms using non-chaotic substitutions and permutations
This paper presents substitution and/or permutation symmetric-key encryption algorithms based on non-chaotic generators. While the substitution algorithm is based on fractals with delay and multiplexer elements, permutations are achieved via a chess-based algorithm. A comparison of four different cases; substitution-only, permutation-only, substitution-permutation and permutation-substitution; is introduced taking into consideration their encryption analysis results and sensitivity. Three different standard images; Lena, pepper and airplane; are tested for each algorithm to validate the
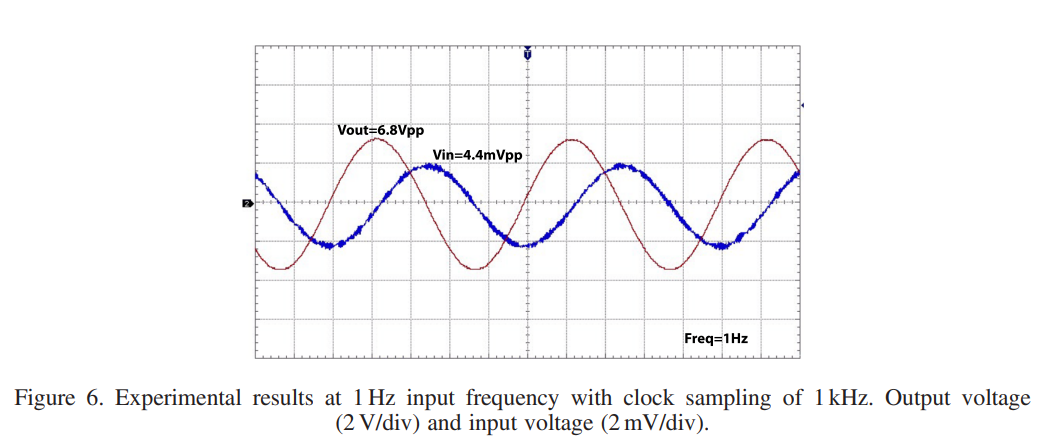
Analysis and realization of a switched fractional-order-capacitor integrator
Using fractional calculus, we analyze a classical switched-capacitor integrator when a fractional-order capacitor is employed in the feed-forward path. We show that using of a fractional-order capacitor, significantly large time constants can be realized with capacitances in the feedback path much smaller in value when compared with a conventional switched-capacitor integrator. Simulations and experimental results using a commercial super-capacitor with fractional-order characteristics confirmed via impedance spectroscopy are provided. Copyright © 2016 John Wiley & Sons, Ltd. Copyright © 2016
Pagination
- Previous page ‹‹
- Page 10
- Next page ››
