The deterministic capacity of relay networks with relay private messages
We study the capacity region of a deterministic 4-node network, where 3 nodes can only communicate via the fourth one. However, the fourth node is not merely a relay since it can exchange private messages with all other nodes. This situation resembles the case where a base station relays messages between users and delivers messages between the backbone system and the users. We assume an asymmetric scenario where the channel between any two nodes is not reciprocal. First, an upper bound on the capacity region is obtained based on the notion of single sided genie. Subsequently, we construct an
Hidden anchor: Providing physical layer location privacy in hybrid wireless sensor networks
In many hybrid wireless sensor networks (HWSNs) applications, sensor nodes are deployed in hostile environments where trusted and un-trusted nodes co-exist. In such hybrid networks, it becomes important to allow trusted nodes to share information, especially, location information and, at the same time, prevent un-trusted nodes from gaining access to this information. We focus on anchor-based localization algorithms in HWSNs, where a small set of specialized nodes, i.e. anchor nodes, broadcast their location to the network and other nodes can use the broadcast information to estimate their own
Synthetic generation of radio maps for device-free passive localization
In this paper, we present the design, implementation, and evaluation of a system that automatically constructs accurate radio maps for device-free WLAN localization systems. The system is capable of generating deterministic and probabilistic radio maps for localization systems. Our system uses 3D ray tracing enhanced with the uniform theory of diffraction (UTD) to model the electric field behavior and the human shadowing effect. We present our system architecture and describe the details of its different components. We also propose an optional module, location-0 correction, that can
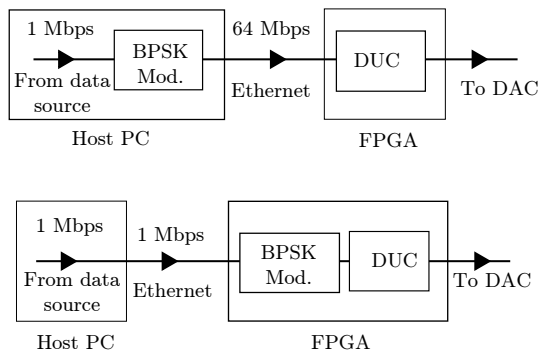
Maximizing USRP N210 SDR transfer rate by offloading modulation to the on-board FPGA
One of the challenges of the design of Software Defined Radios (SDR) is to maintain a high level of reconfigurability without sacrificing data rates. In this paper, we consider the USRP N210, which is an SDR kit made by Ettus Research. It consists of an FPGA connected to an RF front-end. The USRP is operated by a host computer where most of the processing is done while the FPGA is used mainly to control the RF front-end, manage communication with the host, and convert sample rates. The maximal rate supported by the USRP hardware can not be practically achieved due to the bottleneck in the data
Maximizing the signal to leakage ratio in downlink cellular networks
A transmission scheme is developed for the downlink frame of cellular networks. While the mobile stations (MSs) maximize the signal power from the serving base station (BS), each BS aims at balancing the signal power of its users with the interference caused at the MSs of the neighboring cells, based on an approximated performance metric. A closed form solution for the beamforming vectors of the BSs and the MSs is derived. Simulation results show that the proposed scheme achieves substantial gains for different antenna configurations, outperforming well-known schemes in the literature. © 2013
Symbol based log-MAP in concatenated LDPC-convolutional codes
In this paper we study the use of a high rate Low Density Parity Check (LDPC) codes in concatenated coding structures. Specifically, we use the LDPC code as an outer code, with a convolutional code as an inner code. We decode the convolutional code using a symbol based Log-MAP (Maximum a posteriori probability) decoder, and feed the soft outputs of this decoder into a non-binary Galois Field LDPC decoder. We compare this concatenation scheme using 16 QAM modulation with one using a bit based Log-MAP decoder over Additive White Gaussian Noise (AWGN) and Stanford University Interim (SUI-3)
Experimental Path tracking optimization and control of a nonlinear skid steering tracked mobile robot
The skid steering tracked robot is consider one of the famous robots that used in the autonomous agricultural field. The robot model is considered as a coupled nonlinear model. So, a real kinematic model is required to develop the robot motion which will improve the high quality and quantity of the cultivated crops. So, in this research a mathematical model for the skid steering mobile robot (SSMR) and a mathamtical model has been presented to simulate the robot. The model has been validated based on experimental data for the Skid Steering model. The robot motion as position and velocity has
Experimental Lane Keeping Assist for an Autonomous Vehicle Based on Optimal PID Controller
Detection of the lane boundary is the primary task in order to control the trajectory of an autonomous car. In this paper, three methodologies for lane detection are discussed with experimental illustration: Blob analysis, Hough transformation and Birds eye view. The next task after receiving the boundary points is to apply a control law in order to trigger the steering and velocity control to the motors efficiently. In the following, a comparative analysis is made between different tuning criteria to tune PID controller for Lane Keeping Assist (LKA). In order to receive the information of the
Conceptual cost estimation of pump stations projects using fuzzy clustering
Conceptual cost estimates, are prepared at the very early stages of a project, and generally before the construction drawings and specifications are available. At this stage, cost estimates are needed by the owner, contractor, designer, or funding agencies for determination of the feasibility of a project, financial evaluation of a number of alternative projects, or establishment of an initial budget. Traditional approaches rely heavily on experienced engineers. This paper presents a method using fuzzy clustering technique for pump station projects cost estimation. The proposed conceptual cost
Modelling of Continuum Robotic Arm Using Artificial Neural Network (ANN)
Continuum robotic arm becomes the new area of scientific research nowadays. Its technology has grown and touched several vital applications included industry and agriculture thanks to many advantages made it a better choice than the conventional serial robotic manipulator. This paper represents a new designed model of continuum arm robot, which relates the motor shaft angle as the input parameter and transfers the motor torque to combined system of compression springs and results in six outputs: x,y and z 3D coordinates for the center point of the end effector and \theta,~\psi and \gamma to
Pagination
- Previous page ‹‹
- Page 12
- Next page ››
