Cold flow numerical simulation inside local pottery furnace for different designs for the air inlet
One of the many pleasures of living in Egypt is having the opportunity to visit places like a village called Tunis in El-Fayoum governorate which is a touristic village and export art and handicraft such as Pottery for 3-4 decades. The clay processing in the traditional pottery industry contains several stages. The process and quality of the pottery have to be improved to reduce pollution and the manufacturing round time which could be done through improving the heating process. Towards this goal, turbulent three-dimensional numerical simulations for the in-use air inlet and a modified design
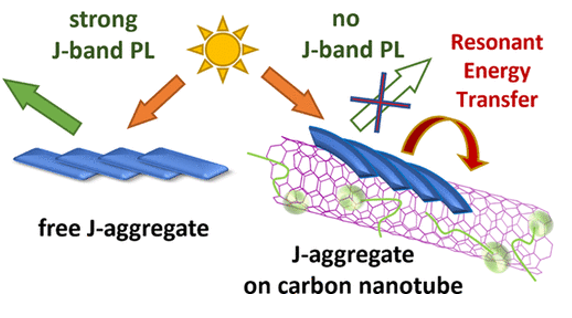
J-aggregates of amphiphilic cyanine dyes for dye-sensitized solar cells: A combination between computational chemistry and experimental device physics
We report on the design and structure principles of 5,5′-6,6′-tetrachloro-1,1′-dioctyl-3,3′-bis-(3-carboxypropyl)-benzimidacarbocyanine (Dye 1). Such metal-free amphiphilic cyanine dyes have many applications in dye-sensitized solar cells. AFM surface topographic investigation of amphiphilic molecules of Dye 1 adsorbed on TiO2 anode reveals the ability of spontaneous self-organization into highly ordered aggregates of fiber-like structure. These aggregates are known to exhibit outstanding optical properties of J-aggregates, namely, efficient exciton coupling and fast exciton energy migration
Cole bio-impedance model variations in daucus carota sativus under heating and freezing conditions
This paper reports on the variations in the parameters of the single dispersion Cole bio-impedance model of Daucus Carota Sativus (carrots) under heating and freezing conditions. Experiments are conducted on six samples with recorded live bio-impedance spectra versus temperature. The Cole model parameters are extracted from the measured data using the Flower Pollination Algorithm (FPA) optimization technique and their variations are correlated with well-known bio-chemical and bio-mechanical variations. This represents a non-invasive method for characterizing and measuring the degree of change
Association between long noncoding RNA taurine-upregulated gene 1 and microRNA-377 in vitiligo
Background: Taurine-upregulated gene 1 (TUG1) is one of the long noncoding RNAs (lncRNAs) that plays a role in melanogenesis. MicroRNA-377 (miRNA-377) is a conserved noncoding RNA that regulates angiogenesis and promotes oxidative stress. Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptors (PPARs) are components of the nuclear hormone receptor superfamily. PPAR-γ activators stimulate melanogenesis. Interleukin (IL)-17 has been implicated in the pathogenesis of several immunological diseases. This work aimed at detecting the expression levels of lncRNA TUG1, miRNA-377, PPAR-γ, and IL-17 among vitiligo
Towards evolving sensor actor networks
Sensor Actor NETworks (SANET) represent a major component of ubiquitous service environments promising interesting solutions to a wide range of problems. Despite the obvious increase in the research activities proposing architectures and protocols for SANETs, we are still no where near the production of industrial-grade SANET software that can be relied upon for mission critical applications. The cost of programming, deploying and maintaining SANET environments is still highly prohibitive due to the lack of industrial tools capable of realizing adaptive SANET software in a cost effective way
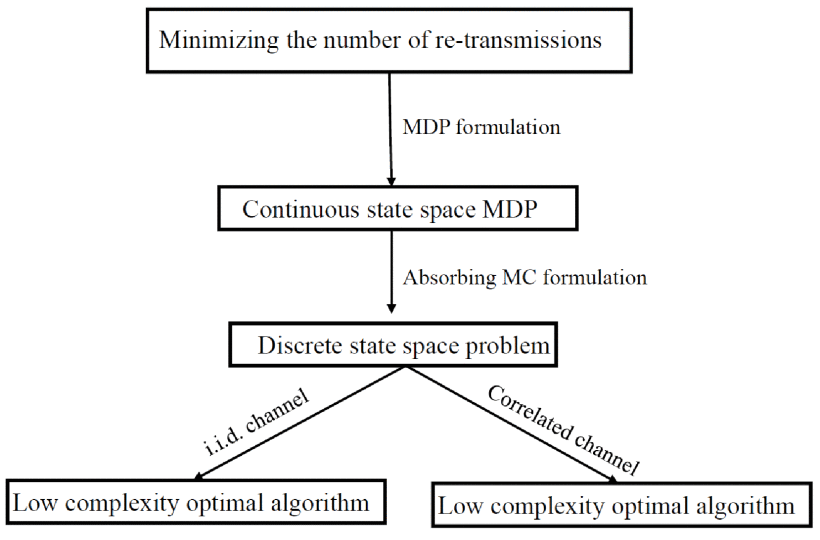
SWIPT Using Hybrid ARQ over Time Varying Channels
We consider a class of wireless powered devices employing hybrid automatic repeat request to ensure reliable end-to-end communications over a two-state time-varying channel. A receiver, with no power source, relies on the energy transferred by a simultaneous wireless information and power transfer enabled transmitter to receive and decode information. Under the two-state channel model, information is received at two different rates while it is only possible to harvest energy in one of the states. The receiver aims to decode its messages with minimum expected number of re-transmissions. Dynamic
Network Coded Cooperation Receiver with Analog XOR Mapping for Enhanced BER
In this paper, we propose a novel physical layer decoding technique for Device-to-Device Network Coded Cooperation (NCC) receivers in the Two Way Relay Channel (TWRC) scenario. The proposed technique is efficiently applicable either when Channel State Information (CSI) are available at the receiver or not. It first employs XOR arithmetic analog mapping to extract a distorted version of the intended signal from the network-coded signal received from the relay. The obtained signal is then combined with the direct signal received from the source, resulting in a higher SNR version of the intended
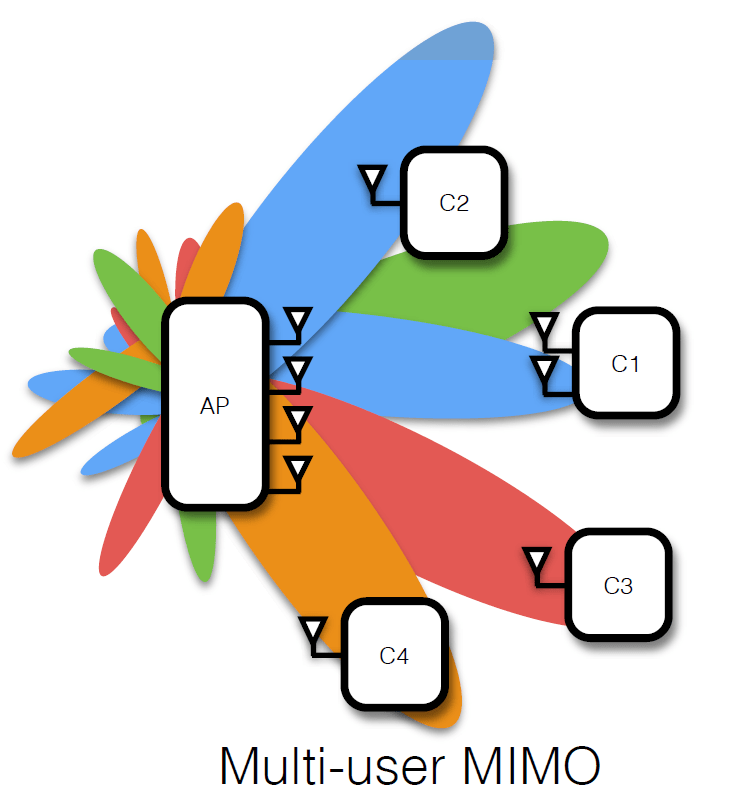
Multiuser MIMO relaying under quality of service constraints
We consider a wireless communication scenario with K source-destination pairs communicating through several half-duplex amplify-and-forward relays. We design the relay beamforming matrices by minimizing the total power transmitted from all the relays subject to quality of service constraints on the received signal to interference-plus-noise ratio at each destination node. We propose a novel method for solving the resulting nonconvex optimization problem in which the problem is decomposed into a group of second-order cone programs (SOCPs) parameterized by K real parameters. Grid search or
New achievable secrecy rate regions for the two way wiretap channel
This work develops new achievable rate regions for the two way wiretap channel. In our setup, Alice and Bob wish to exchange messages securely in the presence of a passive eavesdropper Eve. In the full-duplex scenario, our achievability argument relies on allowing the two users to jointly optimize their channel prefixing distributions, such that the new channel conditions are favorable compared to that of Eve. Random binning and private key sharing over the channel are then used to exploit the secrecy advantage available in the equivalent cascade channel and to distribute the available secrecy
Study of optical power variations in multi-layer human skin model for monitoring the light dose
Monitoring light dose is essential in much clinical procedures like bio-stimulation, neuro-medicine and photodynamic therapy and in many biophotonics applications such as optogenetics and biosensing. However, monitoring the optical power dissipation as light travels in different layers of tissue is essential in determining the required optical dose. Each part in the human body is protected by different thickness of skin layer; therefore, studying the variations of the optical power when light propagates in different thicknesses of the human skin is essential for safe and accurate medical
Pagination
- Previous page ‹‹
- Page 7
- Next page ››
